Exploring the Role of Quillbot, an AI-Driven Dynamic Writing Platform, in Improving EFL Learners' Writing Skills and Fostering Their Motivation: An Integrative Study
Published in Education

The Role of Technology in Enhancing Writing Skills and Engagement
Advancements in technology have significantly influenced the methods used to teach writing in the digital era. Haleem et al. (2022) highlight that incorporating digital tools into educational settings has revolutionized traditional approaches to writing instruction, introducing more dynamic and interactive methodologies. Garlinska et al. (2023) further emphasize that tools like virtual classrooms, online workshops, and cloud-based writing platforms have initiated a substantial shift in teaching practices. These platforms provide functionalities such as instant feedback, collaborative editing, and plagiarism detection. As noted by Nykyporets (2023), these features not only improve students' writing skills but also encourage the development of critical thinking and independent problem-solving skills.
Technology has been shown to have the potential to enrich the writing process by integrating multimodal approaches and promoting digital literacy. It has been demonstrated to facilitate cognitive growth, encourage independent thinking, and support the adoption of effective learning (Chauhan et al., 2023). Digital tools can address the unique needs of struggling writers by leveraging their existing knowledge and aiding in the cognitive processes involved in writing. This is particularly true when employing knowledge transformation strategies that align with writing goals such as topics, genres, and text structure (Rad et al., 2023; Hsu et al., 2023).
In educational settings, there is an increasing interest in the influence of technology integration into writing instruction on outcomes (Ahmed et al., 2024). Effective technology integration involves the incorporation of digital resources, including computers, portable devices, online platforms, and applications, into daily classroom practices (Chang et al., 2021). This method is rooted in the Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge Framework (TPACKF), which underscores the integration of technology, pedagogy, and subject matter expertise to improve students' writing skills, empowering them to craft more comprehensive and grammatically precise essays (Ahmed et al., 2024).
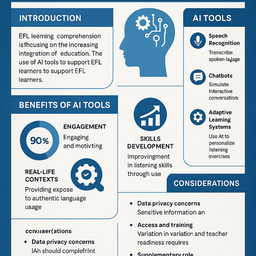
An expanding body of research has demonstrated the potential for AI-powered platforms, such as chatbots, to significantly enhance learner motivation (Silitonga et al., 2023) and promote active engagement (Yashima, 2009; Carayannopoulos, 2018). In comparison to conventional classroom teaching methods, the utilization of chatbot-driven interactions has been demonstrated to engender a more personalized and dynamic learning experience, thereby fostering greater engagement in the educational process (Guo et al., 2023; Peng, 2015; Yashima, 2009). This heightened engagement has been identified as being instrumental in improving EFL learners' Willingness to Write (WTW) and fostering autonomy, thereby empowering learners to take responsibility for their progress and to persist in meeting their writing goals.
For instance, Lee (2019) emphasized the pivotal role of socio-political factors, including instructional goals, teaching strategies, contextual elements such as community dynamics, and personal attributes such as confidence and anxiety, in shaping engagement in writing in digital spaces outside formal education. In a similar vein, Tai and Chen's (2020) research examined the utilization of Google Assistant among EFL learners, revealing that it substantially boosted their confidence and inclination to write while concurrently mitigating anxiety.
The integration of AI into educational settings empowers individuals to effectively engage with computers, robots, machines, and various software tools. A notable innovation in AI is the chatbot, which facilitates endless authentic and natural interactions, serving as a versatile conversational partner to support language acquisition (Huang et al., 2022). These interfaces replicate human-like communication, enabling learners to inquire and receive responses naturally. This capacity is especially beneficial for individuals with limited opportunities to practice language production, as it provides them with access to interactions that resemble those with native English speakers, irrespective of time or location (Walker & White, 2013).
AI-driven chatbots present a pragmatic solution to the challenges encountered by EFL learners with restricted access to native or non-native speakers. These chatbots furnish a malleable and attainable platform for language practice, empowering learners to partake in meaningful interactions unencumbered by the constraints of time, location, or the availability of human partners. The seamless and user-friendly design of these chatbots ensures consistent opportunities for learners to enhance their communication skills in diverse contexts. These bots offer numerous advantages in EFL teaching and learning, including conducting conversations via text and audio, generating intelligent responses, engaging actively, providing pronunciation feedback, and fostering understanding and insight (Walker & White, 2013). Consequently, EFL learners possess the potential to achieve improved learning outcomes (Walker & White, 2013; Fryer et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2022), benefit from increased convenience and autonomy in their learning processes (Walker & White, 2013), experience reduced anxiety and elevated comfort (Kim, 2016), enhance their engagement and confidence, and overcome psychological and transactional barriers in foreign language acquisition (Men et al., 2022).
