Behind the Research: Optimizing Real-Time Thermal Imaging for Agricultural Automation
Published in Computational Sciences

A deep dive into benchmarking lightweight YOLO architectures for okra maturity detection
Introduction
Agricultural automation faces a critical challenge: how can we develop inspection systems that are both highly accurate and fast enough for real-time processing? In our recent study published in The Journal of Supercomputing, my colleagues and I addressed this question by systematically benchmarking four state-of-the-art YOLO nano-variant object detection models for thermal imaging applications in okra maturity grading.
Why Thermal Imaging Matters
Traditional RGB-based inspection systems struggle under variable lighting conditions—a common reality in agricultural settings ranging from night harvesting to indoor packing facilities. Thermal imaging offers a compelling alternative by capturing temperature-dependent information that remains consistent regardless of ambient lighting. For okra specifically, thermal signatures reveal physiological differences in moisture content and thermal mass between maturity stages, providing a robust basis for automated quality assessment.
However, thermal imagery presents unique computational challenges. Single-channel intensity data, reduced texture information, and temperature-dependent contrast require specialized architectural considerations that haven't been systematically evaluated in prior research.
The Research Gap
While YOLO (You Only Look Once) architectures have been extensively benchmarked on RGB datasets such as COCO and ImageNet, comprehensive evaluation on thermal agricultural imagery remained absent from the literature. This gap is particularly significant because:
- Architectural innovations designed for RGB may not transfer effectively to thermal domains
- Real-time industrial sorting requires sub-50 millisecond inference latency
- Deployment on heterogeneous computing platforms (GPU vs. CPU) demands quantitative performance analysis
Our study addresses these gaps by evaluating YOLOv5n, YOLOv8n, YOLOv11n, and YOLOv12n across multiple performance dimensions.
Methodology Highlights
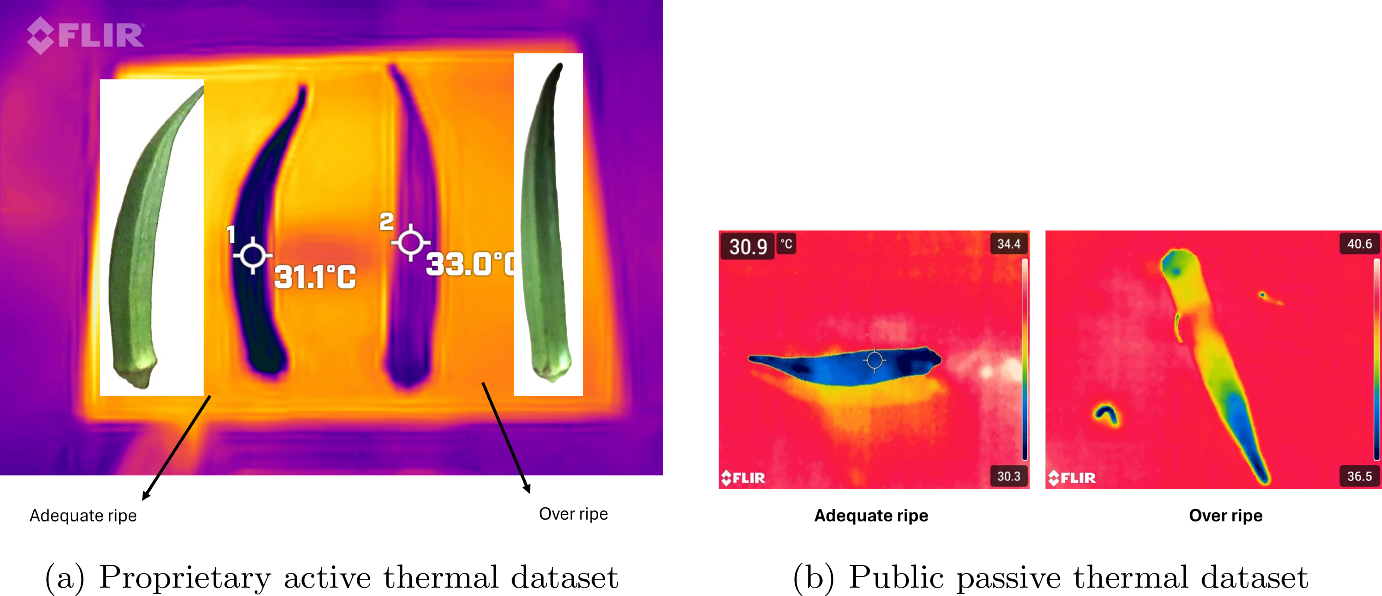
We developed a dual-source thermal dataset combining passive and active thermal imaging modalities. The active thermal approach—involving controlled preheating to 30°C—proved particularly important. Natural thermal contrast between adequately matured and overripe okra averages only 2.8°C under ambient conditions, which can be insufficient under variable environments. Controlled preheating amplifies this contrast to 4–8°C by exploiting maturity-dependent differences in thermal mass and cooling behavior.
