Switching magnetic Skyrmions using electric field
Published in Electrical & Electronic Engineering

To meet the ever-growing demand of faster and smaller computers, increasing number of transistors are needed in the same chip area. Unfortunately, Silicon based transistors have almost reached its miniaturization limits mainly due to excessive heat generation. Therefore, to replace CMOS based devices, many new materials and strategies are being explored now. Among the many alternatives, we focus on nanomagnetic devices where electron spin, instead of charge, is the information carrier.
Nanomagnetic devices are non-volatile: information can be stored in these devices without needing any external power. This could enable computing architectures beyond traditional von-Neumann computing. Additionally, these devices are also expected to be more energy efficient than CMOS devices as their operation does not involve translation of charge across the device. However, the energy dissipated in the clocking circuitry negates this perceived advantage and in practice CMOS devices still consume three orders of magnitudes less energy. Therefore, researchers have been looking for nanomagnetic devices that could be energy efficient in addition to being non-volatile.
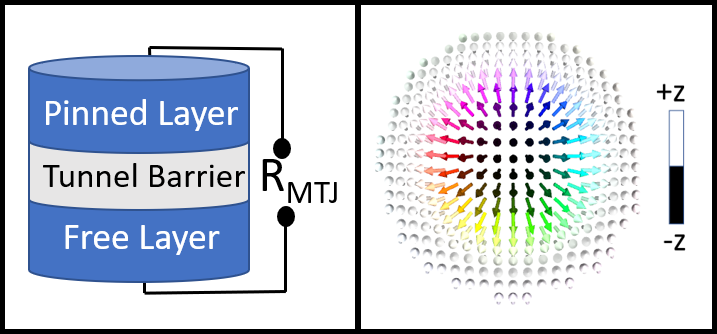
Left: Simplified schematic of an MTJ structure. The resistance of the device changes when the relative magnetic orientation between the free and the pinned layer is changed. Right: Micromagnetic Configuration of a skyrmion. The arrows show the direction of the spins. The spins at the core and the periphery are of opposite polarity and separated by a spin spiral.
Recently, magnetic skyrmions, a flower like magnetic state, has emerged as a viable candidate to be used in room temperature nanomagnetic devices. Most of the studies propose to utilize skyrmion motion in a magnetic track to implement memory devices [1]. However, we thought Magnetic Tunnel Junction (MTJ) devices based on skyrmions that are fixed in space might be advantageous in terms of footprint. In this regard, we previously demonstrated reversal of “fixed” magnetic skyrmions using micromagnetic simulation. The switching is based on electric field instead of electrical current and thus extremely energy efficient [2].
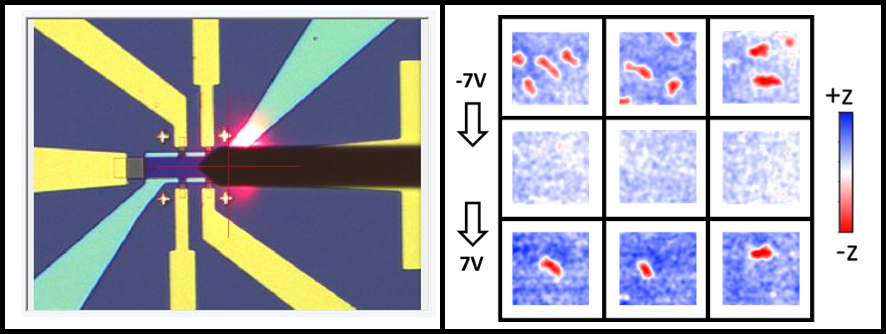
The VCU group and the UCLA group collaborated to show this electric field control of skyrmions experimentally. The UCLA group fabricated a special multilayer Antiferromagnet/ Ferromagnet/ Oxide heterostructure. Next, the film was characterized at VCU employing Magnetic Force Microscopy. Skyrmions could be stabilized in the heterostructure without requiring any external magnetic field due to the coupling between the Antiferromagnetic layer to the Ferromagnetic layer. After that, sequential voltage pulses were applied. When a negative voltage pulse was applied skyrmions were destroyed due to increase of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. On the other hand, application of a positive voltage pulse resulted in creation of skyrmions. These creation and annihilation process were non-volatile. The experimental results were also explained using micromagnetic simulations performed at VCU.
Our new simulation results show that ultrafast operation (>10 GHz) of fixed skyrmion based devices is possible [3]. Neuromorphic computing element can also be fashioned utilizing voltage controlled skyrmion dynamics [4]. Therefore, this demonstration of voltage induced skyrmion switching has potential to lead the way towards realization of a new nanomagnetic computing paradigm.
For more information read our article: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-0432-x
References:
[1] Nature Nanotechnology 8, 152–156 (2013).
[2] Scientific Reports, 6, 31272 (2016).
[3] arXiv:2003.12904 (2020).
[4] Journal of Applied Physics 124 (15), 152122 (2018).
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Electronics

This journal publishes both fundamental and applied research across all areas of electronics, from the study of novel phenomena and devices, to the design, construction and wider application of electronic circuits.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in