The impact of autoimmune co-morbidities in AQP4-NMOSD and MOGAD.
Published in Neuroscience, Biomedical Research, and General & Internal Medicine
Aquaporin-4 neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (AQP4-NMOSD) and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody disease (MOGAD) are rare but serious autoimmune conditions that affect the central nervous system. While both can cause severe neurological damage, AQP4-NMOSD is known to frequently occur alongside other autoimmune diseases, while this association is not commonly reported in MOGAD.
There is a critical gap in understanding how these autoimmune diseases affect recovery from attacks or relapses.
The study question was simple , does having another autoimmune disease make early recovery or relapse worse in AQP4-NMOSD or MOGAD?
To answer this, we examined approximately 400 patients at the University of Oxford, comparing those with and without additional autoimmune conditions, tracking recovery from initial attacks which included visual outcomes after an episode of optic neuritis. We were also interested if autoimmune diseases affected time to having the next clinical relapse.
Additionally, we also reviewed retinal imaging in the form of optical coherence tomography to assess for any additional structural damage to the ocular system.
Our results are summarised as follows :
-
Co-morbid autoimmune diseases were common in AQP4-NMOSD (28%) but less so in MOGAD (11%).
-
Thyroid disease was the most frequent coexisting condition in both groups.
-
Age was a consistent predictor of recovery , with older patients tended to have worse outcome.
-
Visual recovery, motor recovery and relapse timing were not significantly different between patients with and without additional autoimmune diseases.
-
Retinal imaging showed no added damage in those with comorbid AIDs.
This was an interesting study as it benefits the medical community by providing additional understanding to both clinicians and patients, that having another autoimmune disease does not appear to worsen early outcomes in AQP4-NMOSD or MOGAD.
This research work has provided further insight into cases of autoimmune overlap, and contributes to our ability to counsel patients better especially in multi-disciplinary clinical settings.
Article linked and referenced: Samadzadeh S, Chan F, Francis A, Sani L, Paul F, Asgari N, Leite MI, Geraldes R, Palace J. The impact of autoimmune comorbidities on the onset attack recovery in adults with AQP4-NMOSD and MOGAD. J Neurol. 2025 Jun 10;272(7):453. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13180-3. PMID: 40495001; PMCID: PMC12152089.https
Follow the Topic
-
Journal of Neurology

Journal of Neurology is a peer-reviewed international journal focused on all aspects of clinical neurology from diagnosis to treatment.
Your space to connect: The Macular degeneration Hub
A new Communities’ space to connect, collaborate, and explore research on Ophthalmology and Eye Diseases!
Continue reading announcement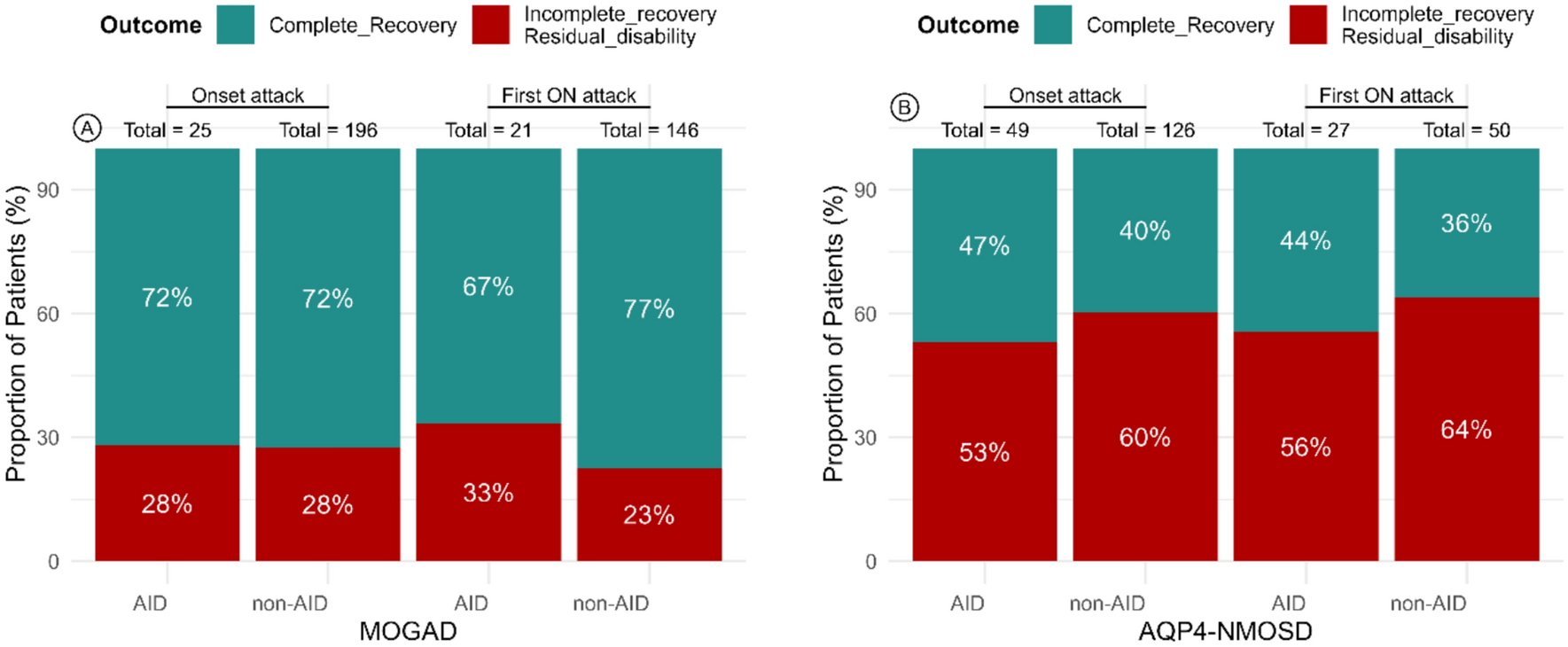



Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in