Multiscale Theoretical Calculations Empower Robust Electric Double Layer Toward Highly Reversible Zinc Anode
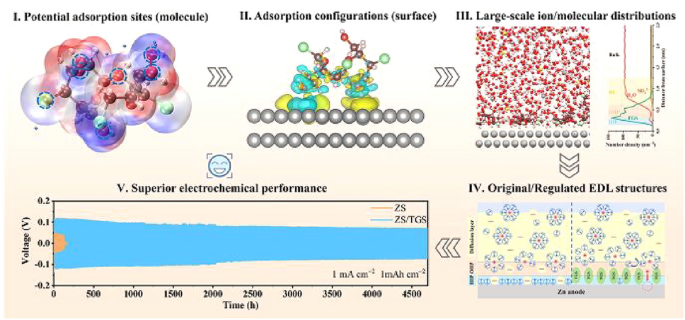
As aqueous rechargeable zinc batteries (ARZBs) edge closer to grid-scale deployment, the zinc metal anode remains dogged by dendrite proliferation and parasitic hydrogen evolution that slash cycle life and safety. Now, researchers from Zhejiang University, led by Prof. Yinzhu Jiang, have delivered a multiscale theoretical-experimental blueprint that deciphers and tames the electric double layer (EDL) at the zinc-electrolyte interface. The work, published in Nano-Micro Letters, introduces a low-cost sugar-derivative additive that rewrites interfacial chemistry, pushing Zn||Zn symmetric cells beyond 4700 h and full cells to >90 % capacity retention after 800 cycles.
Why the EDL Matters
- Reaction Gatekeeper: The EDL controls ion flux, charge distribution and nucleation thermodynamics—yet classical mean-field models ignore molecular-scale heterogeneity.
- Water-Induced Failures: Water-rich inner Helmholtz planes trigger hydrogen evolution and insulating Zn4SO4(OH)6·xH2O by-products.
- Theory-Experiment Gap: Ab-initio or continuum methods alone cannot capture dynamic ion/molecule reorganization under battery-operating conditions.
Innovative Multiscale Framework
- QC-DFT-CMD Pipeline: Quantum-chemistry pinpoints adsorption sites, DFT quantifies energetics, and constant-potential classical MD maps real-time EDL restructuring.
- Additive Design Rules: 4,1′,6′-trichlorogalactosucrose (TGS) is selected for its bulky chlorinated skeleton and abundant –OH anchors that self-assemble into a “water-poor & anion-expelled” EDL.
- Steric-Plus-Electronic Effect: TGS parallel adsorption (−0.97 eV) displaces 94 % of surface water and expels SO42- from the Helmholtz region, flattening interfacial potential gradients.
Performance Breakthroughs
- Anti-Corrosion: HER barrier rises from 0.69 to 0.84 eV; corrosion current plummets from 4.64 to 0.86 mA cm-2.
- Dendrite Suppression: Overpotential increase enforces 3D diffusion-limited deposition, yielding dense (002)-textured plates instead of mossy or dendritic grains.
- Long-Term Stability: Zn||Cu cells deliver 99.5 % CE over 1 100 cycles; Zn||NaV3O8·1.5H2O pouch cells retain 71.8 % capacity after 50 cycles at 2 mA cm-2.
Future Outlook
The study establishes a transferable platform for additive-guided EDL engineering, opening a general pathway toward ultra-stable metal anodes beyond zinc.
Follow the Topic
-
Nano-Micro Letters

Nano-Micro Letters is a peer-reviewed, international, interdisciplinary and open-access journal that focus on science, experiments, engineering, technologies and applications of nano- or microscale structure and system in physics, chemistry, biology, material science, and pharmacy.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in