The AI-STREAM Study: AI is enhanced Breast cancer Screening
Published in Computational Sciences and General & Internal Medicine
Study Methodology
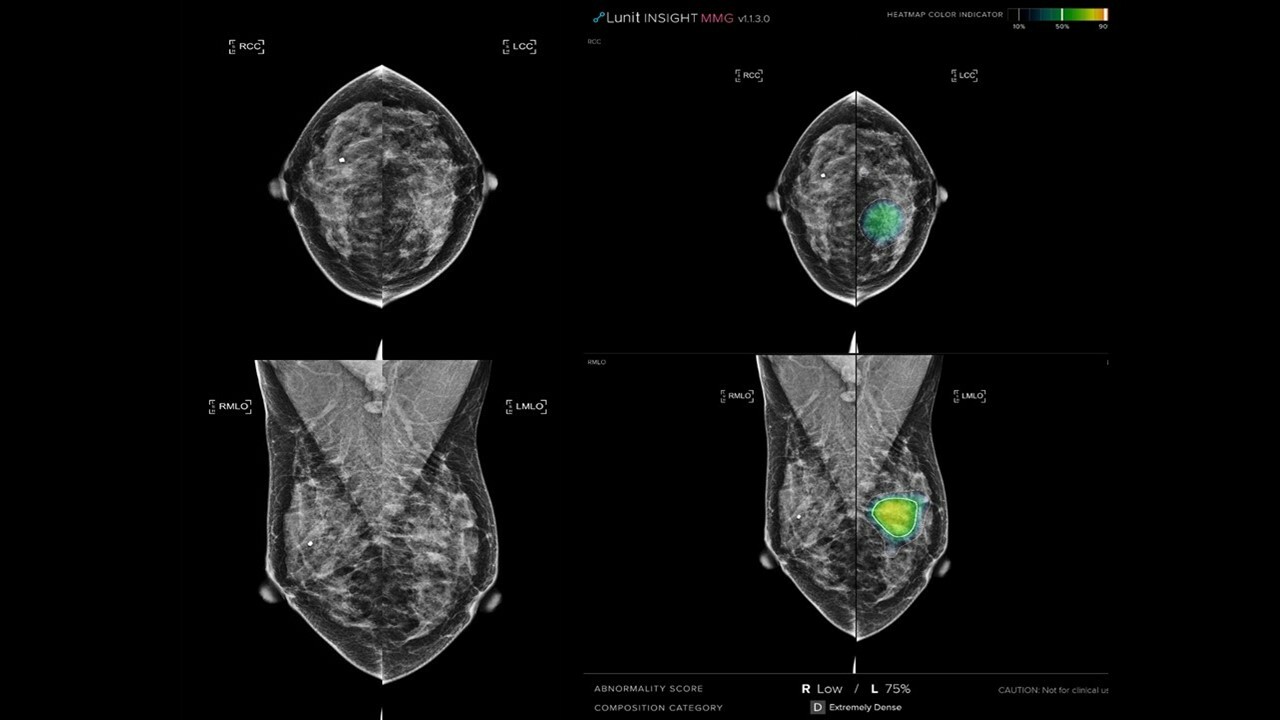
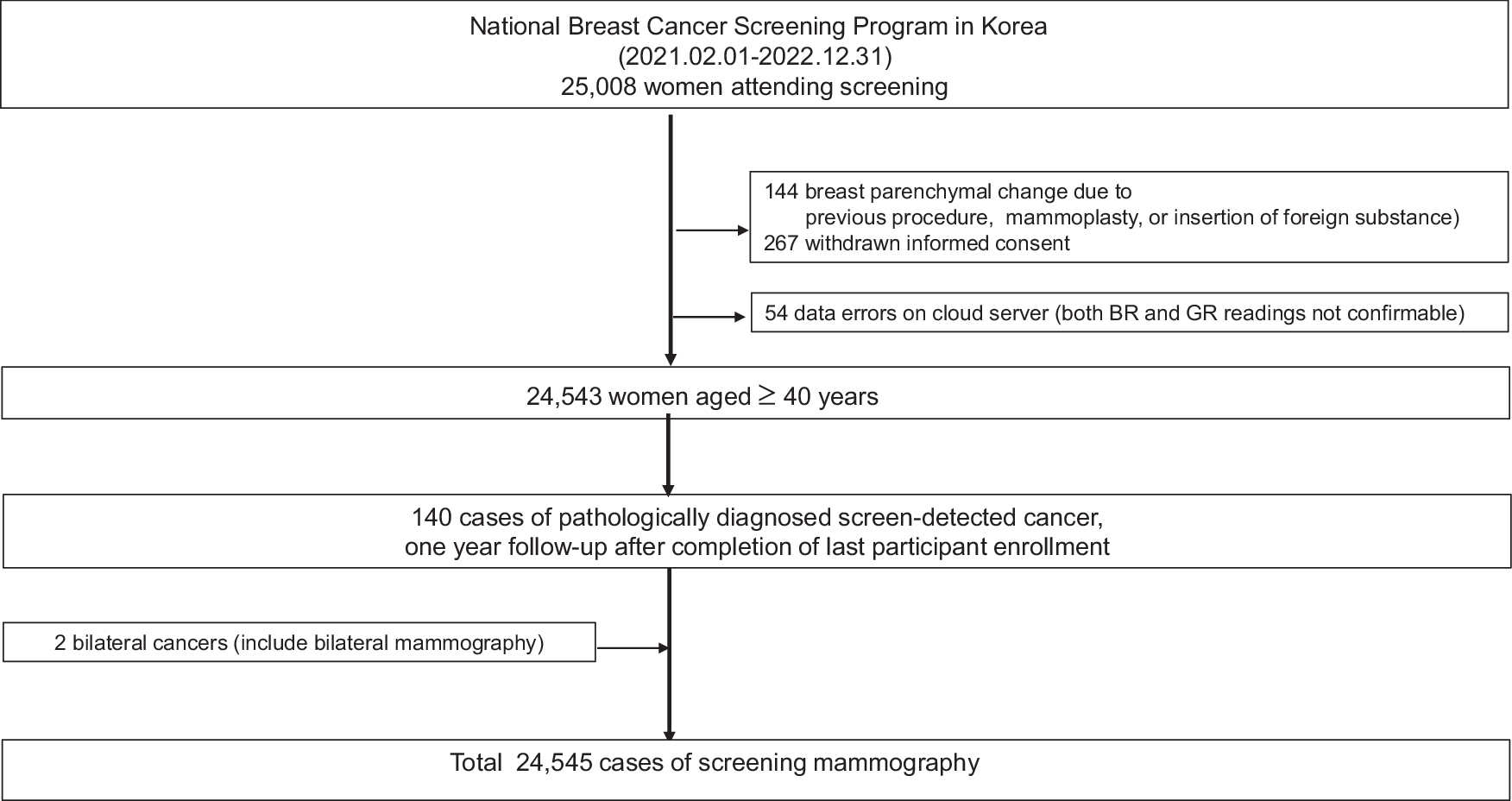
The AI-STREAM (Artificial Intelligence for Breast Cancer Screening in Mammography) study enrolled 25,008 women aged 40 and older, all participating in South Korea’s national breast cancer screening program. The final analysis involved 24,543 participants. Breast radiologists (BR) first interpreted the mammograms without AI assistance and then re-read them using AI-CAD (computer-assisted detection). Even with AI-aided, the radiologist made the final decision on whether a participant should be recalled for further evaluation. Additionally, a separate simulation study also compared the performance of general radiologists (GR) without and with AI assistance.
Key Findings: AI Enhances Cancer Detection
The results of the AI-STREAM study were promising:
- Higher Cancer Detection Rates (CDR):
- Breast radiologists (BR), who specialized in breast, using AI detected 140 cases of cancer, compared to 123 cases without AI—a 13.8% increase in detection rate.
- General radiologists (GR), who were radiologists with relatively few mammography reading experience, saw even greater improvement, with 120 cancers detected when using AI, compared to 95 without it—a 26.4% increase in detection.
- No Significant Increase in Recall Rates (RR) for Breast Radiologists:
- The addition of AI did not result in more unnecessary recalls for further testing among breast radiologists. This is a crucial finding, as it means AI helped detect more cancers without increasing false positives.
- However, general radiologists saw an increase in recall rates (6.89% with AI vs. 6.31% without AI), indicating that while AI improved cancer detection, it also led to more false positive results.
- AI Alone vs. AI-Assisted Breast Radiologists:
- When used as a standalone tool, AI had a cancer detection rate (CDR) of 5.21 per 1,000 screenings, which was comparable to radiologists’ performance.
- However, AI alone had a higher recall rate (6.25%) than radiologists, meaning it flagged more cases that turned out not to be cancer. The study found that AI’s best performance came when it was used to assist breast radiologists rather than AI standalone.
Clinical Implications: AI as a Tool for Improving Screening Accuracy
