Segment Anything Model in Intrapartum Ultrasound Image Analysis
Published in Bioengineering & Biotechnology
Explore the Research
 sciencedirect.com
sciencedirect.com
Just a moment...
About ScienceDirect Shopping cart Contact and supportTerms and conditionsPrivacy policy
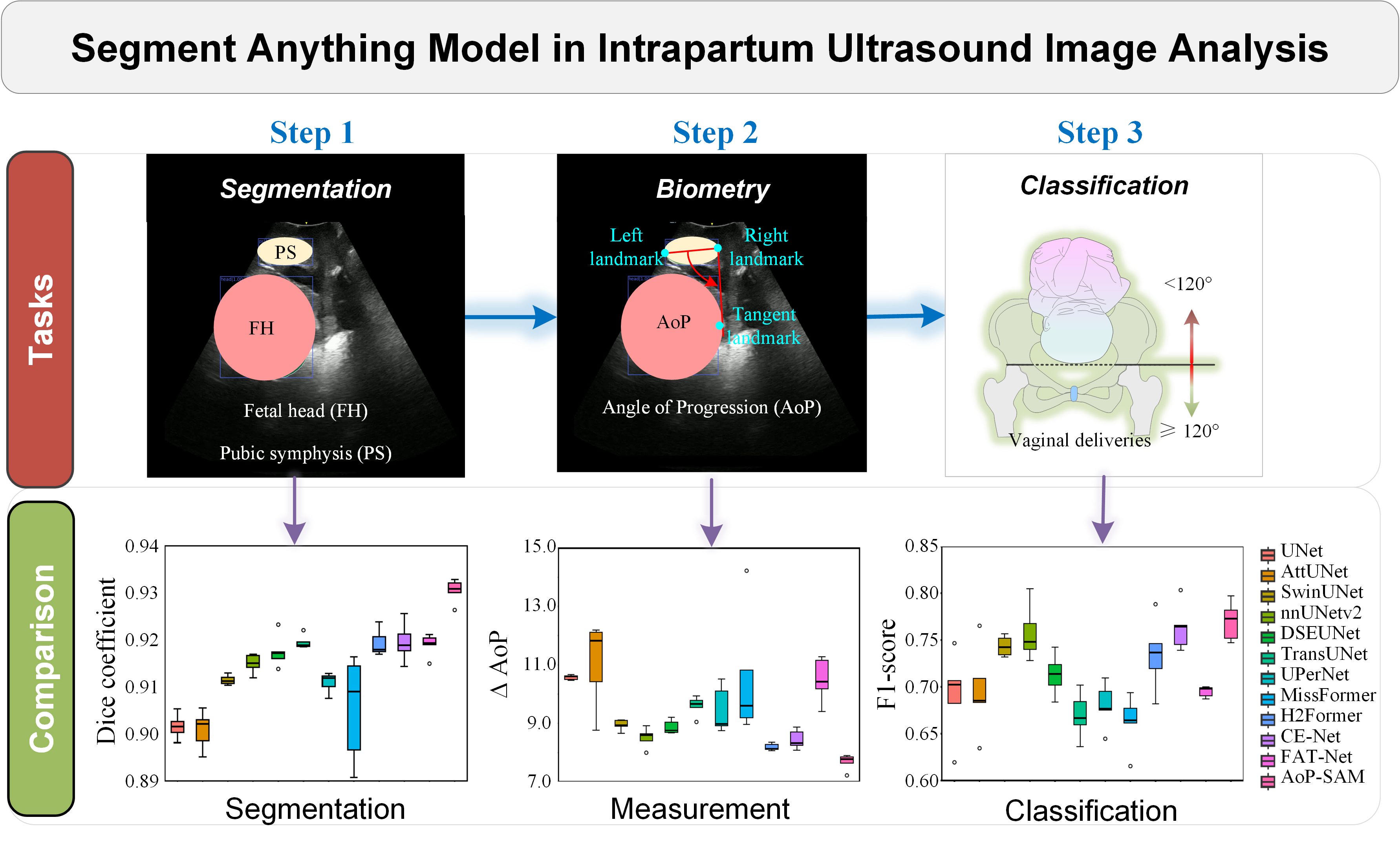
The Angle of Progression (AoP), determined by the contour delineations of the pubic symphysis and fetal head (PSFH) in intrapartum ultrasound (US) images, is crucial for predicting delivery mode and significantly influences labor outcomes. However, automating AoP measurement based on PSFH segmentation remains challenging due to poor foreground-background contrast, blurred boundaries, and anatomical variability in shapes, sizes, and positions during labor. We propose a novel Segment Anything Model (SAM) framework, AoP-SAM, designed to enhance the PSFH segmentation, AoP measurement and outcome prediction, tackling the challenges of small target segmentation and accurate boundary segmentation. It synergistically combines CNNs and Transformers within a cooperative encoder to process complex spatial relationships and contextual information to segment the PSFH. In this encoder, we devise a multi-scale CNN branch to capture intrinsic local details, which compensates for the defects of the Transformer branch in extracting local features. Further, a cross-branch attention module is applied to improve prediction by fostering the effective information exchange and integration between two branches. Evaluations on the benchmark dataset demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Specifically, in the PSFH segmentation task, the AoP measurement task, and the AoP classification task, we achieved a DSC of 0.8745 on the PS structure, a AoP of 7.6743°, and an F1-score of 0.7719, respectively. Compared to the second-ranking method, these results represent improvements of 2.5%, 6.3%, and 1.1%. Our study presents a framework for intrapartum biometry, offering significant advancements in labor monitoring and delivery mode prediction in clinical settings. Future efforts will focus on optimizing AoP-SAM for resource-constrained environments, highlighting its potential for lightweight adaptation. https://github.com/maskoffs/AoP-SAM.
- Bai J, Zhou Z, Ou Z, et al. PSFHS challenge report: Pubic symphysis and fetal head segmentation from intrapartum ultrasound images[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2025, 99: 103353.
- Chen Z, Ou Z, Lu Y, et al. Direction-guided and multi-scale feature screening for fetal head–pubic symphysis segmentation and angle of progression calculation[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 245: 123096.
