Improving soybean yield and oil productivity: an integrated nutrient management approach for sustainable soybean production
Published in Earth & Environment, Sustainability, and Plant Science
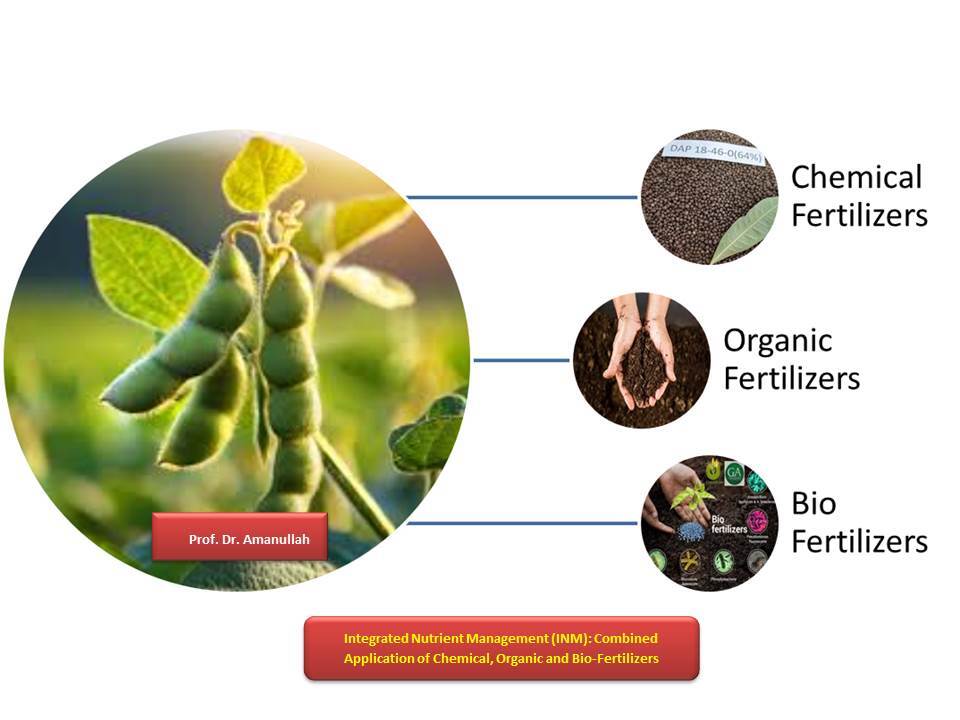
Introduction
As global food demand continues to rise, the importance of sustainable agricultural practices becomes increasingly urgent. Among the essential crops contributing to food security, soybean (Glycine max) stands out as a vital source of protein and edible oil for both human and animal consumption. With its multifaceted utility in food products, feed, and industrial applications, soybean plays a critical role in the global agricultural economy.
Yet, despite its importance, soybean productivity in many regions remains suboptimal due to declining soil fertility, imbalanced nutrient use, and the unsustainable over-reliance on chemical fertilizers. These challenges are compounded by the adverse effects of climate change and land degradation. In this context, Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) emerges as a strategic, science-based approach to not only improve soybean yield and oil quality but also to foster long-term agricultural sustainability.
What is Integrated Nutrient Management (INM)?
Integrated Nutrient Management is the practice of optimally combining organic, inorganic, and biological sources of plant nutrients to maintain or improve soil fertility and crop productivity. It emphasizes the balanced and site-specific application of:
-
Chemical fertilizers (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium),
-
Organic manures (e.g., compost, farmyard manure),
-
Biofertilizers (e.g., Rhizobium, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, mycorrhizae),
-
And in modern contexts, emerging tools like nanofertilizers and precision nutrient application technologies.
The goal of INM is to ensure that crops receive the right nutrient sources, in the right amounts, at the right time, and in the right manner—often referred to as the 4R Nutrient Stewardship principle (Right Source, Right Rate, Right Time, Right Place).
Why Focus on Soybean?
Soybean has a unique role in agriculture due to its nitrogen-fixing ability, thanks to its symbiotic relationship with Rhizobium bacteria, which reduces the need for nitrogen fertilizers. However, other nutrients like phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, and micronutrients are still crucial for optimal growth, flowering, pod development, and oil synthesis.
Additionally, soybean oil is one of the most consumed vegetable oils worldwide. Improving both yield and oil content is essential to meet increasing demands and ensure that soybean production remains profitable and competitive.
