Introducing a new slag to the world of ceramic membranes, Phosphorus Slag
Published in Earth & Environment, Materials, and Sustainability
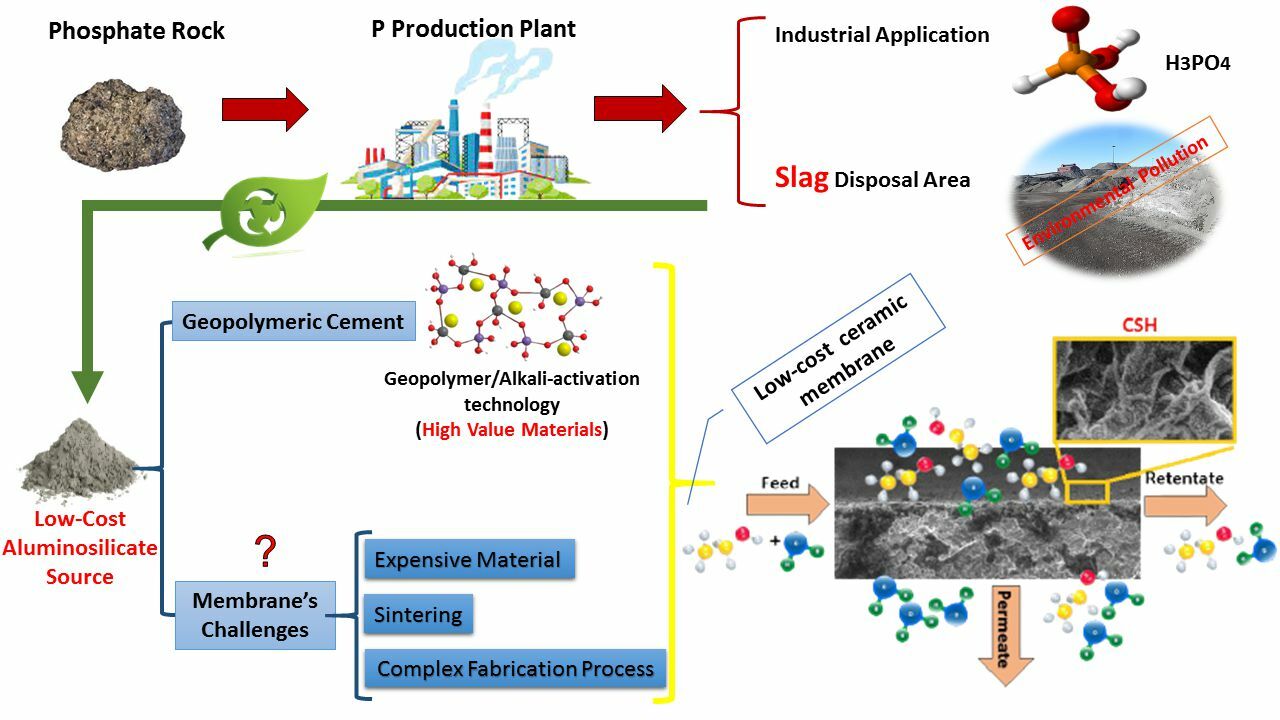
In previous research, my focus was studying the feasibility of using ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) to fabricate low-cost & free-sinter ceramic membranes through alkali activation. The studies demonstrated the high potential of alkali-activated blast furnace slag in the field of ceramic membranes, offering it as an alternative material for preparing dense & porous ceramic membranes. However, a crucial realization was that the type of slag should align with the desired advantages for the final application of ceramic membranes. Over the years, I have continued my research on the relationship between slag types and the properties of ceramic membranes fabricated using alkali-activated slags.
Now, I am pleased to share a part of my research titled ''Phosphoric acid industry waste valorization through fabrication of alkali-activated phosphorus slag-based ceramic membranes: synthesis and optimization for dehydration of ethanol''. This research represents the first attempt to address the challenges of alkali-activated blast furnace slag ceramic membranes by exploring alkali-activated phosphorus slag as a potential material for synthesizing ceramic membranes. Furthermore, a comprehensive analysis was conducted on the interplay between key factors influencing the properties of common alkali-activated cementitious materials and their impact on membrane properties, including hydrophilicity, flexural strength, and topographical properties, thermogravimetric characterization and membrane performance.
I would like to draw your attention to a unique aspect of this study, which focuses on the morphology of alkali-activated ceramic membranes (AACMs). By employing FESEM & AFM imaging techniques at various scales ranging from microns to nanometers, a striking resemblance between the morphology of AACMs and alkali-activated cementitious materials has been established.
This research provides a unique perspective on the world of ceramic membranes, with a focus on addressing and mitigating their challenges (e.g., expensive materials, sintering, complex fabrication method). Moreover, it emphasizes the alignment with the UN-Sustainable Development Goals (UN-SDGs), specifically SDG 12.
Follow the Topic
What are SDG Topics?
An introduction to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Topics and their role in highlighting sustainable development research.
Continue reading announcement




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in