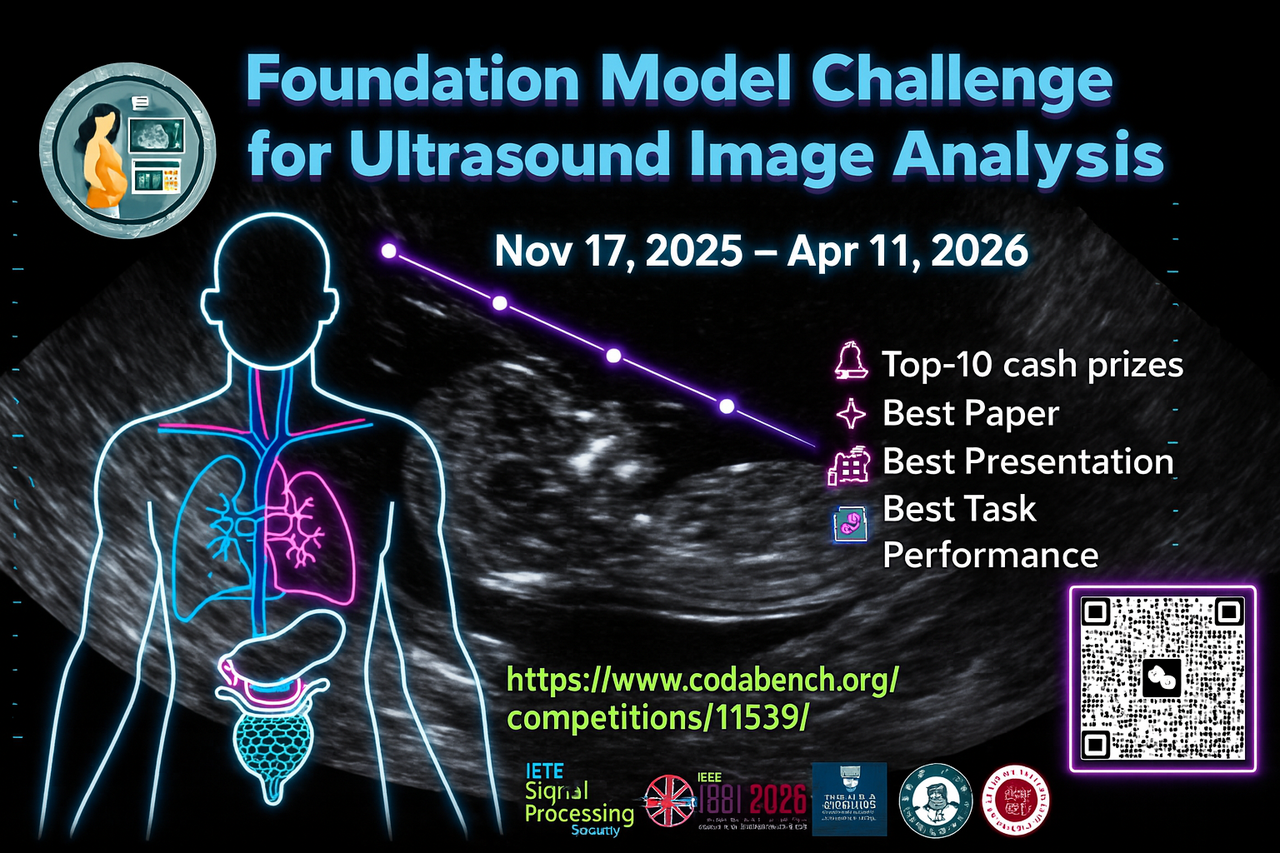
ISBI 2026 Challenge: Foundation Model Challenge for Ultrasound Image Analysis
Published in Bioengineering & Biotechnology, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, and Research Data
Explore the Research

Challenges – ISBI 2026
Challenge: CSV 2026: Carotid Plaque Segmentation and Vulnerability Assessment in Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a vital diagnostic tool, but accurately analyzing images across diverse organs and pathologies remains challenging. Existing methods often lack generalization and are limited to specific tasks. Developing a Foundation Model: To design a generalized model capable of handling multiple tasks in ultrasound image analysis, including classification, segmentation, detection and regression across diverse organs and pathologies.
