Comprehensive risk profiling of occupational harmful factors in the ceramic industry: a case study from Iran
Published in Social Sciences, Chemistry, and Earth & Environment
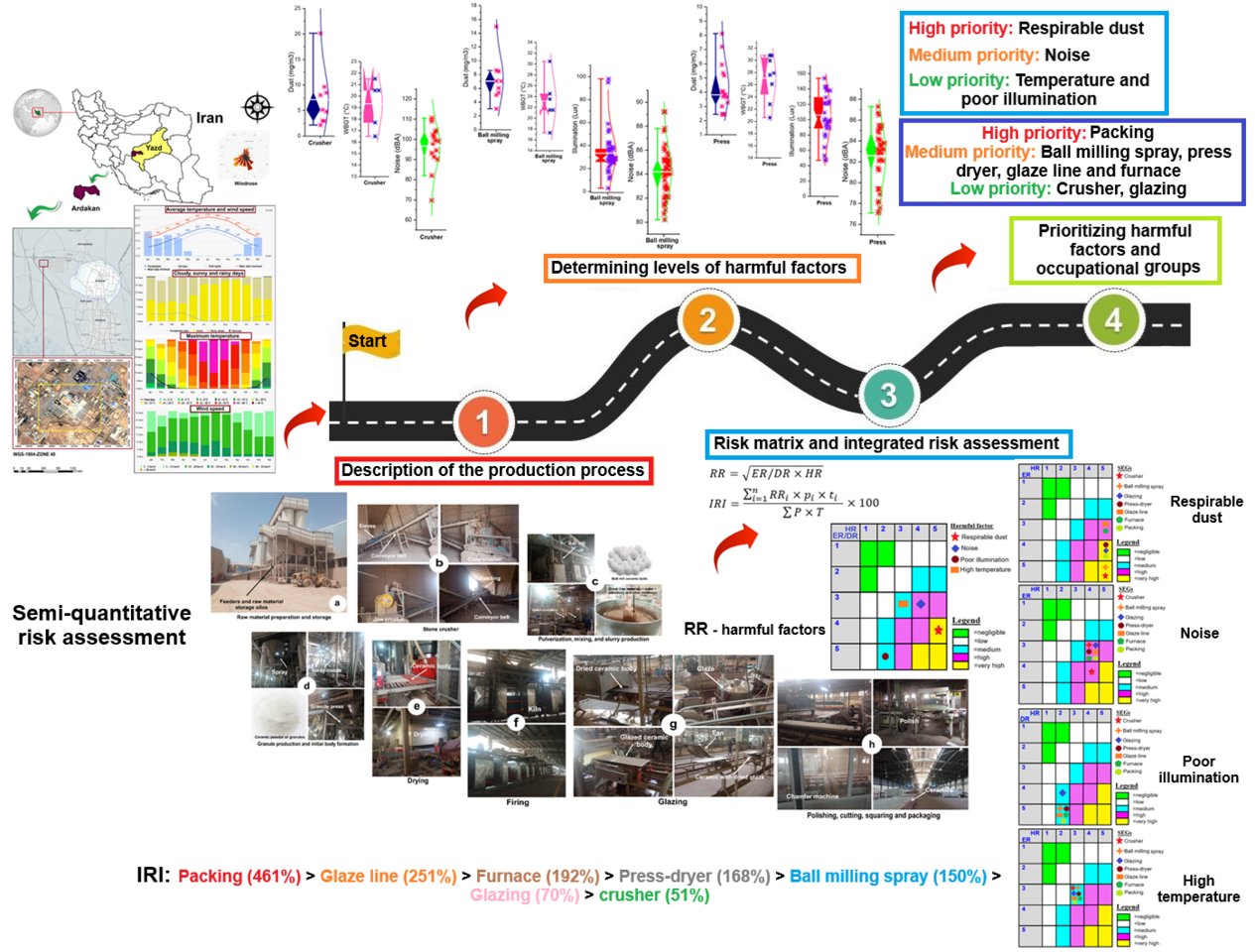
Objective: This study aimed to develop a comprehensive risk profile for four key occupational hazards—heat stress, inadequate illumination, noise, and respirable dust—in a representative ceramic manufacturing facility in Iran. The goal was to prioritize risks and exposure groups to inform targeted health and safety interventions.
Methods: A mixed-methods approach was used:
Measurement: Standard instruments measured respirable dust (NIOSH 0600), noise (Type 2 sound level meter), illumination (lux meter at 0.85 m height), and heat stress (WBGT meter).
Risk Assessment:
Single-Factor Risk Assessment: Calculated a Risk Rating (RR) for each hazard based on Exposure Rating (ER) and Hazard Rating (HR).
Integrated Risk Assessment (IRI): Combined RR with the number of exposed workers and exposure duration to calculate a comprehensive risk index for each Similar Exposure Group (SEG).
Prioritization: The Pareto principle (80/20 rule) was applied to classify hazards and SEGs into high, medium, and low priority for intervention.
