Why We Mapped the State of Patient Safety Culture in Chiropractic Care
Published in Healthcare & Nursing, Biomedical Research, and Public Health
For years, conversations about patient safety in chiropractic care have been dominated by questions about harm—how often adverse events occur, how serious they are, and what risks are associated with spinal manipulation. Yet patient safety, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), is far more than the absence of harm. Patient safety is a culture, a set of shared beliefs and behaviours, embedded within every aspect of care delivery.
When the World Federation of Chiropractic (WFC) launched its Global Patient Safety Initiative (GPSI) in 2023—aligned with the WHO Global Patient Safety Action Plan —it became clear that the chiropractic profession needed an evidence-based starting point. Before developing new policies, tools, or education strategies, we needed to answer a fundamental question:
What do we actually know about patient safety culture in chiropractic, and where are the gaps?
This question became the driving force behind our recent publication, Patient Safety Culture Research Within the Chiropractic Profession: A Scoping Review. The work was later recognized with the 2025 NCMIC–JMPT Research Award at the WFC Biennial Congress—an affirmation of the global relevance of this topic and the profession’s growing commitment to safety.
A Puzzle with Missing Pieces
Going into this project, we expected to find scattered evidence on adverse events or clinical decision-making. What surprised us was how unbalanced the research landscape truly was.
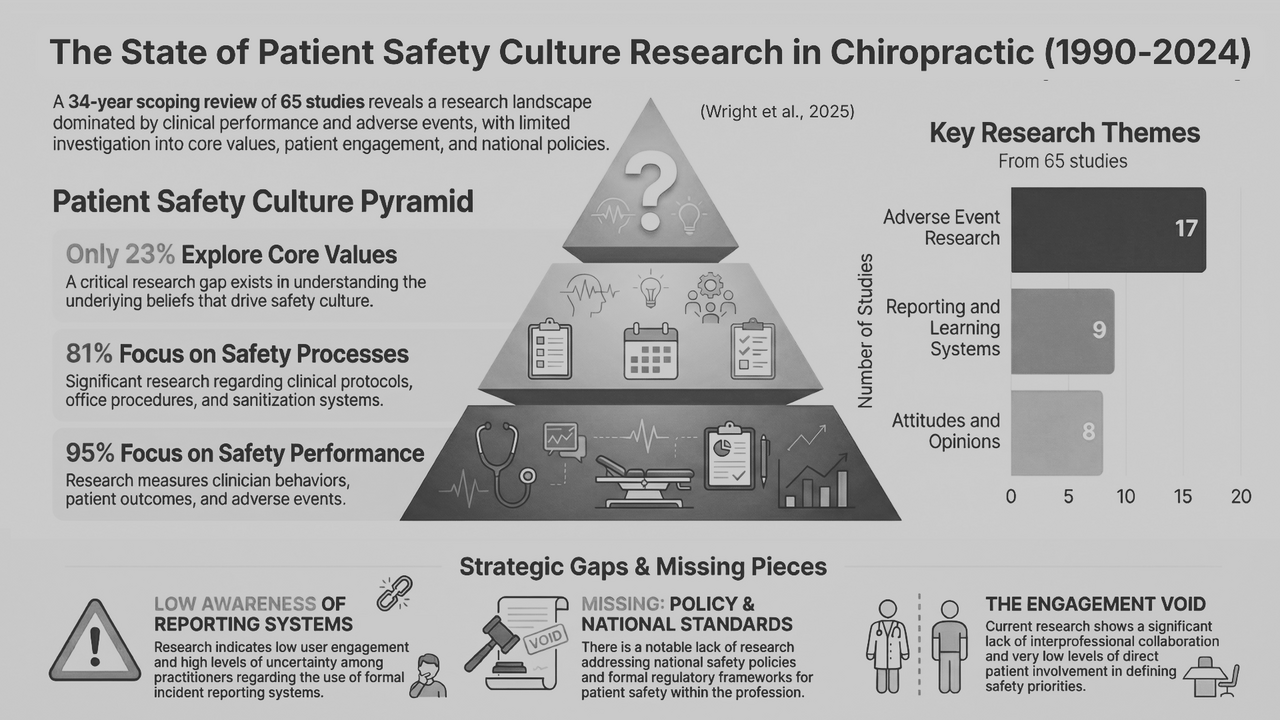
Across 65 studies published over three decades, we found:
• 95% focused on safety performance—primarily adverse event reporting
• 81% examined safety processes, such as clinical decision-making or documentation
• Only 23% addressed the beliefs, values, and attitudes that form the foundation of safety culture
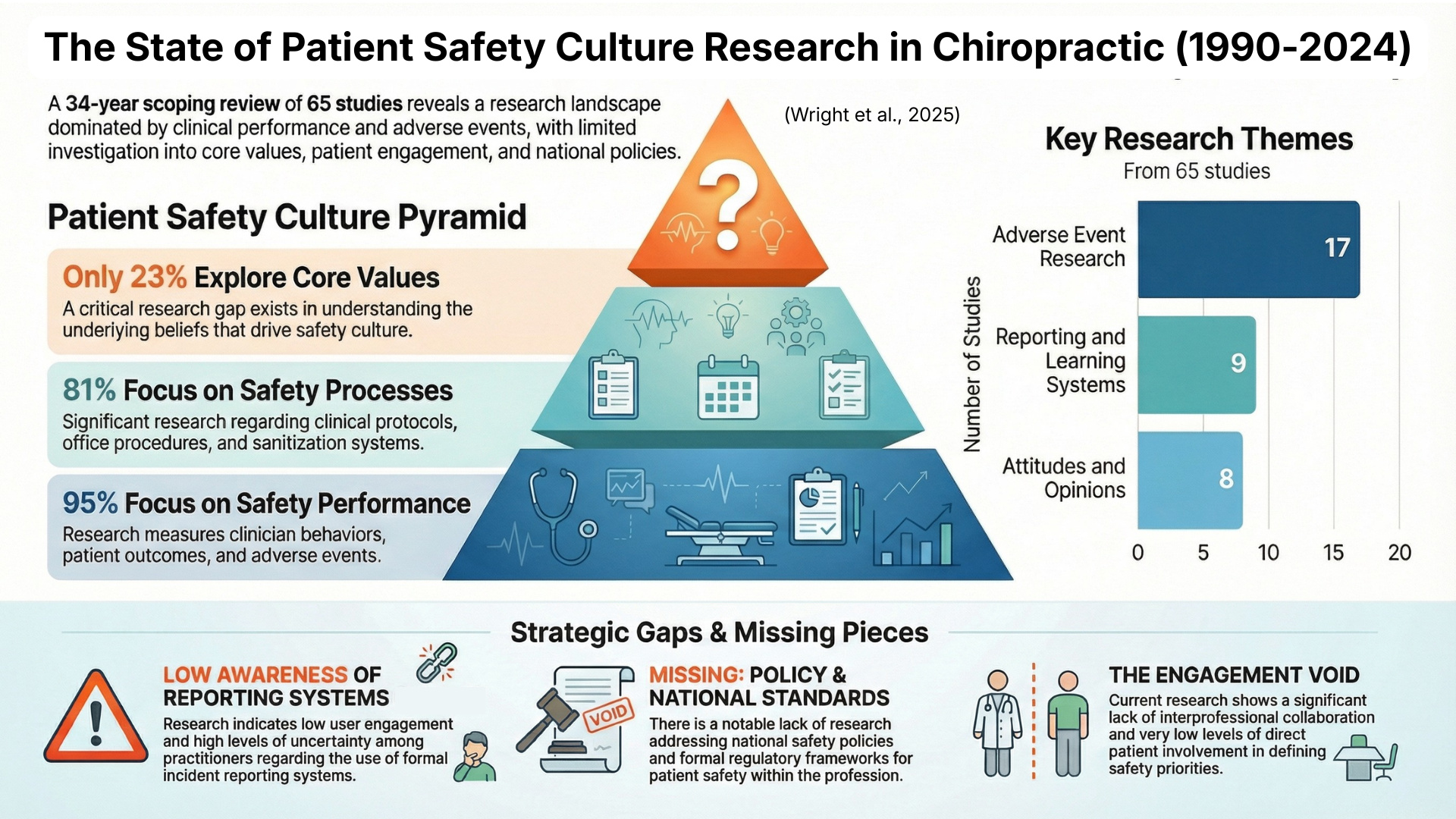
The closest thing to “culture”—the underlying norms that influence how practitioners think about risk, communicate with patients, or learn from mistakes—was nearly absent.
This pattern reflects where the global patient safety movement stood in the early 2000s: focused on errors and events, rather than systems and culture. But while other health professions moved toward a deeper examination of safety climate, leadership, communication, and patient engagement, chiropractic research largely stayed anchored in incident reporting.