The Benefits of INM in Soybean Cultivation
-
Enhanced Yield and Oil Quality
Multiple studies have demonstrated that integrated nutrient application results in higher and more consistent soybean yields compared to exclusive reliance on either organic or chemical inputs. Biofertilizers improve root health and nutrient uptake, while compost and manures enhance soil organic matter and microbial activity, both of which contribute to better grain and oil quality. -
Improved Nutrient Use Efficiency (NUE)
INM optimizes the timing and form of nutrient delivery, reducing nutrient losses due to leaching, volatilization, or runoff. This leads to improved nutrient use efficiency, meaning more of the applied nutrients are taken up by the plant rather than lost to the environment. -
Soil Health and Fertility Restoration
Continuous application of only chemical fertilizers has led to soil acidification, compaction, and biological degradation in many regions. Integrating organic and biological sources replenishes soil carbon, enhances microbial biodiversity, and improves soil structure, aeration, and water retention—key components of long-term soil fertility. -
Reduced Environmental Impact
Excessive use of synthetic fertilizers contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, eutrophication of water bodies, and soil toxicity. INM reduces these risks by lowering chemical dependency and promoting eco-friendly alternatives. -
Cost-Effective and Farmer-Friendly
Incorporating farm-produced compost or locally available biofertilizers can reduce input costs. Moreover, improving yield stability and soil health translates into better returns over time, especially for smallholder farmers.
Relevance in the Era of Climate Change
Agriculture is both a victim and contributor to climate change. Extreme weather, erratic rainfall, and rising temperatures affect crop productivity and soil quality. On the other hand, unsustainable practices, including over-fertilization, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions (e.g., nitrous oxide from nitrogen fertilizers).
INM offers a climate-smart solution, improving the resilience of soybean cropping systems while minimizing their carbon footprint. For instance, by encouraging biological nitrogen fixation and reducing synthetic nitrogen inputs, INM helps lower nitrous oxide emissions. Moreover, practices that build soil organic carbon through composting and cover cropping also contribute to carbon sequestration.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are well-documented, successful adoption of INM in soybean cultivation faces several challenges:
-
Knowledge gaps among farmers regarding balanced nutrient management.
-
Limited access to quality biofertilizers and organic inputs.
-
Need for localized research to develop crop- and soil-specific INM recommendations.
-
Policy and subsidy structures that still heavily favor chemical fertilizer use.
Addressing these requires an integrated effort involving extension services, research institutions, policy reforms, and private sector partnerships to make INM technologies accessible, affordable, and scalable.
Moving Forward: Policy and Practice
To mainstream INM in soybean farming, especially in regions with fragile agro-ecosystems, the following steps are recommended:
-
Capacity Building and Farmer Training: Extension programs should focus on training farmers in INM principles and application techniques.
-
Incentives for Organic and Bio-based Inputs: Policies that promote composting, vermiculture, and biofertilizer production can support the availability of sustainable inputs.
-
Investment in Research and Innovation: Continuous R&D is needed to refine INM packages tailored to different soybean-growing zones.
-
Monitoring and Evaluation Tools: Implementing soil health cards and digital advisory platforms can guide farmers on nutrient needs more precisely.
Conclusion
Improving soybean yield and oil productivity through Integrated Nutrient Management is more than an agronomic technique—it is a pillar of sustainable agriculture. By blending tradition with technology, INM empowers farmers to increase productivity while preserving the environment. As the global community pushes toward food security, climate resilience, and ecological balance, INM stands out as a proven and scalable solution—especially in crops as strategically important as soybean.
Adopting and promoting this approach will not only help meet present demands but also secure a healthier planet for future generations.
Follow the Topic
-
BMC Plant Biology

This is an open access, peer-reviewed journal that considers articles on all aspects of plant biology, including molecular, cellular, tissue, organ and whole organism research.
What are SDG Topics?
An introduction to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Topics and their role in highlighting sustainable development research.
Continue reading announcementRelated Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Plant genome editing: advances and applications in plant biology
Plant genome editing has rapidly evolved into a transformative technology in plant biology, offering novel and effective approaches for functional genomics and molecular breeding research. The increasing use and development of CRISPR-Cas genome-editing technologies have indeed enhanced our understanding of gene functions and regulation, and facilitated the development of crops with improved yields, nutritional characteristics or resilience to environmental stress. As the global populations is rising and climate change poses new challenges, the ability to bioengineer and enhance specific plant traits has become essential to achieve sustainable agricultural practices, and food security and nutrition.
