Dose-related association between radiation exposure from Computed Tomography (CT) scans during trauma hospitalizations and subsequent risk of developing new-onset cancers
Medical imaging, especially Computed Tomography scans, uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed pictures of the inside of the body. These scans are commonly used after serious injuries but their long-term health risks—particularly the risk of developing cancer—are not well understood.
Published in Healthcare & Nursing and Surgery
Like
Be the first to like this
CT-related radiation exposure during adult trauma hospitalizations is associated with a dose-dependent increase in the risk of later cancer incidence and mortality,
particularly hematologic malignancies.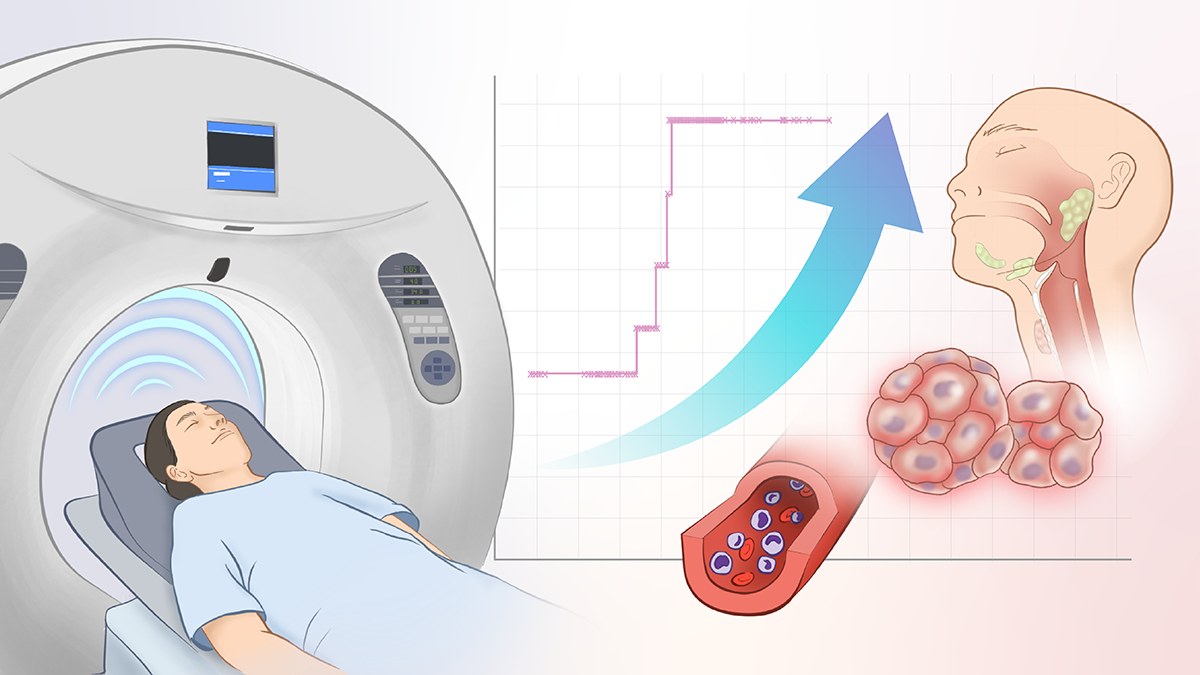

Follow the Topic
Trauma Surgery
Life Sciences > Health Sciences > Surgery > General Surgery > Trauma Surgery
Emergency Medicine
Life Sciences > Health Sciences > Clinical Medicine > Emergency Medicine
Medical Imaging
Life Sciences > Health Sciences > Health Care > Medical Physics > Medical Imaging
-
Communications Medicine

A selective open access journal from Nature Portfolio publishing high-quality research, reviews and commentary across all clinical, translational, and public health research fields.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Reproductive Health
This Collection welcomes submissions related to a broad range of topics within reproductive health care and medicine related to reproductive well-being.
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 30, 2026
Healthy Aging
This collection welcomes submissions based on studying preclinical models, as well as population-wide and clinical studies. Studies that advance our understanding of mechanisms behind healthy aging are also welcomed. Clinical research of interest will include epidemiological studies, observational studies, longitudinal cohort studies, systematic reviews and clinical trials.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 01, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in