Performance and water-energy nexus aspects of stagnant water layer cooled zero-tilt solar photovoltaic module
Published in Social Sciences, Earth & Environment, and Electrical & Electronic Engineering

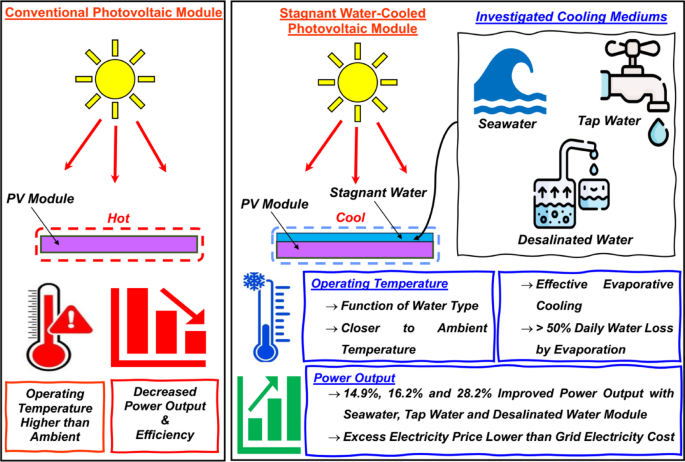
The novelty of this work lies in the simple method adopted by us for cooling the PV module. In earlier studies by various experts, the PV module will be completely immersed in the fluid during immersion cooling to cause reduction in operating temperature. On contrary, in this work, only the top layer of the PV module will be in contact with a stagnant water layer thereby, the costs associated with protection of junction box, support structures for PV float and issues with water quality degradation have been completely eliminated. Moreover, the suitability of thin 1 cm deep seawater, tap water and desalinated water layer for PV module cooling has been reported in detail. Furthermore, the energy-water and economic nexus aspects of this cooling method has also been evaluated in detail, which can be replicated for other similar works too with ease.
We observed many surprising results few are listed below:
- PV module’s operating temperature was closer to the ambient temperature and its energy output was always higher than non-cooled module in all the investigated cases
- Daily average PV module's operating temperature reduction and energy output enhancement was directly dependent on the quality of water used indicating desalinated water to be an effective candidate
- On economic front seawater module outperformed both desalinated and tap water module due to seawater’s abundant availability and no cost (especially in coastal regions)
- No salt deposition was also observed even in seawater module under the weather conditions during summer at Visakhapatnam, India
We have some plans to carry out the research further in this area focusing on impact of water depth, water replacement frequency, module type, module tilt position, dust/slit/salt deposition, microbial growth on module performance, economics, environmental and ecological aspects. In addition, we are also looking to develop a mathematical model to replicate the experimental study in virtual mode. We are looking for collaborations all over the globe to carry forward this work along with us.
If somebody interested can reach me via sharon.mec@iipe.ac.in.
The reported work is one of the minor outcomes of the sanctioned project by the SERB, DST, Government of India (Grant No: SRG/2023/000017) awarded to me (Dr. Sharon Hilarydoss). This funding has helped me to hire a project staff (Mr. Venu Gopal), and an internship student (Mr. Pavan Darbha). I also like to thank my Under Graduate project students namely Mr. Ankit Kumar Jangir, Mr. Hitesh Kumawat and Mr. Aryan Singh, who build this setup as a part of their project work. I thank Prof. Marta Vivar from the University of Jaen, Spain for her advices and support throughout the work. I also thank Ms. Mansi Prasad, internship student who worked hard with us during experiments and paper writing. We thank Springer Nature and Scientific Reports for providing 100% APC waiver for this article.
Follow the Topic
-
Scientific Reports

An open access journal publishing original research from across all areas of the natural sciences, psychology, medicine and engineering.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Reproductive Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 30, 2026
Women’s Health
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
Interesting research.