AI-powered tools and applications have increasingly revolutionized writing instruction by offering tailored learning experiences. As Chaisiri (2023) emphasize, these platforms empower educators to identify individual learners' strengths and areas requiring improvement, allowing them to adjust instructional strategies for optimized outcomes. In a similar vein, Bhutoria (2022) underscores the significance of such technologies in fostering personalized learning, ensuring that students receive support that aligns with their distinct needs and preferences. Furthermore, mobile technologies empower students to engage in public sharing of their work, promoting confidence and skill development through peer feedback (Umamah & Cahyono, 2022). Cahyono et al. (2023) contend that this collaborative approach fosters a supportive learning environment that enhances both individual and group learning experiences. However, as Duncan and Joyner (2022) caution, the adoption of digital writing platforms is not without challenges. These include issues of digital equity, data security, and potential distractions. These challenges must be carefully managed to maximize the benefits of these platforms. These challenges underscore the necessity of a proactive and reflective approach in the development of pedagogical strategies and policies to address the evolving landscape of writing education in the age of artificial intelligence.
The Role of AI-Driven Dynamic Writing Platforms in Enhancing EFL Learners’ Writing Skills and Motivation
The utilization of AI-powered interactive writing tools in educational settings has garnered considerable attention for their potential to enhance the writing competencies of English as a Foreign Language (EFL) learners (Freiermuth, 2020; Dogan et al., 2023). These platforms have been demonstrated to improve writing accuracy, style, and overall quality, while concurrently exerting a favorable influence on student motivation and performance. Notable examples of such tools include Grammarly, QuillBot, WordTune, and Jenni, which have been shown to refine written work and foster engagement (Dogan et al., 2023; Freiermuth, 2020). Notwithstanding the aforementioned benefits, concerns have been raised about the potential for overdependence on such tools and their possible negative effects on learners' critical thinking skills (Dogan et al., 2023). Nonetheless, the growing adoption of these technologies underscores their transformative potential in EFL writing education.
Grammarly, for instance, offers immediate feedback on grammar, punctuation, spelling, clarity, and engagement, thereby transforming the writing process into an interactive learning experience. As Tambunan et al. (2022) have demonstrated, Grammarly has been shown to improve students' grammatical accuracy, punctuation, and sentence structure. The platform's capabilities extend beyond mere error detection, as it provides actionable suggestions aimed at enhancing textual coherence and style. This fosters not only skill development but also confidence in learners.
QuillBot, a widely recognized tool for its paraphrasing capabilities, assists students in avoiding plagiarism by preserving the fundamental essence of their content. Kurniati and Fithriani (2021) emphasize the tool's crucial role in improving paraphrasing skills, a fundamental aspect of academic writing. QuillBot's capacity to streamline complex sentences without compromising their contextual relevance renders it a valuable asset for students engaged in academic assignments or research projects.
WordTune, an additional artificial intelligence-based tool, emphasizes the refinement of tone and the execution of stylistic adjustments. Lam and Moorhouse (2022) posit that WordTune facilitates self-assessment and reflection by encouraging users to examine and improve their writing weaknesses. A distinguishing feature of WordTune, according to them, is its capacity to go beyond conventional grammar checkers by offering a deeper examination of stylistic elements. This feature empowers students to explore a more expansive range of tones and expressions, thereby enhancing their writing repertoire.
AI-powered tools like Grammarly, QuillBot, and Turnitin have demonstrated remarkable potential in fostering academic integrity (Farrokhnia et al., 2023). These platforms not only enhance grammar and writing style but also assist users in paraphrasing content effectively, reducing the risk of plagiarism while preserving the original meaning. However, the extent to which these tools have completely eliminated plagiarism is contingent on various factors. These tools assist users in paraphrasing text, correcting grammar, and providing feedback, thereby helping to prevent the unauthorized duplication of others' work. Nevertheless, the onus falls on the user to ensure ethical usage of these tools, as their improper or excessive use can potentially lead to plagiarism. By providing predictive suggestions and content ideas, Jenni helps reduce cognitive load and enhance writing efficiency, particularly for novice writers) Moorhouse (2022).
