Enhancing dielectric permittivity in barium ferrite: a novel material for energy storage and advanced electronics applications
Published in Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Materials, and Mechanical Engineering
I'm thrilled to share our latest research on advanced materials for energy storage and high-frequency electronics. Our study focuses on Mn–Zn-doped barium ferrite, a material that shows significant improvements in dielectric permittivity and thermal stability, making it ideal for applications in supercapacitors, RAMs, and high-frequency capacitors.(https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-025-06801-z)
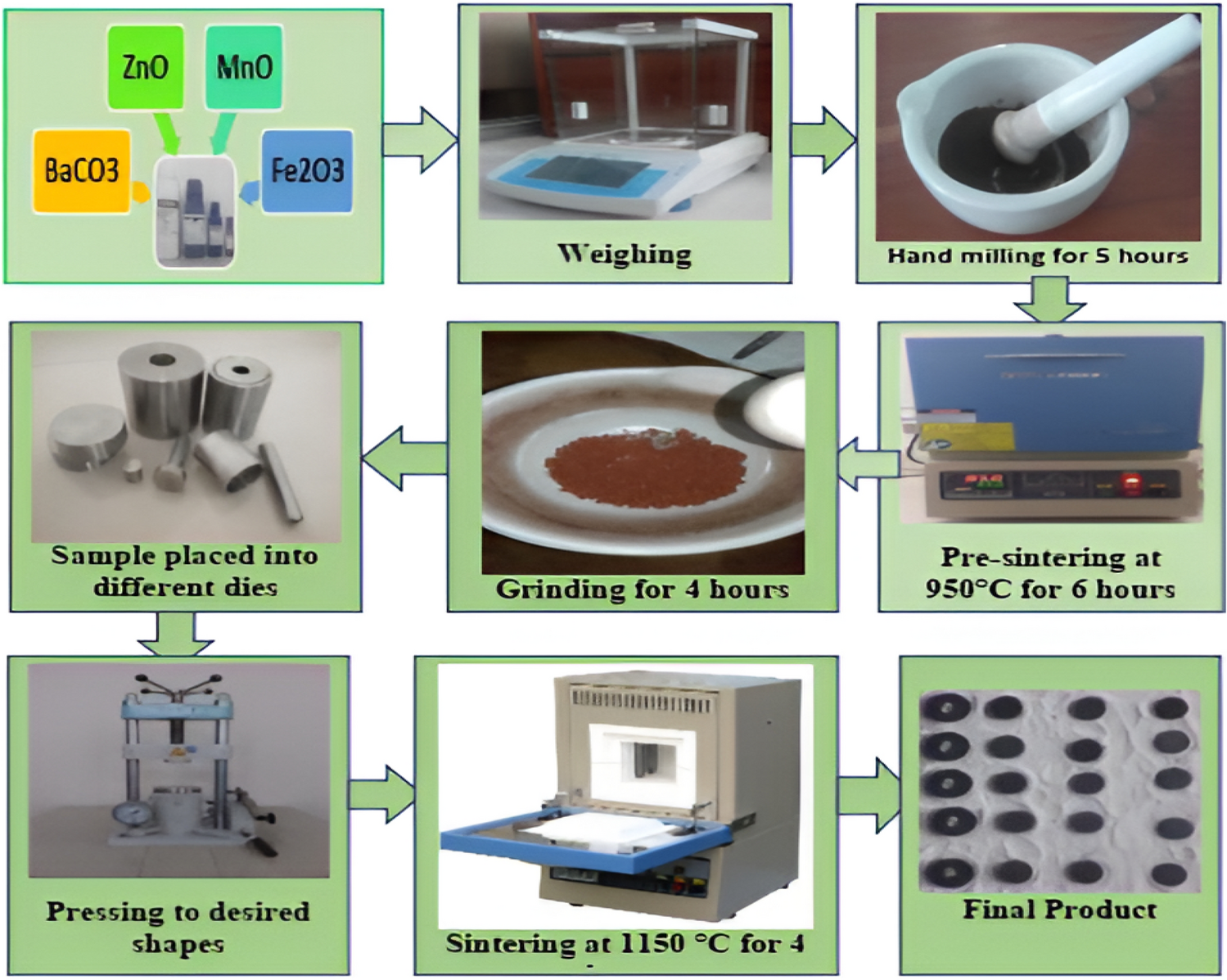
In our experiments, we synthesized BaZn₁₊ₓMnₓFe₁₂₋₂ₓO₁₉ ceramics with varying concentrations of Mn and Zn. Using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and dielectric measurements, we observed that increasing the Mn–Zn ion concentration enhances the dielectric permittivity and positively impacts the thermal stability and Curie temperature of the material. These properties are crucial for the development of efficient energy storage systems and advanced electronic devices.([ResearchGate][2])
One of the key findings is the material's ability to maintain high dielectric permittivity across a range of temperatures and frequencies. This behavior is attributed to the Maxwell–Wagner-type polarization, which enhances the material's low dielectric loss and high permittivity, making it well-suited for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and radar-absorbing materials (RAMs).([ResearchGate][2])
Our research demonstrates that Mn–Zn-doped barium ferrite is a promising candidate for next-generation energy storage and high-frequency electronic applications. The improved dielectric properties and thermal stability open up new possibilities for the design of capacitors, supercapacitors, and other electronic components that require materials with high energy storage capabilities and reliability under varying environmental conditions.
For a more detailed understanding of our work, you can access the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-025-06801-z
Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or would like to discuss potential collaborations. Let's advance the field of energy storage and electronics together
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Applied Sciences

This is a multi-disciplinary, peer-reviewed journal for the disciplines of Applied Life Sciences, Chemistry, Earth and Environmental Sciences, Engineering, Materials Science and Physics, fostering sound scientific discovery to solve practical problems.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Engineering: Energy Management System
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026
Engineering: Computer Aided Engineering Design, Manufacturing and Maintenance
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in