Key Findings:
Exposure Levels:
Average noise: 82.88 dB(A)
Average illumination: 114.83 lx
Average respirable dust: 4.15 mg/m³ (exceeding the NIOSH limit of 3 mg/m³ in most areas)
Average temperature: 21.01°C
Single-Factor Risk:
Respirable dust: Very high risk (RR = 4.47)
Noise: High risk (RR = 3.46)
Poor illumination & heat stress: Medium risk (RR = 3.16 & 3.00)
Integrated Risk (IRI):
The packing group had the highest cumulative risk (IRI ≥ 379%), due to large workforce size and multi-shift operations.
Other high/medium-risk SEGs included furnace, press-dryer, glaze line, and ball milling spray.
Pareto Prioritization:
High-priority hazard: Respirable dust (IRI ≥ 386%)
Medium-priority hazard: Noise (321% ≤ IRI < 386%)
Low-priority hazards: Poor illumination and heat stress (IRI < 321%)
Conclusions:
Respirable dust is the most critical hazard requiring immediate control measures (e.g., local exhaust ventilation, enclosed conveying systems, wet suppression).
The packing department should be the primary focus for integrated interventions (e.g., job rotation, improved PPE, ergonomic breaks).
The study provides a replicable, risk-based framework for prioritizing occupational health actions and optimizing resource allocation in industrial settings.
Follow the Topic
What are SDG Topics?
An introduction to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Topics and their role in highlighting sustainable development research.
Continue reading announcement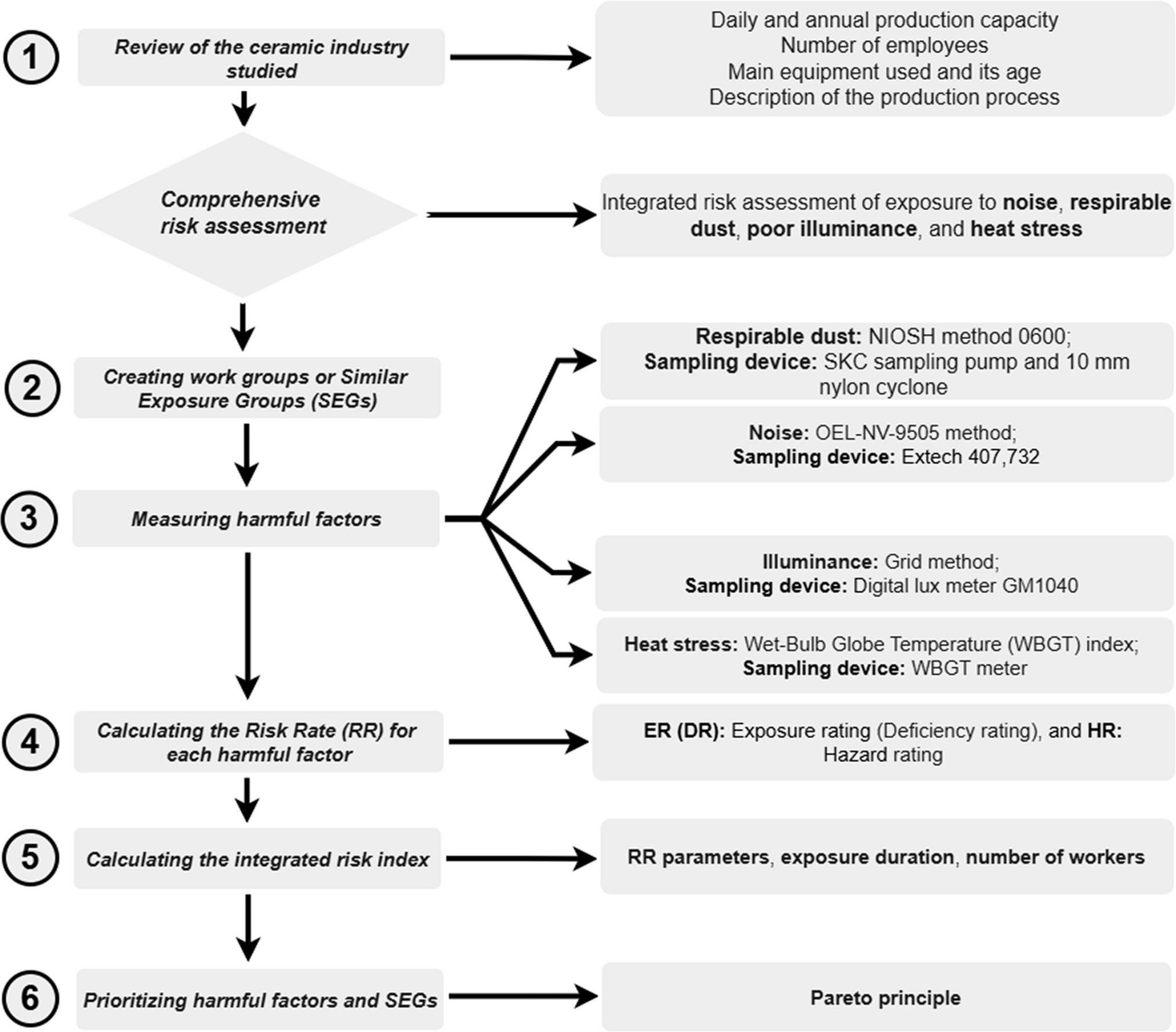





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in