Graph Neural Networks Reshaping Electrocatalyst Design for Green Hydrogen Production
As authors, we aim to address one of the most pressing challenges in sustainable energy: how to accelerate the discovery of efficient electrocatalysts for green hydrogen production.
Key Highlights
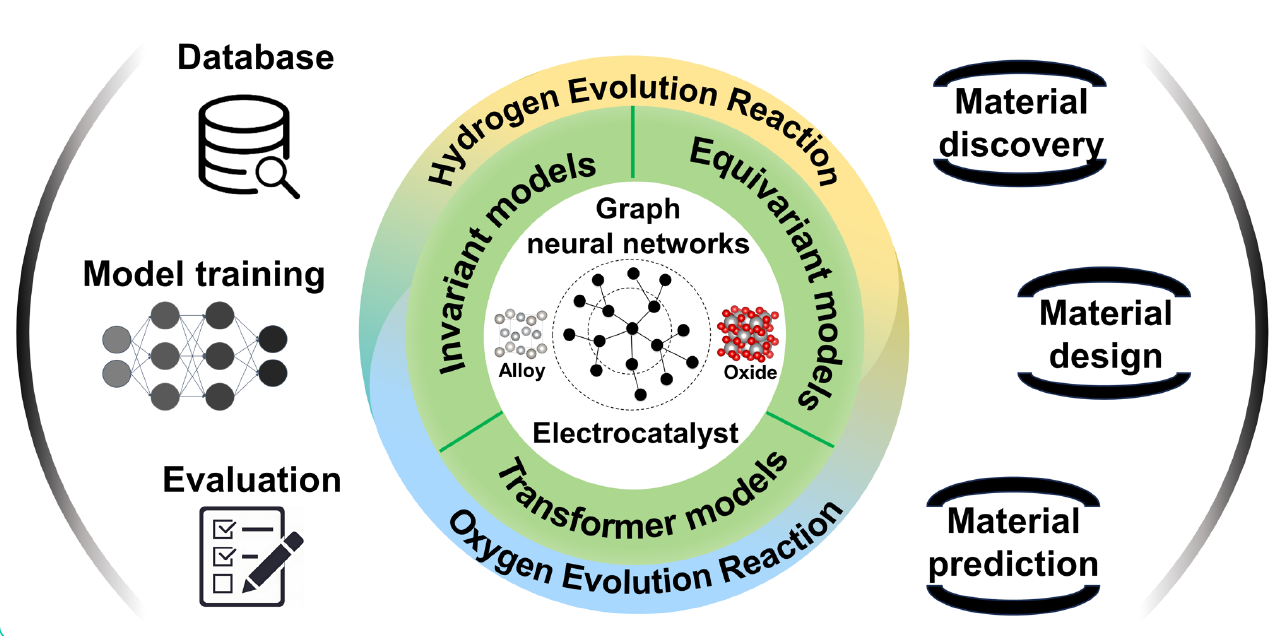
- Paradigm Shift in Catalyst Design: Traditional electrocatalyst discovery relies on costly experiments and DFT simulations. This review highlights graph neural networks (GNNs) as a transformative approach, enabling direct learning from atomic graphs without manual feature engineering.
- Comprehensive Methodological Framework: The article systematically categorizes GNN architectures—invariant, equivariant, and Transformer-based models—and compares them with traditional machine learning approaches, emphasizing their superior ability to capture complex geometric and topological information.
- Applications in HER and OER: GNNs have been successfully applied to design electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER), identifying high-performance non-precious metal catalysts, metastable IrO₂ phases, and efficient single-atom catalysts.
- Integration with AI and Databases: Open Catalyst datasets (OC20/OC22) and physics-informed GNN models are accelerating high-throughput screening, reducing computational costs by over tenfold compared to DFT.
- Future Outlook: The review calls for physics-informed GNNs, multi-objective optimization frameworks, and closed-loop R&D systems integrating computational prediction, automated synthesis, and real-time feedback.
Significance
- Accelerating Green Hydrogen Technology: By reducing reliance on expensive experiments and simulations, GNN-driven design can significantly shorten the development cycle for electrocatalysts, supporting global decarbonization goals.
- Bridging AI and Physical Sciences: This work exemplifies how AI for Science can integrate deep learning with fundamental physics, paving the way for rational catalyst design and autonomous discovery.
Authors
Wenhao Dong, Qi Wang, Liping Ren, Jinjia Wei, Shaohua Shen*, Jie Chen*
Affiliations: Xi’an Jiaotong University; State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering; Xi’an Jiaotong University Suzhou Academy
Follow the Topic
-
Catal

Catal is an open access journal covering full spectrum of catalysis critical advances. From biocatalysts to heterogeneous catalysts, it integrates fundamental and applied sciences. Catal offers a primary platform for researchers and practitioners in the field.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Bio-Catalysis in Circular Bioeconomy and Green Chemistry
This collection emphasizes the role of bio-catalysis in advancing the circular bioeconomy, focusing on enzymatic transformations and eco-friendly processes that valorize renewable feedstocks. Contributions should highlight innovative applications of bio-catalysis in waste-to-value systems, biorefineries, and green chemical synthesis.
Catal invites research articles, reviews and reports on the topic of the development of enzymes, metabolic engineering, and integration of bio-catalysis into industrial processes, aiming to reduce dependency on fossil-based resources and promote sustainable practices.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 31, 2026
Nanocatalysis and Thermocatalysis in Precision Chemical Synthesis
This collection, hosted by Catal, highlights the intersection of nanocatalysis and thermocatalysis in precision chemical synthesis. It aims to disseminate cutting-edge research that drives innovation in catalytic materials, selective processes, and reaction pathways, fostering advancements in the production of fine chemicals and specialty compounds. Aligned with Catal's mission to prioritize impactful catalytic applications, this collection welcomes contributions from established and early-career researchers that advance both theoretical and applied catalysis.
The collection embraces the breadth of Catal’s coverage, including topics such as nanostructured catalysts, thermocatalytic processes, and advanced synthesis strategies. Contributions may explore catalytic mechanisms, computational modeling, or experimental breakthroughs, offering insights into scalable industrial applications and fundamental research. Articles types—original research, reviews, perspectives, and analyses—are all encouraged, ensuring a diverse platform for sharing high-impact advancements in catalysis.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 31, 2026





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in