Detection of anomalous activities around telecommunications infrastructure based on YOLOv8s
Published in Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Computational Sciences, and Behavioural Sciences & Psychology
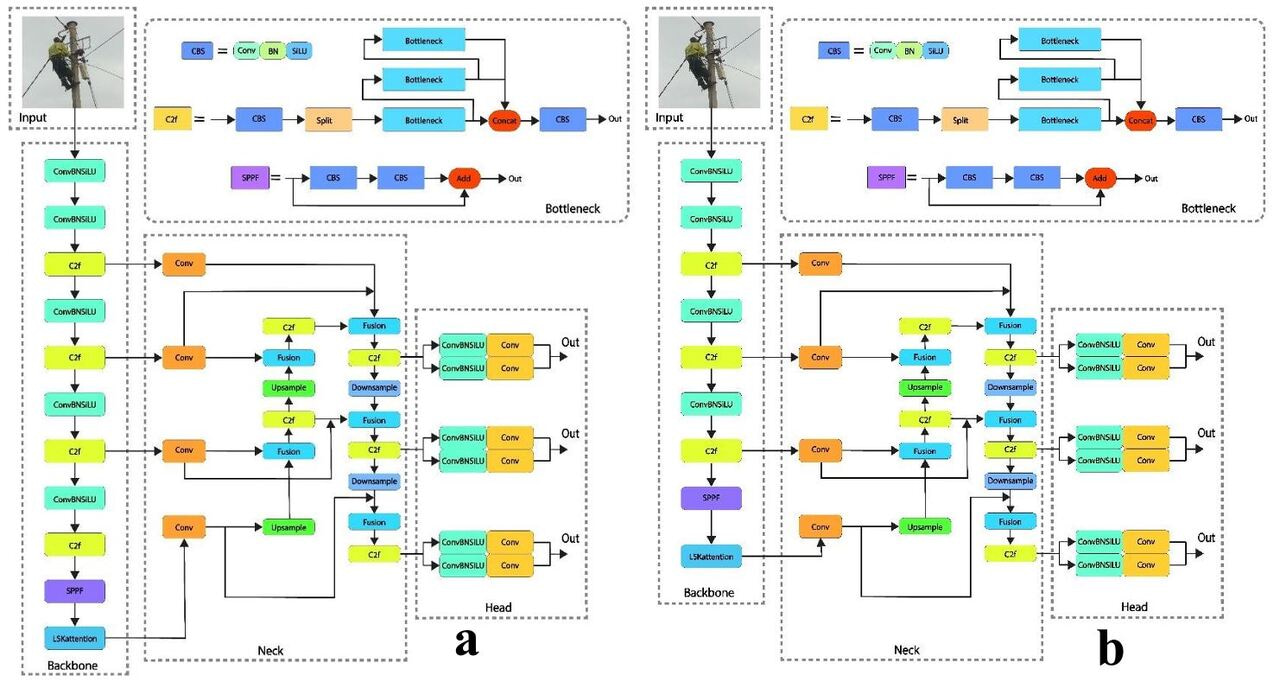
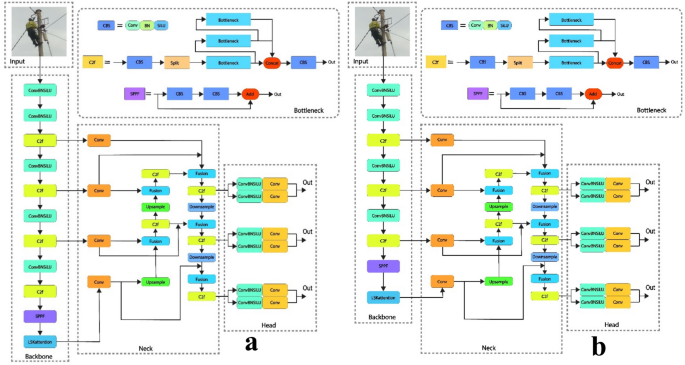
This study explores the deployment of YOLOv8s for detecting anomalies in fiber optic cables mounted on poles, with a focus on climbing activities and environmental impediments. To address the lack of climbing-related annotations in current datasets, a custom dataset was generated, covering a variety of scenarios to enhance model adaptability. During training, various augmentation approaches were used, which greatly enhanced model performance and reduced overfitting. The proposed model was trained and tested over many epochs, with detection performance progressively improving: mAP@0.5 increased from 78.9% at 20 epochs to 87.5% at 50 epochs and 97.3% at 100 epochs, after which further increases plateaued. In comparison, the trained YOLOv8s-modified model outperformed the other models on all key metrics. It achieved a mAP@50 of 97.3% and a mAP@50:95 of 71.5%, outperforming YOLOv8-original at 89.6% and 59.0%, respectively. Additionally, it achieved higher precision (96.9%) and recall (86.6%), demonstrating superior detection accuracy, dependability, and robustness in detecting complex anomalies. These improvements due to model backbone optimizations and the usage of a well-balanced, scenario-rich dataset. This study shows that YOLOv8s is a highly accurate and efficient method for detecting anomalies in fiber optic infrastructure, making it appropriate for real-time deployment in operational field environments.
Follow the Topic
-
Scientific Reports

An open access journal publishing original research from across all areas of the natural sciences, psychology, medicine and engineering.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Reproductive Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 30, 2026
Women’s Health
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
Excellent work.