To eradicate plagiarism, the utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) tools should be centered on fostering originality and promoting proper citation practices. When utilized appropriately, these AI tools can provide English as a Foreign Language (EFL) learners with customized, adaptive assistance for their writing development (Farrokhnia et al., 2023). By addressing common language difficulties and fostering self-guided learning, these tools contribute to enhancing critical writing abilities and fostering long-term motivation in students. However, future studies must examine the long-term impacts of AI tool use on writing independence and critical thinking to ensure a comprehensive approach to technology-assisted learning.
OpenAI's GPT-3 signifies a substantial advancement in the domain of language modeling, demonstrating sophisticated capabilities in producing text that emulates human language and in comprehending complex linguistic nuances. Its capacity to produce coherent, contextually relevant content makes it an excellent tool for stimulating creativity and fostering critical thinking among students (Mhlanga, 2023). By encouraging experimentation with diverse writing styles and concepts, GPT-3 can facilitate both creative and academic writing endeavors. The collective impact of these AI tools underscores the transformative capacity of artificial intelligence in enhancing students' writing abilities.
AI-Driven Platforms and Their Multifaceted Impact on EFL Learners
Mhlanga (2023) examined the functionality of ChatGPT as a virtual tutor, with a focus on its capacity to facilitate goal setting and provide interactive guidance. Notwithstanding its advantages, they sounded a note of caution about the potential pitfalls of overreliance, which could result in superficial engagement with learning materials. In a similar vein, Mogavi et al. (2024) underscored the potential benefits of personalized learning offered by AI tools, while concurrently highlighting the associated challenges, including diminished critical thinking and concerns over academic integrity. To address these concerns, Ali et al. (2023) have proposed that learners engage in self-assessment to cultivate independence from technological reliance.
In a collaborative study, Wiboolyasarin et al. (2024) demonstrated that artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted corrective feedback significantly augmented second-language (L2) writing competencies among Thai exchange students. The research under discussion highlights the profound impact that such tools can have when applied thoughtfully. In a similar vein, Hsu et al. (2023) observed that ChatGPT led to substantial enhancements in grammar, writing proficiency, and vocabulary acquisition among foreign language learners. Nevertheless, they also cautioned about its possible drawbacks, particularly in terms of its potential to limit creativity and critical thinking skills.
Subsequent research by Wei (2023) corroborated the findings, demonstrating that AI-mediated teaching not only enhanced English learners' academic performance but also fortified their motivation and self-regulation skills. Additionally, Karataş et al. (2024b) examined incorporating AI-powered image recognition technology into vocabulary acquisition, reporting reduced anxiety and enhanced knowledge retention, although it did not notably influence self-regulation.
Vanichvasin et al. (2021) demonstrated that AI tools play a significant role in enhancing EFL learners' grammar proficiency and overall writing performance. They further highlighted the facilitation of increased student engagement in academic writing tasks by AI feedback tools. Nevertheless, Kim (2016) and Vladova et al., (2023) noted that despite students' favorable views on the utility of AI in grammar correction and plagiarism detection, ethical and creative challenges persist.
A study by Xu and Wang (2024c) synthesized data from 40 studies, thereby reinforcing the effectiveness of AI-integrated learning tools in improving English learning outcomes. This finding is consistent with the research conducted by Guo and Wang (2024), which identified that AI-enhanced instruction positively impacts learner engagement across a range of cognitive, emotional, and social dimensions. Furthermore, Mozumder et al. (2023) explored the role of AI tools in fostering intrinsic motivation, noting improvements in learner autonomy and critical thinking. However, they also observed that the impact varied based on factors such as nationality and academic discipline. Collectively, these studies underscore the multifaceted benefits and potential challenges of integrating AI technologies into EFL education.
QuillBot and Academic Writing Enhancement
Recent technological advances in artificial intelligence have revolutionized academic writing assistance tools, with QuillBot emerging as a notable platform in this field. Studies investigating the effectiveness of this AI-based writing assistant have shown promising results in various academic contexts (Amyatun & Kholis, 2023). The implementation of the tool in educational settings has shown significant potential for improving students' writing skills, particularly in the development of complex academic texts.
Empirical research conducted by Amanda et al. (2023) highlights several key benefits of QuillBot in academic writing. Their findings suggest that the platform's AI algorithms are effective in assisting users to improve grammatical accuracy, enhance vocabulary selection, and maintain textual coherence. This is particularly beneficial for non-native English speakers, who often face challenges in academic writing.