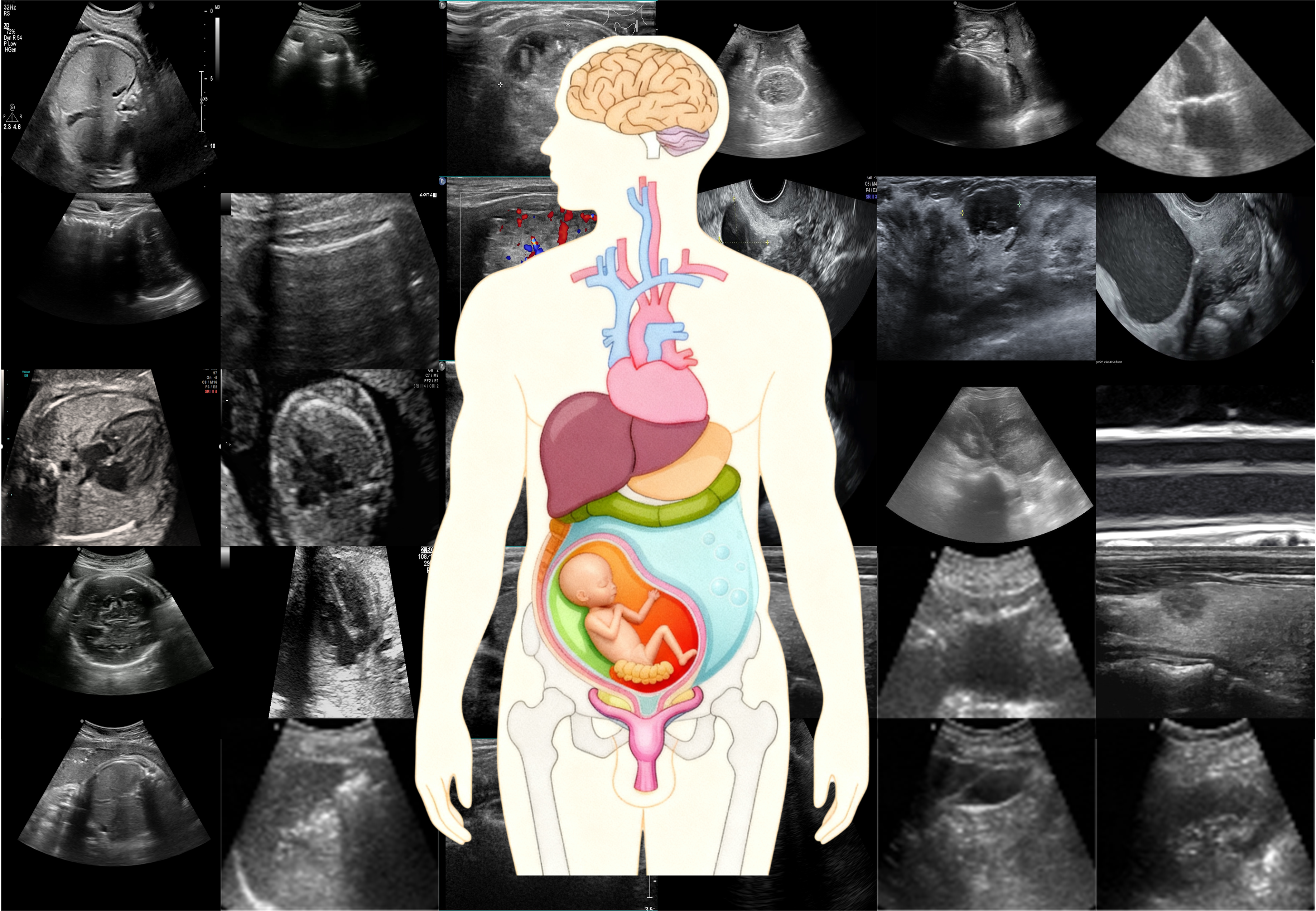
Accurately analyzing ultrasound images across diverse organs and pathologies remains a significant hurdle in clinical practice. Traditional methods for ultrasound image analysis are often limited to specific tasks, such as organ classification or tumor detection, and struggle to generalize across different medical conditions. These task-specific approaches fail to fully leverage the rich, multi-dimensional information contained in ultrasound data, thus limiting their clinical applicability.
Foundation models—large, pre-trained deep learning models capable of handling diverse tasks—have the potential to address these challenges. By leveraging advanced learning techniques, foundation models can be trained to handle a broad range of organ types, pathologies, and diagnostic tasks. This approach promises a more generalized solution that can perform multiple tasks, such as image classification, segmentation, and detection, in a single unified framework.
Multi-task learning, an approach that enables a model to learn several related tasks simultaneously, can be key in improving diagnostic accuracy and clinical outcomes. By learning shared representations across different tasks, these models can develop a deeper understanding of ultrasound images, thus providing more reliable and consistent results across diverse medical applications.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in