

It all began with a salt stain.
One afternoon in a kitchen in Cholula, a picturesque town in Puebla, Mexico, a few drops of tap water dried on the sink, leaving behind a chalky white residue. This everyday scene—familiar to anyone living with hard water—sparked the idea that eventually grew into our research. What at first seemed like a simple nuisance revealed a deeper question: what does it really mean to live using hard water, and how can materials science help with it?
Functional polymeric materials for hard water treatment a comprehensive review.
For one of us, the issue was more than aesthetic. Prolonged use of hard water—rich in calcium and magnesium ions—had triggered episodes of eczema, serving as a personal reminder of how water quality can subtly impact health. That experience inspired us to look closer, and soon we realized that the problem extended far beyond a single kitchen or household.
A common problem with global reach
The hard water situation of Cholula is far from unique. As we delved into literature, we were surprised to discover just how widespread hard water is globally. Most cities around the world rely on hard water supplies.
In the United States, more than 85% of households live with hard water. Across Mexico, groundwater hardness is the norm. In Europe, cities such as London and Oxford often exceed 200 ppm CaCO₃, whereas parts of Africa, Asia, and Australia exhibit significant regional variations, depending on their geology and rainfall.
Globally, the numbers are staggering. Hard water affects household appliances, shortens the lifespan of heaters and pipes, increases soap consumption, and contributes to environmental issues such as scaling and energy inefficiency. More importantly, it can impact health, ranging from skin irritation and hair damage to more complex concerns. Research suggests a relationship between water hardness and chronic disease: moderate levels of calcium and magnesium in drinking water may have protective effects against cardiovascular disease and even reduce the risk of some cancers. However, very hard water has increased risks of bladder cancer, malignant melanoma, hematological malignancies, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and higher rates of breast and prostate cancer compared to soft water.
Understanding this changed the way we thought about that kitchen sink. What appeared to be a local inconvenience was, in fact, part of a global challenge.
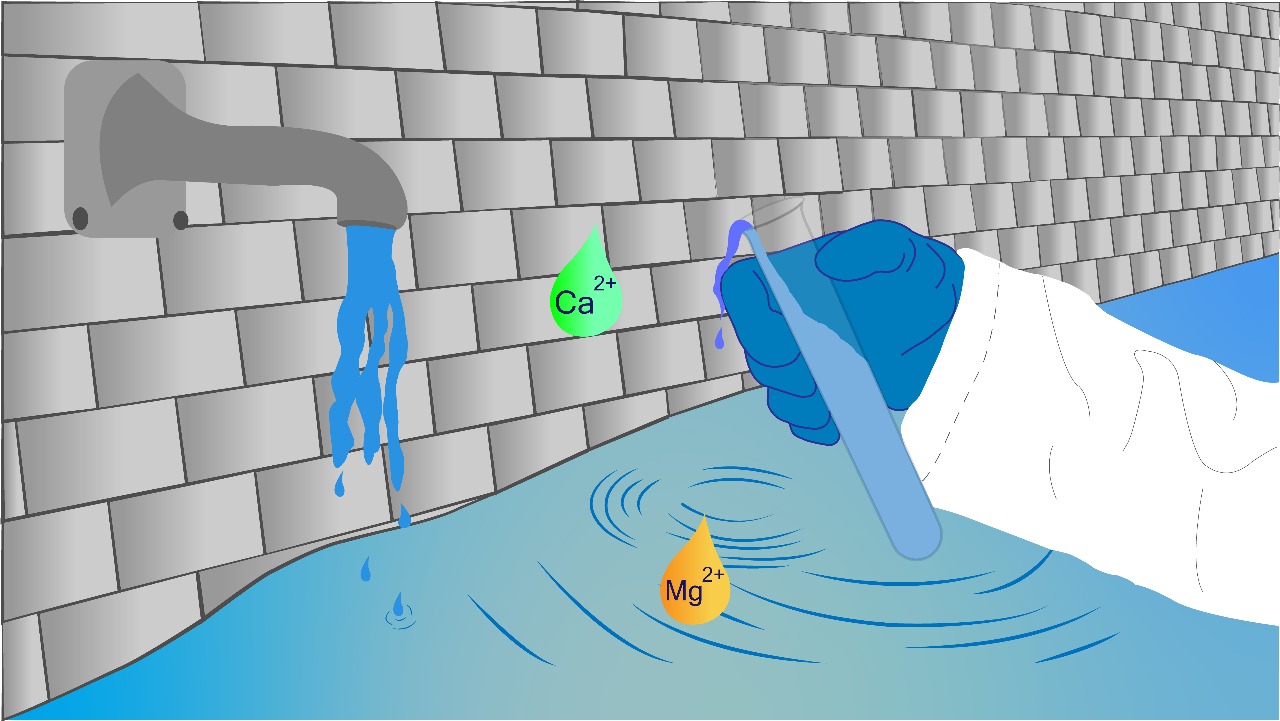
Searching for better solutions
Traditional treatments include ion exchange, chemical precipitation, reverse osmosis, and electrocoagulation. They work, but often at a price: high operational costs, fouling, significant energy demands, and chemical waste. Furthermore, such systems are out of reach for many households.