Our experimental design incorporated rigorous statistical validation across five independent training runs, ensuring reproducibility and significance testing of observed performance differences. This methodological rigor is essential for drawing reliable conclusions in machine learning research.
Key Findings
Training Duration Dependency
One of our most significant findings relates to training efficiency. Under the resource-efficient 10-epoch protocol—reflecting rapid development scenarios—YOLOv8n achieved the highest detection accuracy (66.3% mAP@0.5–0.95), while YOLOv5n delivered comparable performance (66.1%) with superior computational efficiency.
However, extended training experiments revealed a critical insight: attention-based architectures (YOLOv11n and YOLOv12n) achieve higher peak accuracy (73.1% and 72.9% respectively) when training budgets permit 45–67 epochs. This performance ranking inversion suggests that architectural complexity translates to gains only with sufficient training iterations—a crucial consideration for practical deployment.
Platform-Specific Performance
Our benchmarking across heterogeneous computing platforms revealed distinct trade-offs:
- GPU deployment (NVIDIA T4 with TensorRT): YOLOv8n achieved 1.6 ms inference latency, supporting throughput exceeding 625 FPS—well above the ≥20 FPS requirement for real-time sorting
- CPU deployment (ONNX Runtime): YOLOv5n exhibited superior performance at 31.1 ms, making it optimal for edge and embedded scenarios
These findings provide practical guidance for selecting architectures based on deployment constraints.
Architectural Insights
Through gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) analysis, we discovered that decoupled detection heads enable task-specific feature specialization. Classification branches focus selectively on thermal intensity gradients, while localization branches emphasize geometric boundaries—a design principle particularly beneficial for thermal imagery where diagnostic features are spatially distinct.
Ablation studies confirmed that mosaic augmentation improved detection performance by 6.2% without additional latency, while balanced loss weighting outperformed imbalanced configurations in this binary classification task.
Practical Implications
Our research demonstrates that thermal-based YOLO nano-variants are ready for integration into automated sorting pipelines, achieving 75 kg/min throughput with <2% background false positives. The system operates at sustained rates exceeding industrial requirements while maintaining high detection accuracy.
For practitioners, the key takeaway is this: model selection must jointly consider deployment constraints (inference latency, memory footprint) and available training resources (time budget, computational capacity). Simple architectures like YOLOv5n and YOLOv8n excel in rapid-iteration scenarios, while attention-based variants justify their complexity only when extended training is feasible.
Future Directions
Several promising research directions emerge from this work:
- Dataset expansion across cultivars, seasons, and environmental conditions to enhance model robustness
- Multi-class grading spanning the full maturity spectrum
- Multispectral fusion combining thermal and RGB modalities
- Knowledge distillation from transformer-based teachers to lightweight students
- Field deployment trials in commercial facilities for long-term validation
Conclusion
This systematic benchmark establishes quantitative baselines for thermal agricultural imaging and provides practical guidance for architecture selection. The identified strategies—anchor-free detection, decoupled heads, mosaic augmentation, and balanced loss weighting—are transferable to other crops and sensing modalities, offering strong potential for advancing automated agricultural inspection systems.
Article Citation: Ganapathy, M.R., Pugazhendi, P., Periasamy, S., Nagarajan, B. (2026). Benchmarking YOLO nano-architectures for real-time thermal imaging: application to okra maturity grading on heterogeneous computing platforms. The Journal of Supercomputing, 82:97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-026-08226-w
Data Availability: The public thermal dataset is available at Mendeley Data. Code is available at the project GitHub repository.
Follow the Topic
-
The Journal of Supercomputing

The Journal of Supercomputing publishes papers on the technology, architecture and systems, algorithms, languages and programs, performance measures and methods, and applications of all aspects of supercomputing.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
SI - Computational and Mathematical Models using Heterogeneous Computing
Message-passing programming models such as MPI allowed to aggregate multicore systems in larger clusters, that dominated the TOP 500 supercomputing list. However, at that time parallel computing seemed to face some limits that were hard to overcome. Physical limits prevented clock frequencies to increase, and the Law of Diminishing Returns reduced the usefulness of keep adding cores to a multiprocessor. Suddenly, the advent of GPU computing changed the game once again. Being initially developed as a way to accelerate graphical processing, GPUs were reused to speed up certain types of calculations that needed a similar processing to an entire set of independent elements. CUDA programming model allowed programmers to translate to the GPU world many applications, and the TOP 500 list started to show more and more heterogeneous systems that incorporated accelerators to their cluster nodes.
