Discovery of MTHFD1L as the New Binding Target of Pseudolaric Acid A
Published in Chemistry and Cell & Molecular Biology
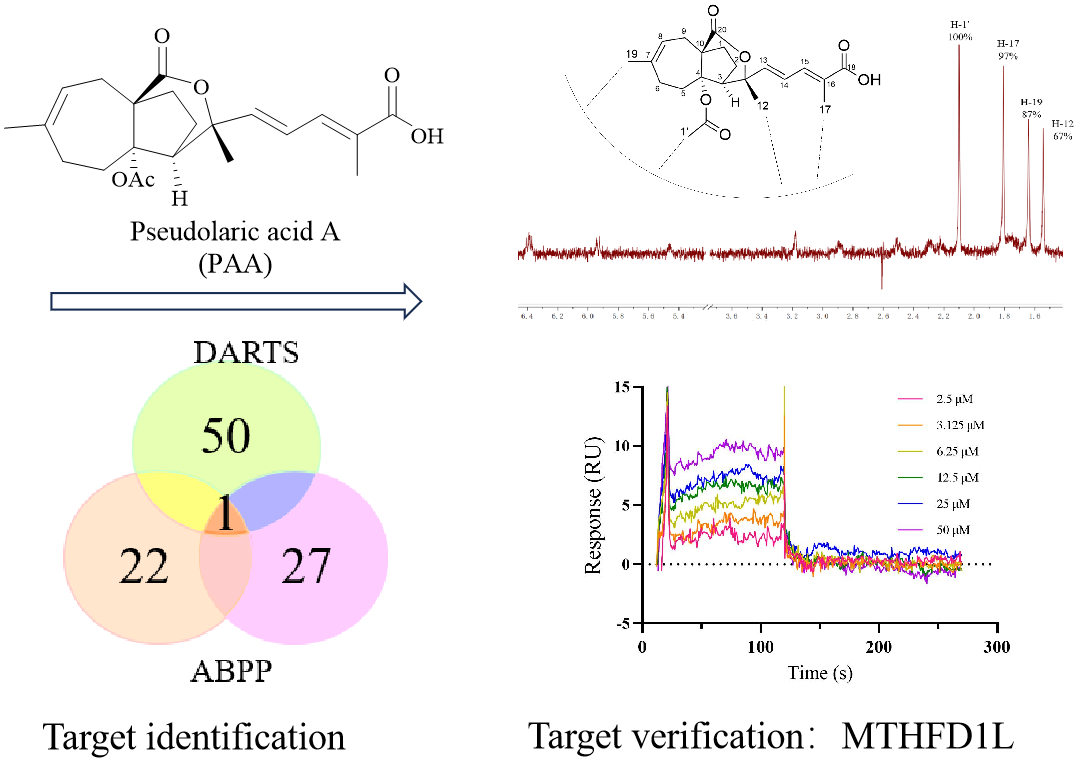
How do we find the target of natural product PAA
Each strategy has its own advantages and drawbacks. Dual-strategy approach integrating ABPP and DARTS methods together mitigated the risk of false positives inherent in individual methods (e.g., probe-induced artifacts in ABPP, non-specific protection in DARTS), providing high-confidence target identification.
- Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS):
This label-free approach identified proteins that are protected from degradation by PAA. 42 potential binding proteins were identified via LC-MS/MS.
2. Activity-Based Protein Profiling (ABPP):
A PAA-derived chemical probe (retaining similar bioactivity to native PAA) was used to label target proteins. Competition with free PAA reduced probe binding, indicating specific targets. Fluorescence detection after SDS-PAGE and subsequent proteomics analysis identified 18 potential targets.