The platform's contribution to academic integrity has also been the subject of scholarly investigation. Fitria (2022) conducted a comprehensive analysis of QuillBot's paraphrasing capabilities, showing that the tool employs sophisticated linguistic transformations while preserving the original meaning of texts. These transformations include syntactic restructuring, lexical substitution and semantic preservation, which help users avoid unintentional plagiarism while developing their academic writing skills.
In addition, the tool's premium features go beyond basic writing assistance. Advanced features include multiple paraphrasing modes, each designed to meet specific academic writing needs. The platform's text summarisation capability has proven particularly valuable for researchers undertaking extensive literature reviews, allowing them to efficiently process large volumes of academic text while maintaining accuracy and relevance (Fitria, 2022).
While AI-powered writing tools such as QuillBot have received considerable attention in academic circles, previous research has primarily focused on conventional aspects of writing improvement, overlooking their transformative potential in fostering learner autonomy and motivation. Although preliminary studies by Amanda et al. (2023) and Amyatun and Kholis (2023) suggest positive outcomes in terms of writing improvement, they have not fully explored the platform's dual impact on both technical writing skills and learners' psychological engagement. The current study addresses this gap by investigating how QuillBot's AI-driven features not only improve language skills, but also cultivate a more positive attitude towards writing as a creative and collaborative process. Through its innovative approach of providing personalized feedback and dynamic scaffolding, this research demonstrates how AI-based writing platforms can revolutionized traditional writing instruction by empowering learners to become active participants in their educational journey while maintaining high standards of academic writing.
Discussion
This study, based on Engeström's (1987) activity theory, examined the impact of QuillBot's AI-driven writing instruction on EFL learners' writing skills and motivation. The results showed significant improvements in both areas, in line with recent research trends. For example, studies by Zhao (2022) and Li and Chan (2024) documented similar positive outcomes in AI-assisted language learning environments. QuillBot's success can be attributed to its creation of a supportive, non-judgmental environment that encourages learners to experiment with their writing without fear of criticism, a finding that resonates with Wu and Zhang's (2022) observations.
In today's digital landscape, where technology permeates various aspects of life, including gaming, social interaction, and knowledge acquisition (Huang et al., 2023), QuillBot represents a significant advancement in AI-based writing support. The platform's approach to writing instruction provides learners with a safe space to practice, effectively reducing anxiety about making mistakes while building confidence in their writing abilities. Recent research by Chen et al (2023) supports this finding, demonstrating how AI writing tools can reduce writing anxiety while improving coherence, vocabulary use and grammatical accuracy. This enables learners to extend their learning beyond traditional classroom boundaries.
Furthermore, Tambunan et al. (2023) emphasized the crucial role of AI platforms in facilitating self-directed learning, a finding that aligns closely with our observations of QuillBot's impact. The platform's ability to provide immediate, personalized feedback, combined with its various interactive features, creates an environment conducive to autonomous learning while maintaining high levels of engagement.
Ngeström's Activity Theory (1987) provides a valuable framework for understanding the results of QuillBot's AI-driven writing instruction. According to this theory, learning takes place within a complex system of interrelated elements such as subject, object, tools, rules, community and division of labor. In the context of this study, QuillBot acted as a scaffolding tool, facilitating structured interactions through its automated prompts and tailored feedback system. This scaffolding approach, as posited by Wang et al. (2023), fostered learners' incremental development of writing skills while increasing their self-efficacy and motivation.
The division of labor within this system was clearly demonstrated as learners actively engaged with QuillBot by responding to writing tasks, while the platform provided immediate guidance and personalized feedback. The community dimension was manifested through interactions within a wider network of QuillBot users, fostering a collaborative and supportive environment. Lio et al. (2023) emphasized that such AI-mediated ecosystems effectively reduce anxiety and cultivate trust, a finding that is strongly supported by our observations of QuillBot's impact.
While QuillBot offers many advantages for writing instruction, participants noted that the platform sometimes falls short of the depth and sophistication of human instruction. Consistent with Fryer and Carpenter's (2006) observations, QuillBot's limitations primarily relate to its difficulty in accurately interpreting complex or nuanced written expression. This challenge is particularly evident for novice learners, as the platform sometimes struggles to fully understand and respond appropriately to their intended meanings. In addition, learners identified the lack of authentic human interaction as a significant limitation, noting that QuillBot cannot fully replicate the socio-cognitive and psychological support that human tutors provide during writing tasks.