In support of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2: Zero Hunger), BMC Plant Biology is launching the Collection ‘Plant Genome Editing: Advances and Applications in Plant Biology’. This collection invites submissions that highlight current research and future perspectives in plant genome editing, covering e.g. advances in gene-editing techniques (e.g. CRISPR/Cas systems) and their applications in plant functional genomics and molecular breeding, as well as biotechnological applications aimed at enhancing crop productivity. We invite researchers and experts in the field to submit research articles that explore, but are not limited to, the following topics:
Advances in CRISPR/Cas9-based genome engineering in plant biology
Advanced CRISPR/Cas variants: CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cas12a systems in plant genome editing
Applications of engineered Cas9 and newly discovered RNA guided DNA endonucleases in plants
Novel approaches for tissue culture-free genome editing in plants
Targeted epigenetic modifications using CRISPR/Cas
RNP-mediated genome editing
Applications of prime editing in plant molecular breeding and crop trait improvement
CRISPR/Cas applications in plant biotechnology: improving crop yield, quality and stress-resistance
Advances in genome editing technologies for next-generation plant breeding
Emerging technologies for delivering the CRISPR/Cas system in crop species
CRISPR/Cas applications in plant synthetic biology
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 27, 2026
Leaf senescence and molecular breeding
Leaf senescence is a complex biological process that involves the degradation of chlorophylls and the eventual death of leaf tissues, affecting plant growth and yield. As the final, postmitotic stage of plant life, leaf senescence is a crucial functional shift from nutrient assimilation to remobilization, critical for plant survival. Its timing is regulated by age, hormones, and environmental stress. Consequently, researchers are intensively devising strategies based on known regulatory mechanisms to manipulate initiation and progression of leaf senescence for enhancing crop resilience and productivity.
While many Senescence-Associated Genes (SAGs) have been identified, fundamental knowledge gaps persist, such as: when exactly is leaf senescence initiated? How are signals transmitted between organelles, cells, and tissues? How can we fully map the molecular pathways of cell senescence? Recent advances in genomics and molecular biology have revealed complex regulatory networks that govern this process, enabling to investigate the interactions between molecular, genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. The integration of single-cell, multi-omics and CRISPR/Cas9 approaches now enables deeper mechanistic exploration and more precise manipulation of senescence pathways.
At the same time, molecular breeding for optimized or ‘stay-green’ traits is rapidly accelerating, driven by the global demand for climate-resilient and high-yielding crops in support of the United Nations’ SDG 2 (Zero Hunger). Combining mechanistic insights with genome engineering, precision editing, pan-genome–informed allele mining, high-throughput phenotyping, and genomic selection has opened new opportunities to design crops with fine-tuned senescence timing, improved nutrient-use efficiency, and enhanced stress tolerance and photosynthetic productivity. In this context, BMC Plant Biology invites submissions to the Collection Leaf senescence and molecular breeding, aiming to gather research that advances our understanding of senescence mechanisms and translates this knowledge into crop improvement. We invite researchers and experts in the field to submit research articles that explore, but are not limited to, the following topics:
- Multilayered regulation of leaf senescence
- Genetic and epigenetic control of leaf senescence
- Post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation of leaf senescence
- Hormonal regulation of leaf senescence: regulation by classical and peptide hormones
- Regulatory functions and mechanisms of non-hormonal small molecule signals (e.g. NO, H2S) in leaf senescence
- New mechanisms for stress-induced leaf senescence
- Role of environmental factors on the regulation of leaf senescence
- Role of reactive oxygen species in leaf senescence
- Plant metabolic changes during leaf senescence
- Subcellular structural dynamics and functional remodelling in chloroplast and mitochondria during leaf senescence
- Novel signaling components in regulating leaf senescence in crops
- Integration of leaf senescence traits in molecular breeding programmes
- Pan-genome, GWAS, and QTL analyses for senescence traits
- Marker-assisted selection, genomic selection, and genome editing for senescence improvement
- High-throughput and image-based phenotyping of senescence in crop breeding
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Aug 19, 2026





