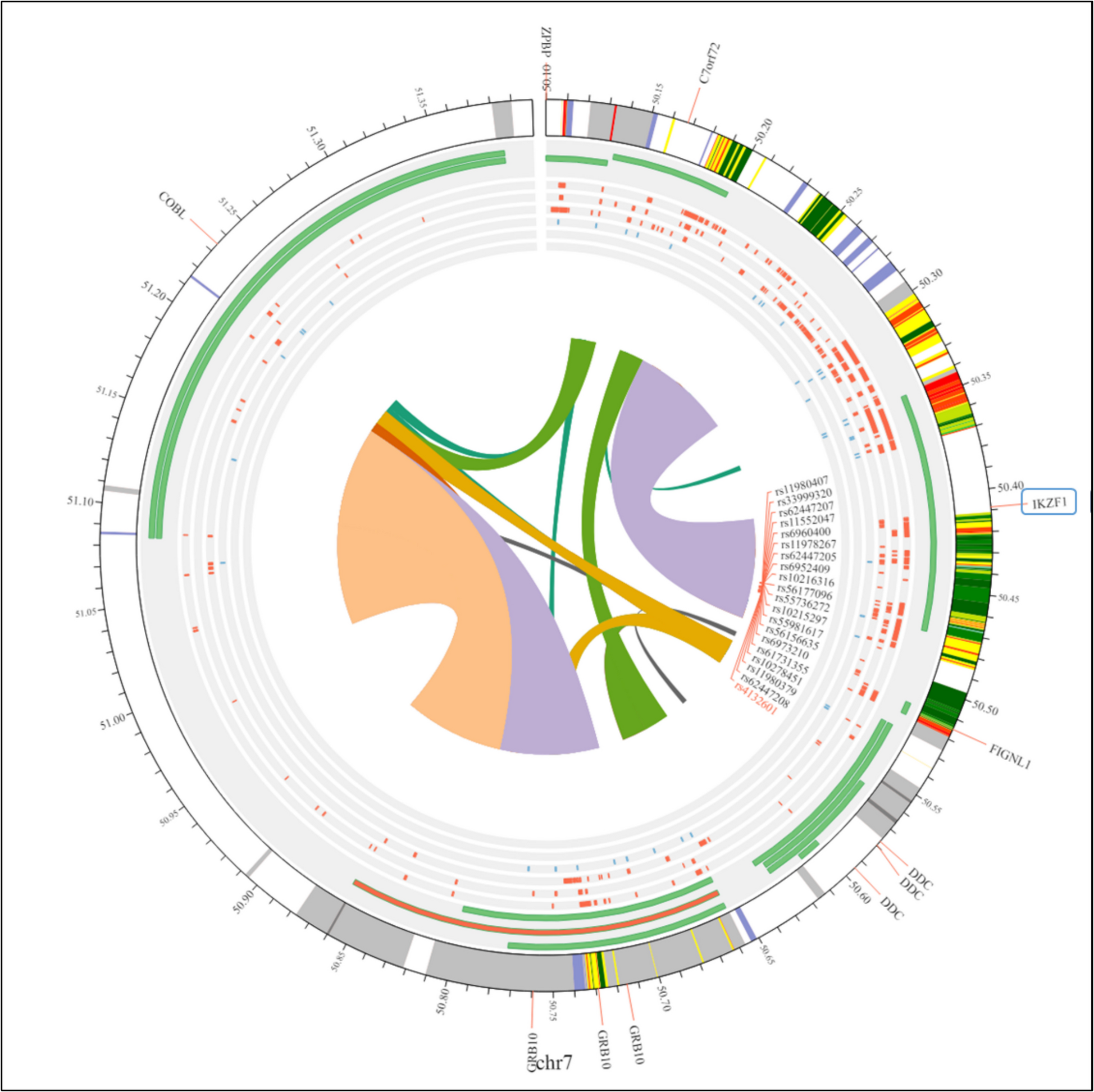
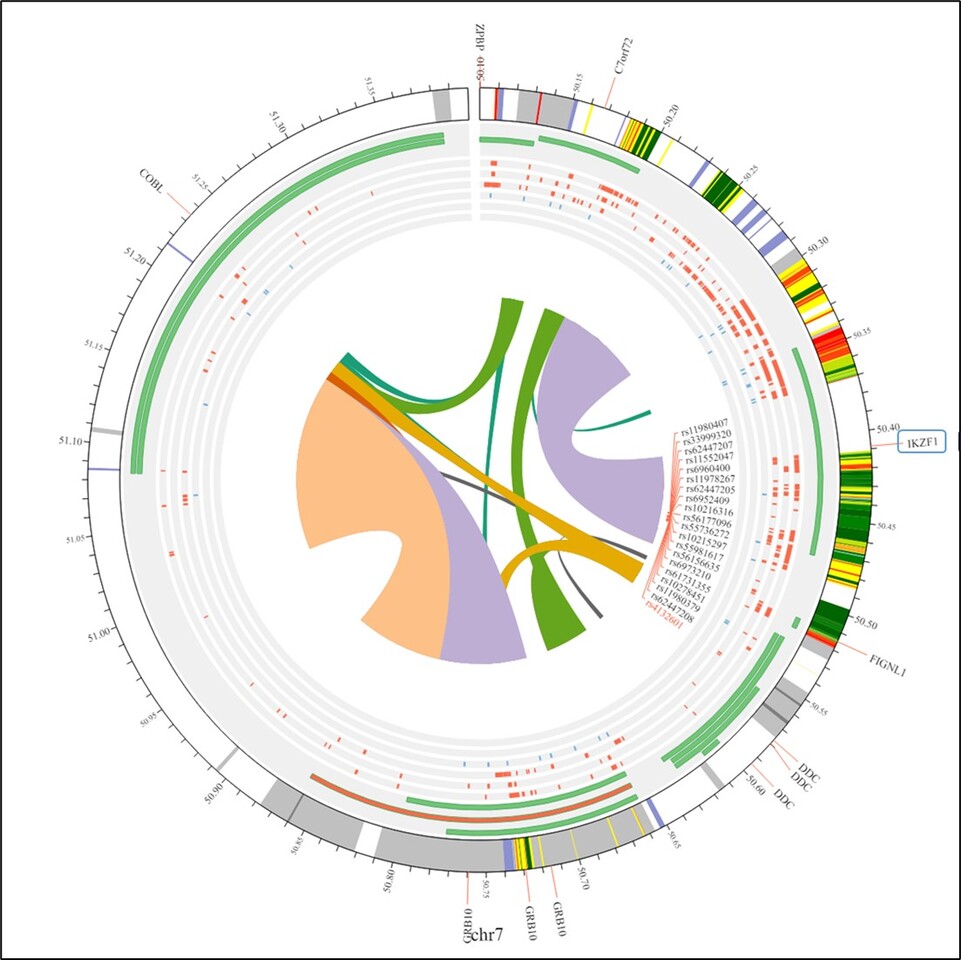
Investigating the impact of IKZF1 SNPs rs4132601 and rs11978267 on acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comprehensive meta-analysis
Leukemias are a diverse group of hematologic disorders primarily affecting white blood cells, with varying clinical presentations, prognoses, and responses to treatment.
Published in Cancer
Like
Be the first to like this
The article titled "Investigating the Impact of IKZF1 SNPs rs4132601 and rs11978267 on Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis" concludes that both rs4132601 and rs11978267 polymorphisms in the IKZF1 gene are significantly associated with an increased risk of developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), particularly in certain ethnic populations. The meta-analysis, which included data from numerous case-control studies, discovered that the existence of risk alleles for these SNPs correlated with an increased susceptibility to ALL, implying that they might serve as genetic biomarkers for early diagnosis and risk stratification in clinical practice.
Follow the Topic
Cancer Biology
Life Sciences > Biological Sciences > Cancer Biology