Cooled MarkII blade surface pressure and temperature distribution by a conjugate heat transfer analysis using Reynolds stress baseline turbulence model
Published in Mechanical Engineering
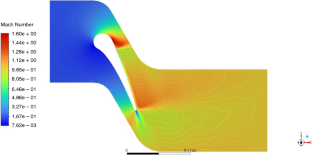
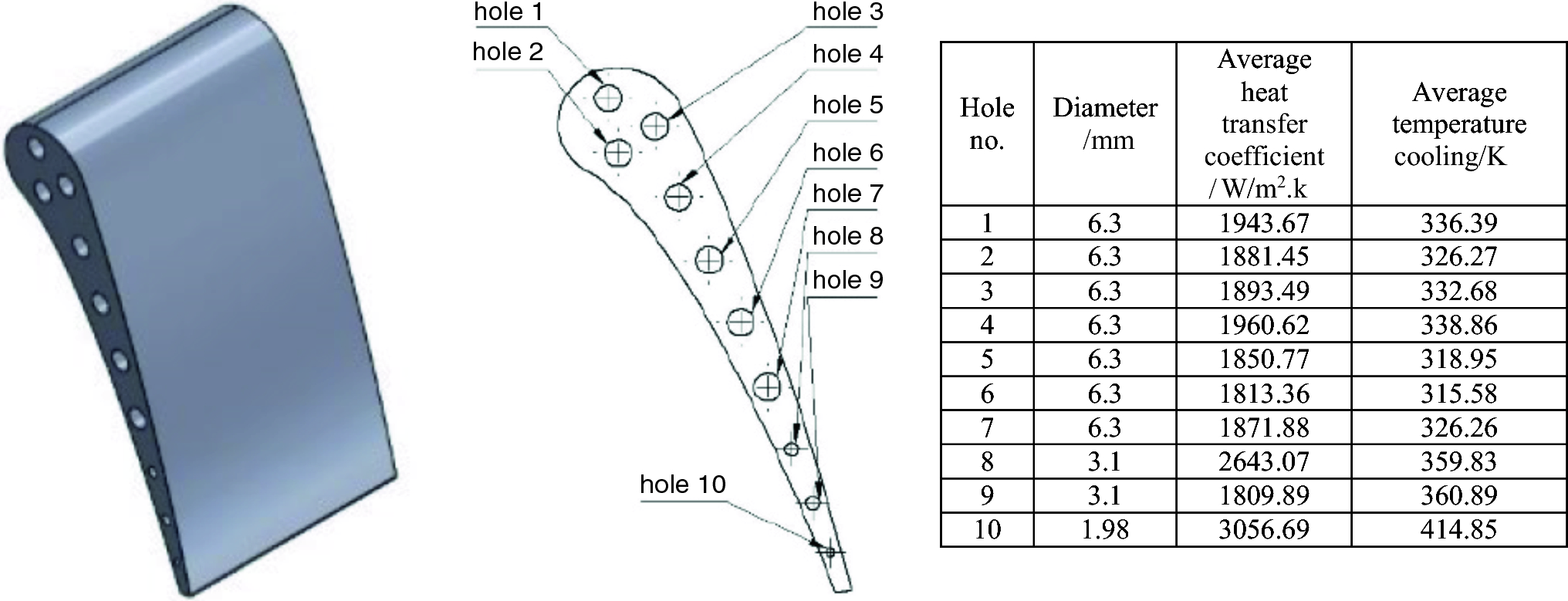
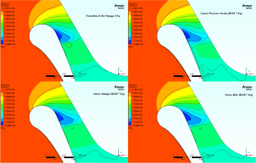
"In this study, we explore the conjugate heat transfer on the MarkII blade surface using the Reynolds Stress Baseline Turbulence Model. The analysis reveals significant insights into the pressure and temperature distribution across the turbine blade, with potential applications in optimizing turbine performance. We used FLUENT and ANSYS software for simulation and validation against experimental results."
Follow the Topic
-
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry

Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry publishes high quality papers covering all aspects of thermal analysis, calorimetry, thermodynamics, heat and energy.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Thermal Safety of Energetic Materials
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Dec 31, 2026
Novel aspects and trends in thermal analysis and calorimetry in Central and Eastern Europe (CEEC-TAC8)
We are pleased to introduce the special issue entitled „Novel aspects and trends in thermal analysis and calorimetry in Central and Eastern Europe“, regarding the 8th Central and Eastern European Conference on Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (CEEC-TAC8), that was held between 16th and 19th of September 2025 in Mostar, Bosnia and Herzegovina. The CEEC-TAC8 conference gathered 147 registered participants from 26 countries, presenting a total number of 155 scientific works. Of those, 2 are Award Plenary Lectures (APL), 5 are Plenary Lectures (PL), 12 are Invited Lectures (IL), 2 Parallel Sessions of Oral Presentations – 40 contributions (OP) & 3 Sessions of Poster Presentation – 96 contributions (PS). Each session of oral presentations comprised of 20 works, while each poster presentations included 32 works. The topics of the conference were divided into two groups: a) Theory, Kinetics, Energetics, Materials Science and Engineering; b) Calorimetry, Thermodynamics, Structural changes, Polymers, Nanomaterials and Organic Functional Systems.
At this edition, Awards were offered to exceptional scientists: i) Prof. Dimitris Achilias from Greece (Distinguished TA&C Researcher in Central & Eastern Europe) and ii) Dr. Tadas Dambrauskas from Lithuania (Outstanding Young TA&C Researcher in Central & Eastern Europe). It was organized by the Central and Eastern European Committee for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (CEEC-TAC), in collaboration with the National Associations for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry from Central and Eastern European countries, the University of Mostar, Faculty of Science and Education (University of Mostar), Faculty of Humanistics and Social Sciences (University of Mostar), University of Split, Faculty of Chemistry and Technology (University of Split), Babeş-Bolyai University, Institute of Physical Chemistry-Ilie Murgulescu, and Committee for Thermal Science and Calorimetry of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The special issue „Novel aspects and trends in thermal analysis and calorimetry in Central and Eastern Europe“ is intended to hosted by the Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (JTAC); participants to the CEEC-TAC8 conference are allowed to send maximum two articles to JTAC for this special issue.
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 31, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in