Effective implementation of QuillBot also depends on access to adequate technological infrastructure, including reliable devices and high-speed internet connectivity, which can be a practical challenge in certain learning environments. Previous research has identified specific limitations of AI-based writing systems such as QuillBot, including limited contextual understanding (Kim et al., 2020), inconsistent accuracy of responses (Lu et al., 2006), and difficulty in managing complex writing inputs (Ayedoun et al., 2015). These findings highlight the need to address these limitations in order to increase the effectiveness of QuillBot in language learning contexts, particularly in supporting learners who require more nuanced guidance and feedback. The collective evidence suggests that while QuillBot serves as a valuable supplemental tool for writing instruction, its current limitations require careful consideration in implementation and highlight the continued importance of human guidance in the learning process.
While AI-driven writing platforms such as QuillBot offer significant benefits to EFL learners, our findings, viewed through the lens of Engeström's activity theory, suggest that they should complement rather than replace human instruction. Activity system analysis suggests that the optimal learning environment emerges from a synergistic relationship between AI tools and human pedagogical expertise. This hybrid approach, which integrates AI-based platforms with conventional teaching methods, has the potential to generate a more comprehensive and enriching learning experience that addresses both technological constraints and the socio-cognitive needs of learners. The AI system acts as a mediating tool within the broader activity system, providing immediate feedback and structured guidance, while human instructors contribute the nuanced understanding and socio-emotional support that Wang et al. (2023) identify as crucial for sustained engagement. This integration allows for a dynamic interplay between automated assistance and human insight, creating what Lio et al. (2023) describes as a "scaffolded ecosystem" that supports both technical skill development and psychological comfort. By acknowledging both the capabilities and limitations of AI platforms within an activity theory framework, educators can design learning environments that leverage technological advantages while preserving the essential human elements of language teaching. This balanced approach not only mitigates the identified limitations of AI systems but also enhances the overall effectiveness of EFL writing instruction through a carefully orchestrated combination of human and artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
This study provides compelling evidence of the transformative potential of QuillBot, an AI-based interactive writing platform, in EFL learning contexts, while acknowledging its current limitations and the need for human instructional presence. Through the systematic implementation of QuillBot's AI-mediated tools, which demonstrate adaptive and interactive capabilities, learners demonstrated quantifiable improvements across multiple dimensions of writing proficiency, including fluency, coherence, lexical diversity, and grammatical accuracy. The research uniquely positions itself at the intersection of technological innovation and pedagogical practice, demonstrating how QuillBot can effectively complement traditional teaching methods.
A distinctive contribution of this research is its nuanced examination of the dual effects of QuillBot's AI-mediated features, which not only improve technical writing skills, but also promote positive affective engagement with the writing process. The findings, viewed through the lens of activity theory, demonstrate how QuillBot serves as a mediating artefact within a complex learning ecosystem, facilitating both cognitive development and psychological comfort. Unlike traditional classroom-based approaches, QuillBot's AI-driven model provides personalized feedback, real-time adjustments and dynamic scaffolding, enabling learners to address individual challenges while maintaining autonomy in their learning trajectory.
From a broader theoretical perspective, this research advances the field of Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) by highlighting QuillBot's potential to improve language skills, while emphasising the critical role of human instruction in addressing socio-cognitive needs. The findings underscore the importance of a hybrid approach that strategically integrates QuillBot with traditional pedagogical methods, providing educators with innovative frameworks for developing more interactive and effective writing programs. This balanced integration represents a significant step forward in understanding how AI-powered platforms such as QuillBot can best be used to support language learning, while retaining the essential human elements that facilitate deep learning and engagement.
Future research directions should focus on developing more sophisticated features within QuillBot that can better understand contextual nuances and provide more personalized feedback, while maintaining the crucial balance between automated assistance and human instruction. In addition, investigations into the long-term effects of hybrid learning approaches incorporating QuillBot on student achievement and motivation would further enhance our understanding of the optimal integration of AI tools in language teaching.
The integration of AI-based writing platforms such as QuillBot into EFL learning environments represents a significant advance in educational technology, marking a transformative shift in the way language skills are acquired and developed. These platforms have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in improving various aspects of writing proficiency, including fluency, coherence, lexical diversity and grammatical accuracy, while at the same time increasing learner motivation and engagement. By providing personalized feedback and dynamic scaffolding, these AI tools create an interactive learning environment that allows students to progress at their own pace while maintaining high levels of engagement. The dual impact of these platforms is particularly noteworthy, as they not only improve technical writing skills, but also cultivate positive attitudes towards writing as a creative and collaborative process.