So, that’s when we turned our attention to whether polymers can help with.
Polymers are fascinating due to their versatility in shaping, mechanical properties, and thermal properties, and chemical tunability. Their chemistry can be tailored to interact with specific ions, surfaces can be modified for enhanced selectivity, and their structures—such as hydrogels, membranes, and composites—can be designed for regeneration and reuse. This flexibility opens possibilities that conventional technologies struggle to match.
In our work titled, Functional Polymeric Materials for Hard Water Treatment: A Comprehensive Review, we examined the state of the art:
- Hydrogels, with their remarkable swelling and ion capture capacity, can remove Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺ with high efficiency.
- Polyelectrolyte systems, like PAA/PVA, calcium chelate, can be processed into membranes or fibrous mats.
- Dextrin-based nanosponges, porous and selective, offer good regeneration cycles.
- Bio-based composites, combining natural polymers with synthetic ones, balance sustainability with performance.
Two sides of the polymer story
Of course, no solution is perfect. Polymers offer several clear advantages, including tunability, selectivity, potential cost-effectiveness, and, in some cases, biodegradability. They can be engineered to be reusable, reducing waste. Some systems already demonstrate over 90% removal of hardness ions under laboratory conditions.
But they also face challenges. Many remain at the proof-of-concept stage, tested with simplified water samples rather than real-world supplies. Some rely on petroleum-derived monomers or energy-intensive processes, raising sustainability concerns. Even biodegradable polymers may have mechanical limitations or degrade slowly under natural conditions. And scalability remains a key barrier—what works in the lab may not yet be viable for households or municipal plants.
In short, polymers hold great promise, but the journey from lab bench to real-world application is still unfolding.
Beyond chemistry: equity and impact
What struck us most while writing this review was not just the science, but the human dimension. Hard water disproportionately affects marginalized communities, where access to expensive technologies like reverse osmosis is limited. In such contexts, this search for polymer-based solutions is more than a technical challenge—it is also a question of equity and sustainability. Designing affordable, regenerable, and environmentally compatible polymer systems, they could transform daily life for millions of people.
From stains to solutions
For us, this journey began with a stubborn salt mark in a Cholula kitchen and the personal struggles that many share, such as skin irritation, scaling pipes, and damaged appliances. It has since expanded from a global perspective, recognizing that the same challenge unites households worldwide.
Our review seeks not only to summarize the progress in functional polymers for hard water treatment, but also to invite further collaboration and innovation. The problem is widespread, but so is the potential for science to address it.
From a single kitchen sink to a worldwide challenge, polymers may one day transform hard water treatment—making it more equitable and sustainable.
Functional polymeric materials for hard water treatment a comprehensive review.
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Materials

This is a broad, open access journal publishing research from across all fields of materials research.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Reuse and Recycling of Waste in the Construction Sector
The construction sector is one of the largest producers of waste, contributing significantly to global environmental challenges. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable practices, particularly in the reuse and recycling of construction and demolition waste, municipal solid waste, and industrial waste. Addressing the environmental impact of this waste is critical for sustainable development. This collection explores innovative strategies, technologies, and policies aimed at minimizing waste, promoting resource efficiency, aiming to reduce landfill dependency, and advancing sustainable building practices within the construction industry.
This collection invites comprehensive research and practical insights into various aspects of waste management in the construction sector, including:
1. Construction and Demolition Waste: Innovative methods for recycling and reusing concrete, asphalt, metals, wood, and other materials from construction and demolition sites.
2. Municipal Solid Waste: Strategies for integrating recycled municipal solid waste materials, such as glass, plastics, and organic matter, into construction projects.
3. Industrial Waste: Techniques for repurposing industrial by-products and waste materials in construction, including slag, fly ash, and manufacturing residues.
4. Policy and Regulation: Examination of governmental policies, regulations, and incentives that facilitate the reuse and recycling of various waste types in construction.
5. Sustainable Construction Practices: Implementation of circular economy principles in construction, including design for disassembly, modular construction, and sustainable material sourcing.
