Electrostatic Regulation of Na+ Coordination Chemistry for High‑Performance All‑Solid‑State Sodium Batteries
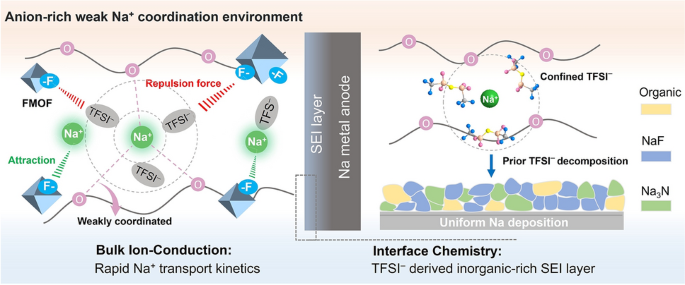
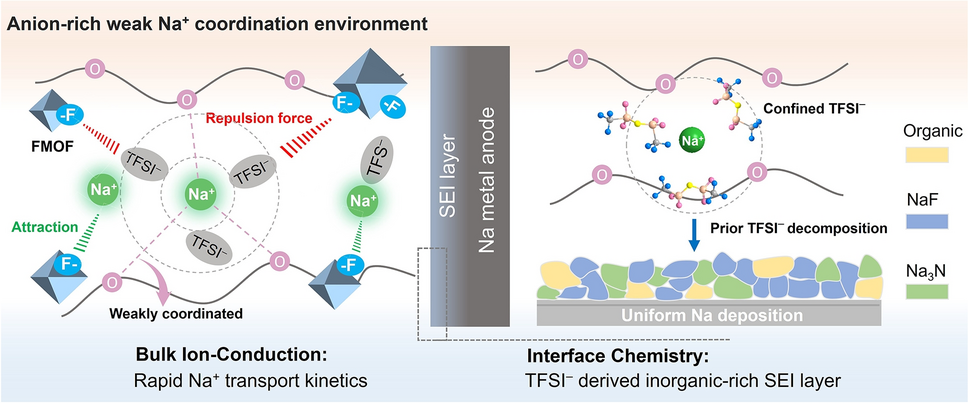
As demand for safer, higher-energy batteries surges, all-solid-state sodium-metal batteries (ASSMBs) promise a low-cost, non-flammable alternative to Li-ion technology. Yet their practical use is stymied by sluggish Na+ transport and poor interfacial stability. Now, a joint team from Jiangnan University, Henan Academy of Sciences and University of Bayreuth, led by Prof. Suli Chen, Dr. Qiongqiong Lu and Prof. Qingsong Wang, presents an electrostatic-engineering strategy that redesigns the Na⁺ coordination shell inside polymer electrolytes and delivers >2000 stable cycles at 2 C—a new benchmark for ASSMBs.
Why Electrostatic Control Matters
- Faster Na+ Conduction: Weakening Na+–ether oxygen bonds cuts desolvation barriers, boosting ionic conductivity to 1.01 mS cm-1 at 60 °C.
- Stable Na-Metal Interface: An anion-rich solvation sheath forms an inorganic-rich, NaF/Na3N SEI that suppresses dendrites for 2500 h of symmetric-cell cycling.
- High-Power Performance: Full cells retain ≈100 % capacity over 2000 cycles at 2 C, outperforming most reported solid-state sodium systems.
Innovative Design and Features
- Fluorinated MOF (UiO-66-(F)4) as Electron-Rich Beacon: High-density F sites electrostatically attract Na+ and repel TFSI-, driving salt dissociation while forcing anions into the primary solvation structure.
- Weakened Na+–PEO Coordination: RDF, ss-NMR and Raman analyses confirm shortened Na–O(ether) bonds and increased Na–O(TFSI-) contacts, creating a “weak” solvation environment that accelerates bulk and interfacial transport.
- Mechanically Robust Membrane: 9 wt % FMOF yields 4.4 MPa tensile strength and 1350 % elongation, suppressing dendrites while maintaining processability.
- Scalable Fabrication: Solution-casting produces < 80 µm, flexible, transparent films in an Ar glove box—compatible with roll-to-roll assembly.
Applications and Future Outlook
- Practical Pouch Cells: An 11.6 mg cm-2 NVP cathode paired with PEO-FMOF delivers 86 % capacity retention after 250 cycles at 0.5 C and survives folding/cutting abuse tests, highlighting safety for wearable or flexible devices.
- Universal Electrostatic Concept: The FMOF platform can be extended to Li+, K+ and Zn2+systems, offering a general toolkit to tune cation solvation in any solid polymer electrolyte.
- Next Steps: The team is scaling film width to > 10 cm, optimizing MOF cost and exploring dry-electrode hot-pressing for greener manufacturing.
This work demonstrates that electrostatic engineering at the molecular level can simultaneously solve the ion-transport and interfacial challenges that have long hindered solid-state sodium batteries. Stay tuned for more high-power, long-life energy-storage innovations from the collaborative labs of Jiangnan University and BayBatt!
Follow the Topic
-
Nano-Micro Letters

Nano-Micro Letters is a peer-reviewed, international, interdisciplinary and open-access journal that focus on science, experiments, engineering, technologies and applications of nano- or microscale structure and system in physics, chemistry, biology, material science, and pharmacy.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in