This research makes a significant contribution to the field of Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) by demonstrating how AI technologies can effectively support both language development and learner autonomy. The findings emphasized the importance of integrating such technologies into language teaching programmers, providing teachers with innovative methods for creating more interactive and effective writing lessons. Looking to the future, further research into developing AI systems for more sophisticated personalized feedback and understanding the long-term effects of hybrid learning approaches on motivation and achievement will be crucial to optimizing these educational tools and ensuring their effective implementation in different learning contexts.
Practical Implications for the EFL Context
The findings of this study have significant practical implications for the implementation of QuillBot in EFL contexts and provide valuable insights for various stakeholders in language education. The research demonstrates the transformative potential of QuillBot in increasing learners' engagement with writing tasks while significantly improving their overall writing skills. QuillBot's rich and interactive environment facilitates focused practice in key dimensions of writing, including grammatical accuracy, vocabulary expansion, and the development of coherent text structure. A distinctive feature of QuillBot's AI-driven instruction is its sophisticated ability to provide instant, personalised feedback that addresses individual learner needs while maintaining a supportive learning atmosphere.
In particular, the study highlights QuillBot's role in creating a low-anxiety learning environment that is conducive to language development. By giving learners the flexibility to progress at their own pace, without the immediate pressure of assessment, QuillBot fosters greater confidence and encourages the natural development of fluency and creativity. This learner-centred approach fundamentally changes the dynamics of traditional writing instruction, making the process more engaging and effective for EFL learners.
QuillBot effectively addresses common constraints in traditional classroom settings, such as time constraints and large class sizes, by providing unlimited opportunities for writing practice. Learners can use QuillBot's features beyond the formal classroom setting, developing greater autonomy in tackling writing tasks and improving their skills. For EFL teachers, integrating QuillBot as a supplementary tool into writing courses creates additional opportunities for skill refinement and practice. The integration of the platform with traditional interactive writing tasks enables teachers to create a more comprehensive and supportive learning environment.
The research strongly recommends that teacher educators and instructors receive training in the effective use of QuillBot in various writing activities. Furthermore, the findings highlight the need for further research into the implementation of QuillBot in language teaching, with a particular focus on the development of more sophisticated features for personalised and adaptive feedback. These advances would deepen our understanding of how QuillBot can best support language acquisition and drive future innovations in language learning technology.
This research contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting the integration of AI-assisted writing platforms in EFL contexts, while specifically highlighting QuillBot's unique ability to foster both technical writing skills and learner motivation. The findings suggest that the implementation of QuillBot represents a significant step forward in creating more effective, engaging and personalized writing instruction in EFL contexts.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
I hereby submit my manuscript, entitled "Exploring the Role of AI-Driven Dynamic Writing Platforms in Improving EFL Learners' Writing Skills and Fostering Their Motivation: An Integrative Study," for your consideration in the Journal of Educational Technology Systems. This study investigates the intersection of artificial intelligence and foreign language education, focusing on how AI-driven platforms can transform writing instruction for EFL learners by enhancing linguistic proficiency and fostering motivation.
The present manuscript employs a mixed-methods approach to evaluate the efficacy of AI-powered writing tools. By analyzing data from IELTS-based assessments, motivation scales, and semi-structured interviews with EFL learners, the study reveals significant improvements in coherence, vocabulary, grammatical accuracy, task accomplishment, and learner motivation among students who used AI platforms. These findings emphasize the potential of AI tools to foster learner autonomy, engagement, and personalized educational experiences, thereby addressing a critical gap in current literature on technology-enhanced language teaching.
This research makes a distinctive contribution to the field by integrating both quantitative and qualitative insights in order to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of AI-based platforms in developing EFL learners' writing skills. It emphasizes the transformative capabilities of these tools in creating tailored, interactive learning environments, while also reflecting on challenges and limitations. The study's practical implications are intended to guide educators and curriculum designers in leveraging AI technologies to enhance writing instruction and learner motivation.
Given the journal's focus on the integration of technology into educational systems, it is anticipated that this manuscript will align with its aims and resonate with its readership. The study explores the interplay between AI technologies and language instruction, thereby bridging the theoretical and practical domains, and contributing to a deeper understanding of how innovative tools can enhance educational outcomes