Coffee Berry Disease Pressure in Ethiopian Arabica Coffee Highlights the Need for High-Density Genetic Mapping and GWAS-Based Resistance Breeding
Published in Microbiology, Genetics & Genomics, and Plant Science
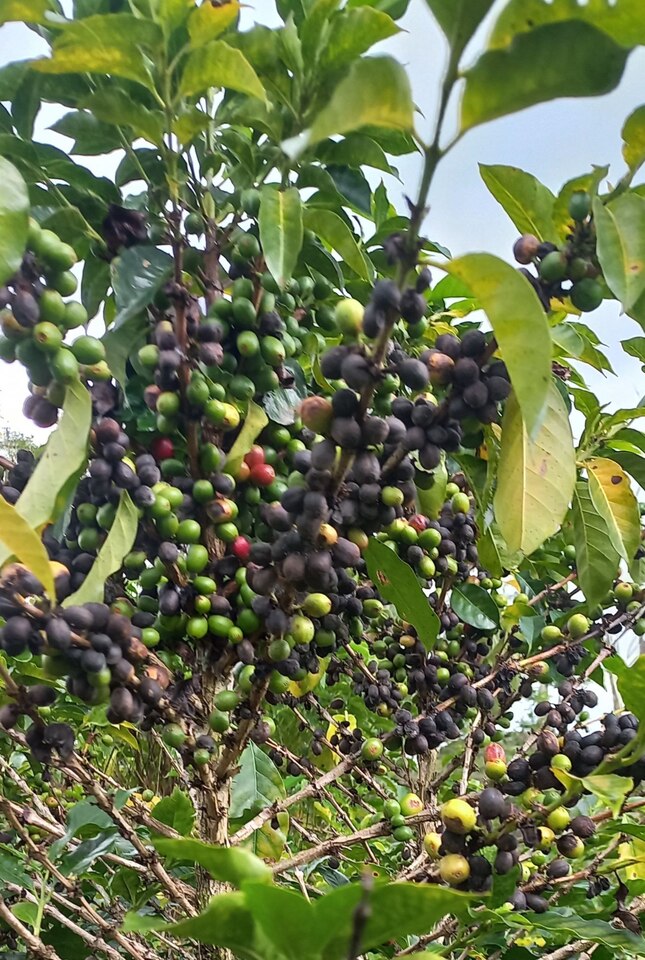

The findings from this study highlight a clear disconnect between the severity of Coffee Berry Disease in Ethiopia and the availability of genetically validated resistant cultivars. Although farmers possess extensive indigenous knowledge and have successfully identified CBD-tolerant genotypes in forest coffee populations, these selections remain largely uncharacterized at the molecular level. This gap limits their broader use in breeding programs and increases the risk of genetic erosion.
Integrating field-identified resistant genotypes into high-density genetic mapping and GWAS frameworks would allow resistance traits to be anchored to specific genomic regions in Arabica coffee. Such approaches can transform farmer-led selection into durable breeding outputs by identifying resistance loci and developing diagnostic SNP markers for marker-assisted selection. In the context of increasing CBD pressure driven by climate variability and microclimatic instability, genomics-informed breeding represents a critical next step for safeguarding Ethiopia’s unique Arabica coffee genetic resources and strengthening long-term disease resilience.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in