We have studied the normal-charge transport properties of a single-crystalline high-temperature superconductor YBa2Cu3O6.67 (YBCO6.67) under the application of uniaxial stress. We find the influence of charge order on the resistivity in the stress response, which is reminiscent of classical charge-density-wave (CDW) compounds. On the other hand, the Hall effect was found to be weakly dependent on uniaxial stress. Therefore, we argue that liquid-like dynamical charge correlations are important to understand the prominent macroscopic transport properties in underdoped cuprates.
The underdoped cuprates exhibit a number of unusual electronic ordering phenomena, including CDW and pseudogap above the superconducting transition temperature Tc. Specifically, at the hole density per Cu ion of the CuO2 planes close to 0.125 (=1/8), a plateau of Tc appears on the superconducting dome and the charge order was found to be a leading competing order of superconductivity. The CDW transition is usually associated with a resistivity anomaly in classical CDW compounds as a consequence of influences on Fermi surfaces and/or scattering rates of itinerant quasiparticles. In cuprates, however, the resistivity anomaly is seen only at the pseudogap temperature, which is typically much higher than the CDW onset, and there are no indications of CDW.
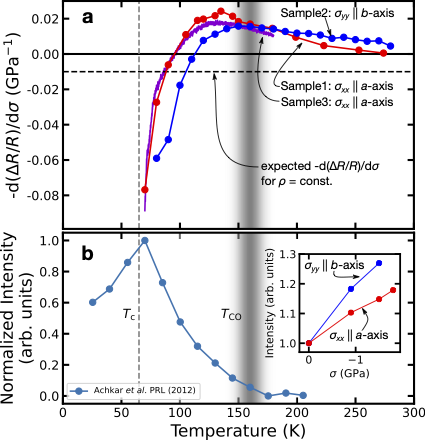
Fig. 1: Comparison of transport and diffraction signatures of charge order. For details, see the article.
Our experimental strategy is to directly investigate the macroscopic charge transport properties of YBCO6.67 under the identical experimental conditions employed in recent x-ray scattering experiments, in which the charge order is strongly amplified by uniaxial stress. We obtained a remarkable correspondence between the stress response of the resistivity and x-ray diffraction signatures of CDW in their in-plane anisotropy and temperature dependence (Fig. 1).
Moreover, the unusual transport behaviors under magnetic fields such as quantum oscillations and Hall effect have been interpreted as a consequence of the Fermi surface reconstruction due to the static charge order. In the present work, we observed that the Hall coefficients, including its sign reversal upon cooling, depend very weakly on uniaxial stress, which strongly enhances charge order. To reconcile this disparity, we discuss possible roles of the dynamical charge correlations recently pointed out by a number of resonant inelastic x-ray scattering experiments on the prominent transport phenomena in underdoped cuprates.
On the experimental front, our study has demonstrated the power of uniaxial stress to obtain the direct comparison between atomic-scale correlation functions and macroscopic transport phenomena of quantum materials.
See more details in https://www.nature.com/articles/s41535-022-00532-9 .
Follow the Topic
-
npj Quantum Materials

An open access journal that publishes works that significantly advance the understanding of quantum materials, including their fundamental properties, fabrication and applications.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Intertwined Orders in Quantum Materials – In Memory of Daniel Khomskii
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 13, 2026
Altermagnetic Materials and Phenomena
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Apr 30, 2026






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in