The findings from AI-STREAM suggest that AI-assisted mammography can significantly improve the early detection of breast cancer. The study showed that AI helps radiologists—both specialized and general—detect more cancers, which could have the potential to reduce breast cancer mortality rates. AI’s role is particularly beneficial when it assists human radiologists rather than functioning as a standalone tool.
For breast radiologists, the integration of AI assistants to improve cancer detection without increasing unnecessary recalls, a major advantage in real-world clinical settings.
AI as a Future Tool in Breast Cancer Screening
As breast cancer screening programs become more widespread, incorporating AI can help streamline the process, improve diagnostic accuracy, and support radiologists in managing their increasing workloads. Although this is a preliminary analysis with a relatively small number of detected cancers, the results suggest that AI assistance can improve the early detection of breast cancer while minimizing unnecessary recalls. However, a longer follow-up period, ideally two years, is needed to evaluate the true impact of AI-CAD on interval cancers detected after two years (the biennial screening interval in South Korea) and whether it leads to an increase in interval cancers with poor prognosis. The final results of the AI-STREAM study, reflecting these additional insights, will be announced after 2026, following data analysis linked to the National Cancer Register.
Conclusion: The Role of AI in Healthcare
The AI-STREAM study demonstrates the potential of artificial intelligence to improve breast cancer detection through mammography. By assisting radiologists in interpreting mammograms, AI enhances the detection of early-stage cancers, leading to better patient outcomes. As AI technology evolves, its integration into healthcare will likely continue to expand, offering even more benefits for both medical professionals and patients.
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Communications

An open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical and Earth sciences.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Women's Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
Advances in neurodegenerative diseases
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 24, 2026
Latest Content
Why is Singapore Identified in Global Research as Number One? How Physical Activity and Education Excellence Created a Global Leader




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in