Today, we are facing a new revolution. The popularization of Deep Learning techniques makes different vendors to add specific support for these kinds of algorithms in the accelerators present in the market. Deep Learning is a world that requires high-performance computing, massive parallelism, and it is causing the development of new heterogeneous architectures.
Is in this context where the symposium on High-Performance Computing at the “Computational and Mathematical Methods in Science and Engineering” conference takes place. Starting in 2000, CMMSE have gathered specialist from all around the globe to discuss recent advances in different topics related to the use of high-performance computing to speed up the execution of mathematical methods. The particular format of the CMMSE conference, with lively discussions in a relaxed atmosphere, allows the presentation of cutting-edge, ongoing work, that receive direct feedback from the audience, thus enriching the research carried out. In an era of big conferences that attract several hundreds of researchers that should compete for the attention of the audience, the CMMSE conference keeps the spirit of specialist meetings, where all the speakers are equally accessible and where interesting discussions are carried out after each presentation.
This special issue of the Journal of Supercomputing will contain revised papers, selected from those presented at the 25th and 26th Computational and Mathematical Methods in Science and Engineering, held in Cadiz in July 2025 and July 2026. The Associated Editors selected around 20% of all the contributions sent to the conference, covering both foundational and practical issues in the use of parallel computing to solve complex applications, for publication in this special issue.
In summary, we believe that the interesting contributions included in this issue are good examples of how the high-performance-computing community works day after day to speed up the performance of different real-world problems, increasing the usefulness of current and future parallel systems and imagining new ways to develop concurrent code.
Submitted papers should present original, unpublished work, relevant to one of the topics of the special issue. All submitted papers will be evaluated on the basis of relevance, significance of contribution, technical quality, scholarship, and quality of presentation, by at least three independent reviewers. It is the policy of the journal that no submission, or substantially overlapping submission, be published or be under review at another journal or conference at any time during the review process. Please note that the authors of selected papers presented at CMMSE 2025 are invited to submit an extended version of their contributions by taking into consideration both the reviewers’ comments on their conference paper, and the feedback received during presentation at the conference. It is worth clarifying that the extended version is expected to contain a substantial scientific contribution, e.g., in the form of new algorithms, experiments or qualitative/quantitative comparisons, and that neither verbatim transfer of large parts of the conference paper nor reproduction of already published figures will be tolerated. The extended versions of CMMSE 2025 papers will undergo the standard, rigorous journal review process and be accepted only if well-suited to the topic of this special issue and meeting the scientific level of the journal. Final decisions on all papers are made by the Editor in Chief.
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Sep 01, 2026
Section - Architectures, Systems and Hardware Security
All aspects of high-performance hardware and architectures, including optimizing and evaluating processors, systems issues, and security, especially at the hardware level and sustainability of systems.
Topics include but not limited to the following:
T
• Architectural support for programming languages or software development.
• Architectures to support extremely heterogeneous composable systems (e.g., chiplets)
• Design-space exploration/performance projection for future systems
• Evaluation and measurement on testbed or production hardware systems
• Hardware acceleration of containerization and virtualization mechanisms for HPC
• Interconnect technologies, topology, switch architecture
• I/O architecture/hardware and emerging storage technologies
• Memory systems: caches, memory technology, non-volatile memory, memory system architecture (to include address translation for cores and accelerators)
• Multi-processor architecture and micro-architecture (e.g., reconfigurable, vector, stream, dataflow, GPUs, and custom/novel architecture)
• Sustainable design aspects, including power and energy efficiency and power-management strategies
• Resilience, error correction, high availability architectures
• Scalable and composable coherence (for cores and accelerators)
• Secure architectures, side-channel attacks, and mitigation, covering all attack vectors, including all forms of side-channel attacks, piracy, reverse engineering, tampering, and hardware Trojan attacks, including countermeasures at different stages of system design - i.e., architecture definition, design, validation, and deployment
• The security of hardware and system security at all levels of abstraction
• Interactions between hardware and systems, and between hardware and firmware/software, including in the context of security and trust
• Software/hardware co-design, domain-specific language support
• Interactions among architectures, compilers, programming languages, and operating systems
Architectures, Systems and Hardware Security research relates to multiple United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through advances in health care, education, and energy, among other fields. This Section particularly welcomes submissions related to SDG 9 “Industry, Innovation, And Infrastructure.”
An essential aspect of supercomputing involves solving computer-intensive problems. Paper submissions are expected to address problems that require significant computational resources.
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
.png)

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in