MTHFD1L: a new protein target of PAA
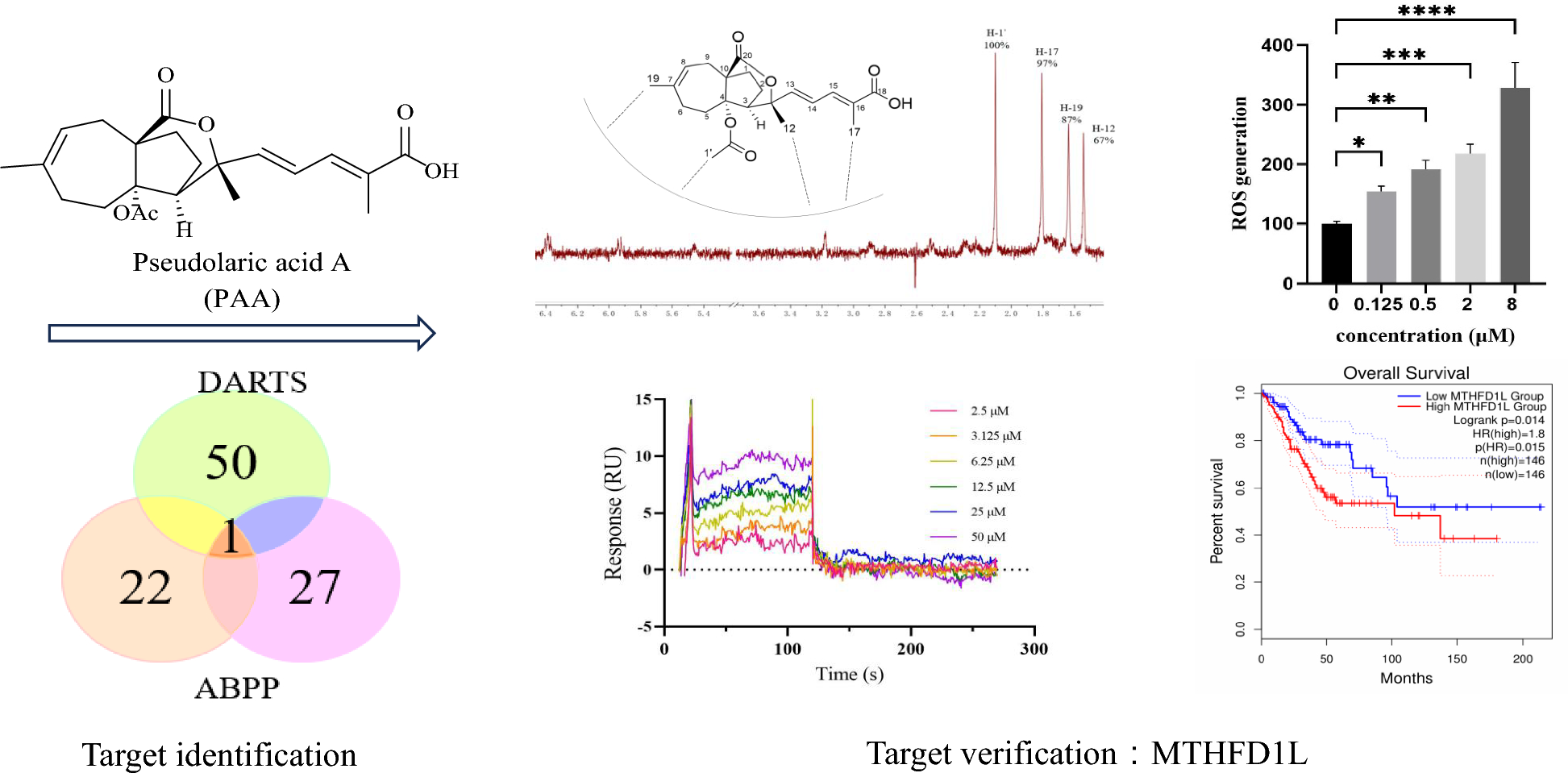
Cross-referencing results from DARTS and ABPP identified Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase 1-Like (MTHFD1L) as the sole overlapping target We therefore propose MTHFD1L is the most potential binding target of PAA. To validate and confirm our proposal, multiple techniques including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) saturation transfer difference (STD), surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and etc, were utilized to investigate the direct interaction between MTHFD1L and PAA in the molecular level. Important groups of compound PAA were identified and the results were consistent with the structure-activity relationship (SAR) study.
MTHFD1L Targeting Mediates PAA's Anticancer Mechanism
PAA induced the accumulation of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) which mediates the antitumor effect. Knockdown of MTHFD1L using siRNA in HeLa cells significantly reduced cell viability, aligning with prior reports of MTHFD1L's role in cancer cell proliferation. Comprehensive transcriptome and bioinformatic analysis has aided the understanding of the important role of MTHFD1L gene and led to the identification of MTHFD1L as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker.
Future perspectives
This work is a follow-up study of the discovery of binding targets of bioactive natural product PAA. We warmly welcome more scientists to join in the exploration of new targets of natural products. With their diverse chemical compositions and complex mechanisms of action, natural products hold great potential for the discovery of novel therapeutics and new drug targets. Collaboration across fields will be key to unlocking the full value of nature’s pharmacy.
This study was published in Natural Products and Bioprospecting in the research article titled "Identification and verification of methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1-like protein as the binding target of natural product pseudolaric acid A"
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13659-025-00502-1).
Follow the Topic
-
Natural Products and Bioprospecting

This is a single blind peer-reviewed open access journal that devoted to rapidly disseminate research results in all areas of natural products.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in