Our findings confirmed what many clinicians and leaders have felt intuitively, that we cannot improve what we do not measure, and we have not been appropriately measuring the cultural aspects of safety that matter most.
Why This Review Matters Now
This review comes at a pivotal moment. The WHO has made eliminating preventable harm a global priority. Health systems worldwide are investing in safety leadership, interprofessional communication, patient engagement, and reliable reporting systems. And increasingly, patients expect transparency and accountability from all health professions.
Our findings highlight several opportunities for the chiropractic profession:
• Developing standardized adverse event definitions and reporting systems
• Embedding safety culture training into chiropractic education
• Building collaborative research across disciplines
• Engaging patients in defining what safe chiropractic care looks like and feels like
• Strengthening leadership and policy structures that support a safety-first mindset
These are not small tasks. But they are achievable—and essential.
Looking Forward
This scoping review is not the final word on patient safety in chiropractic. —Our authorship team welcomes chiropractors and chiropractic patients to join us at the beginning of a long-term agenda.
Our hope is that this work will serve as a foundation for the WFC Global Patient Safety Initiative and inspire researchers, educators, regulators, clinicians, and patients to create and sustain a stronger, clearer, and more unified approach to safety.
Patient safety culture is not built overnight. But with deliberate effort, open dialogue, and evidence-based strategies, the chiropractic profession can take meaningful steps toward ensuring safer care for every patient, in every setting, around the world.
Follow the Topic
-
Chiropractic & Manual Therapies

This journal aims to improve patient care by publishing basic science, clinical and health services research that is relevant to chiropractors, manual therapists and related fields, including physical therapy, osteopathy, sports medicine, and rehabilitation.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Patient safety in chiropractic care and manual therapies
In May 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the protection of patients a global health priority through the resolution WHA 72.6, titled "Global action on patient safety." Yet, despite its recognized importance and advancements in technology and treatment, safety concerns in healthcare persist worldwide. By prioritizing high standards of care and vigilance, chiropractors may contribute to a safer healthcare system for all stakeholders, particularly patients.
This thematic series in Chiropractic & Manual Therapies (C&MT) is led by a diverse, international team of editors with a track record aligned in patient safety. Namely, senior epidemiologist Prof. Sidney Rubinstein, nurse scientist Dr. Stacie Salsbury, early career researcher Dr. Brian Coleman, whose expertise lies in implementation science and technology, and Prof Simon French, co-Editor-in-Chief at C&MT. Our editorial team invites authors to submit manuscripts focused on patient safety in chiropractic care. Submissions are encouraged in all formats accepted by the journal, including original research articles, systematic and scoping reviews, case reports, and study protocols. In addition, the series welcomes scholarly commentaries, debates, and letters to the editor that explore barriers and propose solutions to fostering and sustaining a strong global patient safety culture within chiropractic.
Submissions may include, but are not limited to, the following patient safety topics:
- Intervention or quality improvement studies of strategies to enhance the patient safety culture in chiropractic clinical settings, including individual practices, multi-specialty group practices, and hospital-based practices.
- Studies investigating perceptions of patient safety in chiropractic from key stakeholders, including patients, family members, chiropractors, and other healthcare professionals.
- The epidemiology of patient safety events where the occurrence and patterns of patient safety events relevant to chiropractic care are evaluated.
- Studies addressing patient safety considerations for special populations seeking or receiving chiropractic care, such as older adults or pregnant patients.
- Studies exploring the intersection of population characteristics and patient safety within chiropractic settings.
- Studies evaluating the effectiveness of curricular content and/or simulation-based training in enhancing chiropractic student and practitioner competency and proficiency in safety-related assessment and management.
Behind the Paper. From the authors, read about "Why We Mapped the State of Patient Safety Culture in Chiropractic Care."
Online conference. Following the end of this Call, we will organize an online-conference for all authors to present their work and discuss the importance of their findings
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 3, Good Health and Well-Being.
All submissions in this collection undergo the journal’s standard peer review process. Similarly, all manuscripts authored by a Guest Editor(s) will be handled by the Editor-in-Chief. As an open access publication, this journal levies an article processing fee (details here). We recognize that many key stakeholders may not have access to such resources and are committed to supporting participation in this issue wherever resources are a barrier. For more information about what support may be available, please visit OA funding and support, or email OAfundingpolicy@springernature.com or the Editor-in-Chief.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Sep 15, 2026




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in