Quantum-inspired neural networks for time-series air pollution prediction and control of the most polluted region in the world
Published in Earth & Environment, Mathematical & Computational Engineering Applications, and Mathematics
For our study, we selected New Delhi, specifically the Anand Vihar air pollution station, known for its high concentrations of PM. We proposed an approach to predict Particulate Matter(PM2.5) levels based on various pollutant and meteorological parameters.
Our model is an improved version of the quantum temporal convolutional network (QTCN), enhancing the traditional quantum convolutional neural network (QCNN) model. To evaluate our model’s performance, we used several metrics, including mean squared error (MSE), root mean squared error (RMSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), mean absolute error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2 score). Our proposed model achieved MAE and MAPE values of (59.031) and (80.642), respectively. Additionally, the RMSE exhibited a reduction of (32.493) % in comparison to the traditional QCNN framework, whereas the R2 score demonstrated an enhancement of (14.86) %.
The quantum-inspired model we have developed showcases its superior capabilities and demonstrates a significant advancement in forecasting air pollution levels, thus contributing valuable insights into environmental monitoring and public health. This research underscores the potential of using advanced computational techniques to address pressing challenges in air quality management, ultimately fostering a deeper understanding of the dynamics that govern atmospheric pollutants.
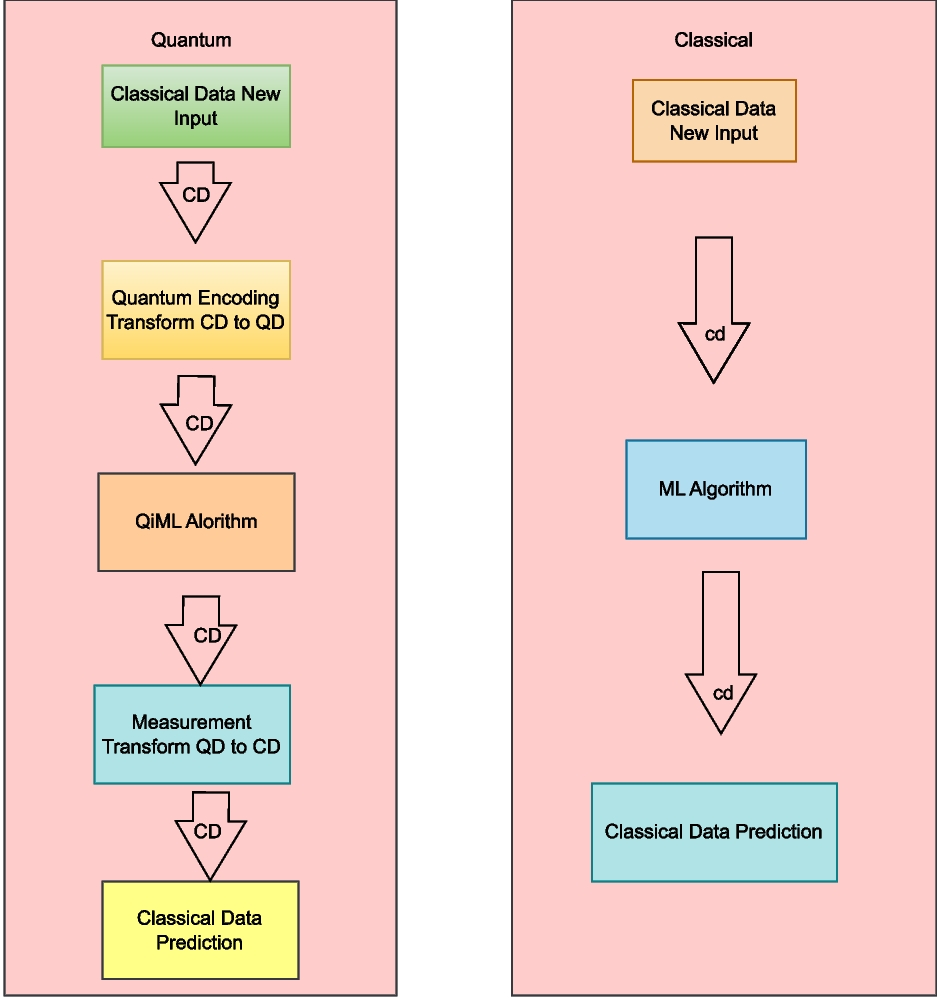
The digital era is increasing exponentially day by day. We moved the high computational power of AI to quantum computation. In the last two decades, we improved complex computational power. Also, it will touch on the challenges facing quantum computation today and future perspectives in the age of digital technology. Using sentiment analysis, it may also examine how rapidly advancing technologies could affect society and morality. The authors have collected the pollutant and meteorological parameters to better understand how pollutants move and react in the atmosphere. The annual World Air Quality Report finds New Delhi to be the most polluted capital city in the world. We selected the most polluted air pollution monitoring station, Anand Vihar, Delhi. Classical machine learning models commonly address the complexity of the environmental data and higher-dimensional feature space problems. However, noise datasets contain inaccuracies due to sensors recoding saturation values continuously. It is necessary to utilize robust parameterized quantum circuits to allow the model to approximate complex functions with fewer parameters than classical deep networks, reducing the risk of overfitting.
Hardware and Software used for the pre-processing and execution of the Quantum Convolutional Neural Network and the enhanced Quantum Temporal Convolutional Network algorithms have been performed on a computational workstation featuring an Intel® Xeon® Silver 4210 CPU operating at a frequency of 2.20 GHz, coupled with 64 GB of Random Access Memory and utilizing a 64-bit Windows operating system. The scikit-learn library from the Machine Learning toolkit has been employed within the JupyterLab 3.2 environment, utilizing the Python programming language.
Follow the Topic
-
Quantum Machine Intelligence

This journal publishes original articles on cutting edge experimental and theoretical research in all areas of quantum artificial intelligence.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Quantum Techniques in Machine Learning 2025
This topical collection will include extended versions of original results presented at the 9th International Conference on Quantum Techniques in Machine Learning, QTML 2025, which was held on 16-21 November 2025 in Singapore
QTML is an annual international conference focusing on the interdisciplinary field at the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning.
This call is for all the unpublished results that were presented at the conference either orally or as a poster and that can be extended (possibly taking into account the comments from the audience) into a full research paper.
Topics include but are not limited to:
• Quantum algorithms for machine learning applications
• Hybrid quantum-classical approaches for learning and optimization
• Encoding and processing of data in quantum systems
• Theoretical foundations of quantum learning
• Quantum variational circuits and their applications
• Quantum state and process tomography with learning-based approaches
• Tensor methods and quantum-inspired machine learning
• Quantum state reconstruction from data
• Quantum-enhanced robustness in machine learning models
• Machine learning techniques for experimental quantum information science
• Fuzzy logic in quantum machine learning
• Quantum kernel methods and their applications
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in