- Lu Y, Zhi D, Zhou M, et al. Multitask deep neural network for the fully automatic measurement of the angle of progression[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2022, 2022.
- Lu Y, Zhou M, Zhi D, et al. The JNU-IFM dataset for segmenting pubic symphysis-fetal head[J]. Data in Brief, 2022, 41: 107904.
- Bai J, Sun Z, Yu S, et al. A framework for computing angle of progression from transperineal ultrasound images for evaluating fetal head descent using a novel double branch network[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2022, 13: 2565.
- Zhou Z, Lu Y, Bai J, et al. Segment Anything Model for fetal head-pubic symphysis segmentation in intrapartum ultrasound image analysis[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024: 125699.
- Jiang J, Wang H, Bai J, et al. Intrapartum Ultrasound Image Segmentation of Pubic Symphysis and Fetal Head Using Dual Student-Teacher Framework with CNN-ViT Collaborative Learning[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 448-458.
- Ou Z, Bai J, Chen Z, et al. RTSeg-Net: a lightweight network for real-time segmentation of fetal head and pubic symphysis from intrapartum ultrasound images[J]. Computers in biology and medicine, 2024, 175: 108501.
- Qiu R, Zhou M, Bai J, et al. PSFHSP-Net: an efficient lightweight network for identifying pubic symphysis-fetal head standard plane from intrapartum ultrasound images[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2024: 1-12.
- Chen G, Bai J, Ou Z, et al. PSFHS: intrapartum ultrasound image dataset for AI-based segmentation of pubic symphysis and fetal head[J]. Scientific Data, 2024, 11(1): 436.
- Chen Z, Lu Y, Long S, et al. Fetal head and pubic symphysis segmentation in intrapartum ultrasound image using a dual-path boundary-guided residual network[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2024.
- Bai, J., Lekadir, K., Ni, D., Slimani, S., Campello, V. M., Ohene-Botwe, B., Lu, Y., Chen, G., Hou, H., Qiu, D., & Zhou, Z. (2024). Intrapartum Ultrasound Grand Challenge 2024. 27th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2024). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10979813
- Jieyun Bai, Zhanhong Ou, Yaosheng Lu, Dong Ni, Gaowen Chen, Gaowen Chen, Zhanhong Ou, Zhanhong Ou, Gaowen Chen, & Yaosheng Lu. (2023). Pubic Symphysis-Fetal Head Segmentation from Transperineal Ultrasound Images. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2023 (MICCAI 2023). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7861699
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in