Interval-Valued Fuzzy Approach for Multi-Attribute Decision-Making in Water Quality Assessment
Published in Mathematics
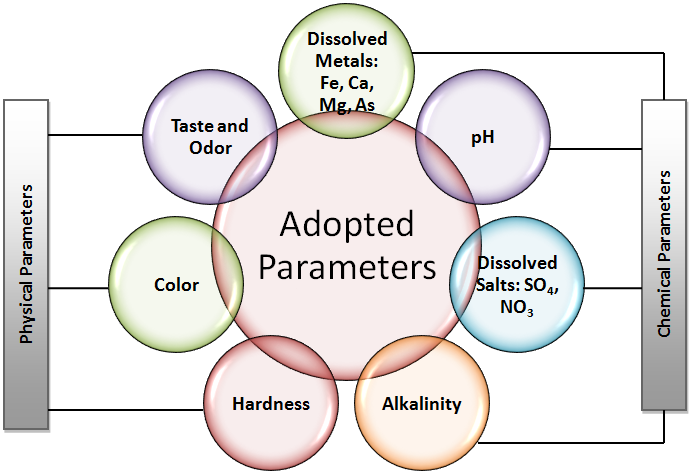
Artificial intelligence and engineering are crucial for managing urban and industrial water resources, addressing declining drinking water quality, and analyzing water wellness, despite uncertainties. This article seeks to characterize an innovative mathematical framework called an interval-valued fuzzy parameterized interval-valued fuzzy soft set (IVFpIVFSS), better equipped to handle the uncertainties associated with multiple attribute decision-making (MADM) issues like drinking water quality assessment (DWQA). It features two interval-valued settings: the first is for interval-valued fuzzy parameterization, which is intended to assess the parameters’ degree of uncertainty, and the second is for approximating the alternatives based on these parameters. Based on set-theoretic operations, appropriate parameters, and their respective interval-valued fuzzy parameterized grades, a decision-assisted system is established with the proposal of an algorithm for DWQA in certain areas. The flexibility of the study is assessed by its comparison with published literature based on structure and computations. The proposed IVFpIVFSS provides a robust approach to addressing the uncertainties in MADM challenges like DWQA, demonstrating improved capabilities for managing water quality in complex and uncertain environments.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in