6. Environmental and Economic Impacts: Evaluation of the environmental benefits and economic feasibility of recycling and reusing different types of waste in the construction sector, including life cycle and cost-benefit analyses.
7. Technological Advances: Development and application of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics, to optimize waste management and recycling processes in construction.
8. Material Innovation: Research new materials and products derived from recycled waste, assessing their performance, durability, and potential applications in construction.
9. Case Studies and Best Practices: Documentation of successful projects and initiatives that highlight effective reuse and recycling strategies in the construction industry.
By bringing together cutting-edge research and practical insights, this collection aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state and future directions of waste reuse and recycling in the construction sector. Contributions from academics, industry professionals, policymakers, and other stakeholders are encouraged to foster a multidisciplinary dialogue and drive meaningful change in the industry.
Keywords: Construction Waste Management; Recycling Techniques; Reuse Strategies; Sustainable Construction; Municipal Solid Waste; Environmental Impact; Circular Economy; Industrial Waste Recycling
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026
Materials in Structural Engineering: Challenges and Innovations under Extreme Loading Conditions
In the realm of materials science and engineering, the quest for robust, resilient materials capable of withstanding extreme loading conditions and demanding service environments is more pressing than ever. The field of structural engineering, at the forefront of this endeavor, faces constant challenges posed by natural disasters, industrial accidents, high-temperature exposure, and deliberate acts of violence. The ability of structures to endure such events depends crucially on the properties and performance of the materials from which they are constructed. Discover Materials, as part of the Discover journal series committed to advancing materials research, provides an ideal platform for addressing these challenges and exploring innovative solutions.
The Collection, titled “Materials in Structural Engineering: Challenges and Innovations under Extreme Loading Conditions,” aims to delve deeply into the intersection of materials science and structural resilience across experimental, numerical, and applied perspectives. This collection is driven by the urgent need to develop materials that can withstand diverse forms of extreme loading, including blast and impact forces, as well as thermal, durability-related, and environmental effects, while maintaining structural integrity. Real-world scenarios underscore the importance of this research: from safeguarding critical infrastructure against terrorist attacks to preparing communities for natural disasters like earthquakes and hurricanes, and ensuring long-term performance of materials in practical applications, the resilience of materials directly impacts public safety and economic stability.
This Collection will encompass a diverse array of topics essential to advancing our understanding and capabilities in structural engineering. Key themes include but are not limited to:
(1) Experimental studies on the behavior of structural materials subjected to blast and impact forces, high temperatures, and other severe service conditions, aiming to uncover fundamental mechanisms and develop protective measures;
(2) Analytical modeling approaches to simulate and predict the response of structures under extreme loading conditions, including coupled mechanical and thermal effects, facilitating the design of resilient systems;
(3) Numerical simulations that leverage advanced computational methods to model complex interactions between materials and dynamic forces, including finite element and related numerical techniques;
(4) Application of machine learning techniques to analyze vast datasets and extract actionable insights for enhancing structural resilience and performance prediction.
At its core, this topic collection aligns with Discover Materials’ mission to catalyze innovation in materials research across diverse applications. By publishing pioneering research in structural engineering, the collection aims to not only expand our fundamental understanding of materials behavior but also to accelerate the development of materials with enhanced properties for a safer and more sustainable built environment including conventional, advanced, and emerging material systems.
Authors are invited to submit original research articles, reviews, and case studies that contribute to the understanding of structural materials under extreme loading conditions and related performance scenarios. Submissions should emphasize practical applications and theoretical advancements relevant to the fields of structural engineering and materials science.
This Collection will serve as a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and policymakers involved in the design, analysis, and implementation of materials in structural applications spanning laboratory studies, numerical investigations, and real-world case studies. It aims to foster collaboration and innovation in addressing the challenges posed by extreme loading scenarios through cutting-edge research and technological advancements.
Feature Conferences: 1. 2025 International Conference on Materials, Mechanical, and Civil Engineering Technologies (MMCET 2025), to be held in Tokyo, Japan, from December 17th to 19th, 2025. 2. 2025 2nd International Symposium on Civil Engineering and Smart Structure Technology (CESST 2025), to be held in Zhengzhou, China, from December 5th to 7th, 2025. High-quality papers presented at the conference will be invited for consideration in this Collection, ensuring a rigorous peer-review process. We welcome innovative research that advances knowledge in this critical field.
Keywords:
Structural Engineering; Extreme Loading Conditions; Blast and Impact Forces; Concrete Testing; Resilient Infrastructure; Material Performance; Simulations; Finite Element Modeling; High-Temperature Effects; Durability; Composite Materials; Numerical Methods
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Sep 30, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in