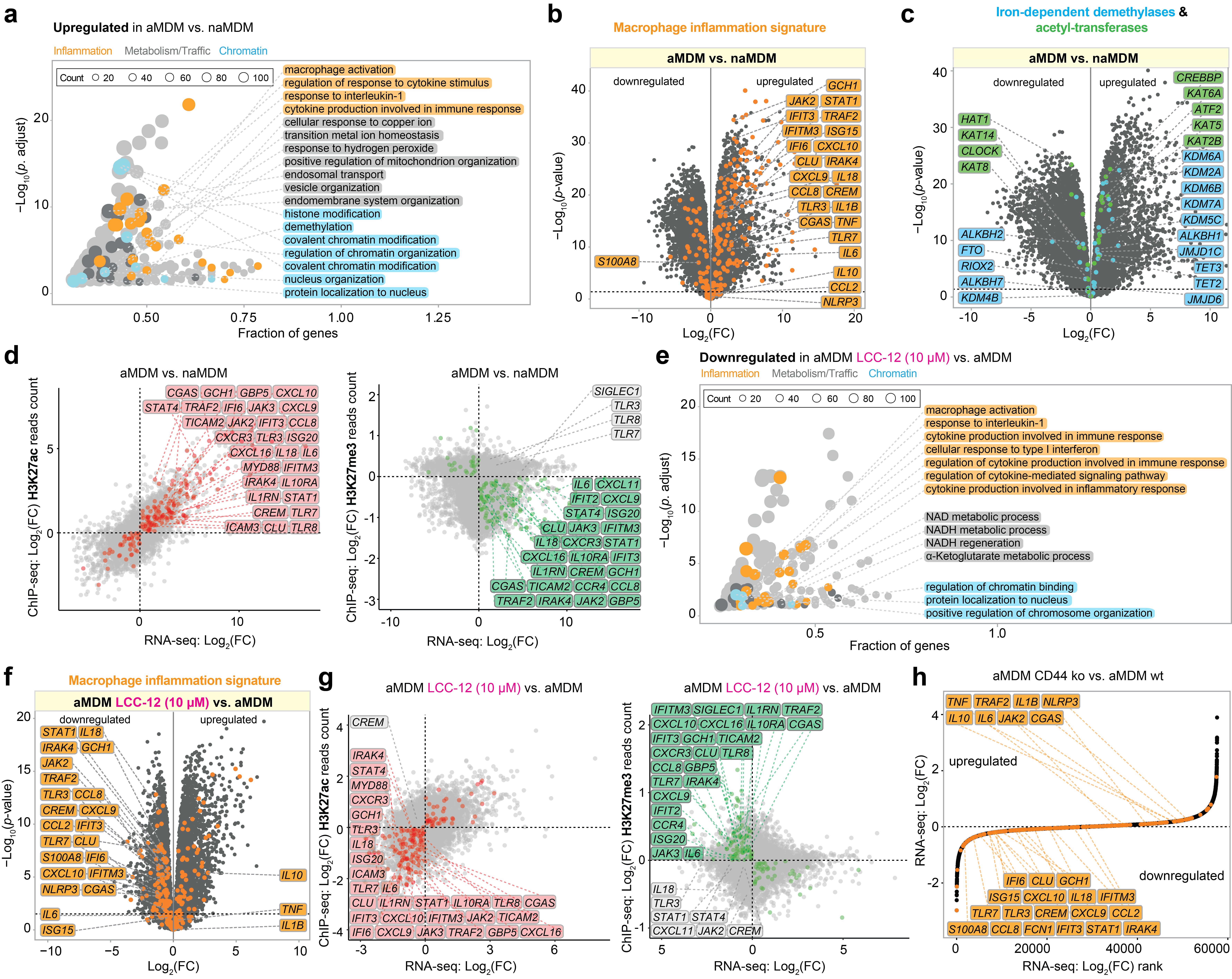
Multiomics Dataset on Primary Macrophages
Published in Research Data

In our latest work published in Nature we generated an extensive dataset using RNA-Seq, ChiP-Seq, metabolomics and proteomics on primary cells. We want to share this here in the Research Data Community as we think this is a very useful resource. On the whole, our study encompassed a novel mechanism of endocytosis, design of a new molecule to inhibit inflammation, the discovery that copper is implicated in the interconvertion of NAD(H), metabolomic and epigenetic characterisation and in vivo studies on inflammation. Because the paper is so rich, we think that an emphasis of the depth of the multiomics dataset is useful for people to read about.
Of course, according to Springer/ Nature policies, all the raw data and data are freely available and can be used by the scientific community.

Importantly, we performed RNA-Seq on several donors and performed ChiP-Seq on 5 epigenetic marks: H3K27me3, H3K9me2, H3K27ac, H3K16ac, H3K9ac. This is quite unique, as often studies just look at one or two marks. However, we wanted to give a greater picture and this could now be used to look into the specific contribution of each of these activating and repressive marks and determine their exact contribution to gene expression.
We hope these datasets will be useful for the community and are happy to work with anyone who would like to take this further.
Reference: Solier et al., A druggable copper-signalling pathway that drives inflammation, Nature, 2023, 617, 386–394, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06017-4
Follow the Topic
-
Nature

A weekly international journal publishing the finest peer-reviewed research in all fields of science and technology on the basis of its originality, importance, interdisciplinary interest, timeliness, accessibility, elegance and surprising conclusions.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in