Pet dogs are willing to work for food, but do not show a preference
Published in Zoology & Veterinary Science
Contrafreeloading refers to the phenomenon that animals will choose to work for food when given the choice between working for their food and similar freely available food (1-3). This behavior has been shown in both domesticated (e.g. pigs (4)) and non-domesticated species (e.g. giraffes (5)).
Recently, a study showed that pet cats do not have a preference to contrafreeload (6). If pet cats do not show this preference, we wanted to find out if dogs, another domesticated companion animal species, show similar behavior to their companion animal counterparts, or to other domesticated species.
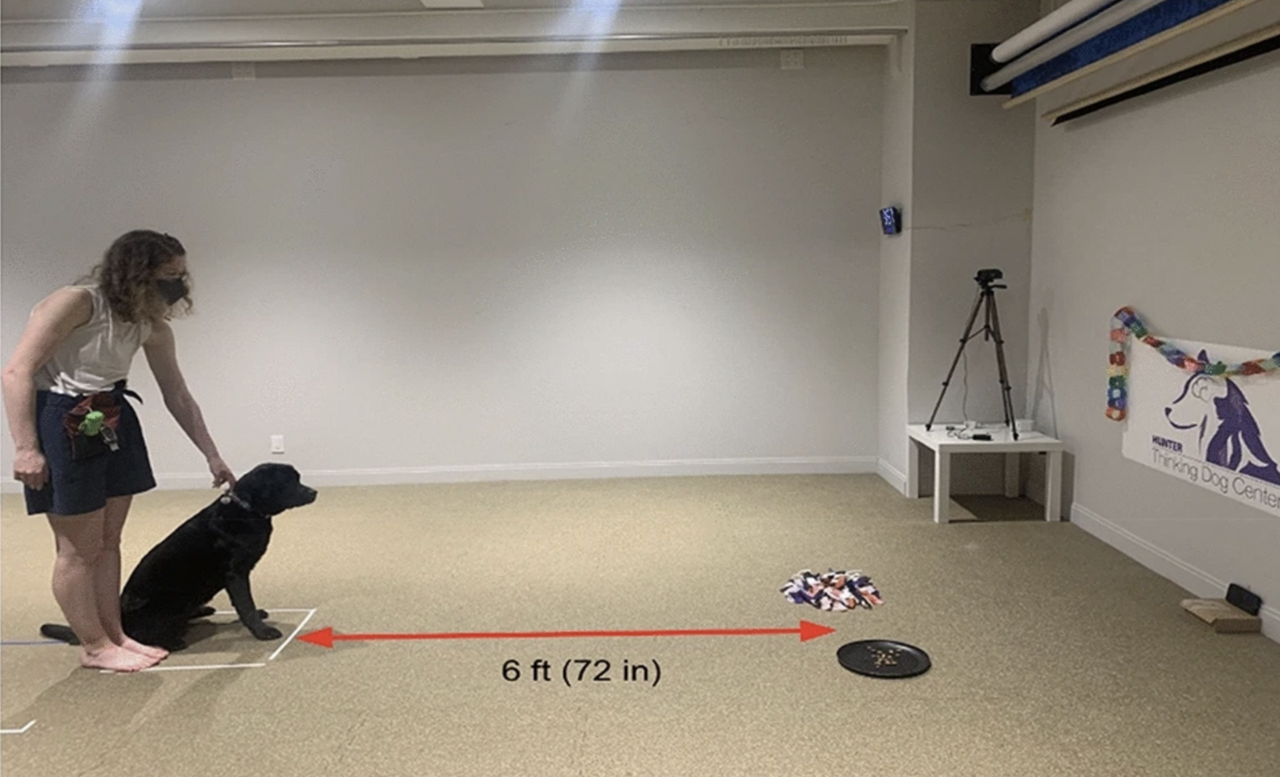
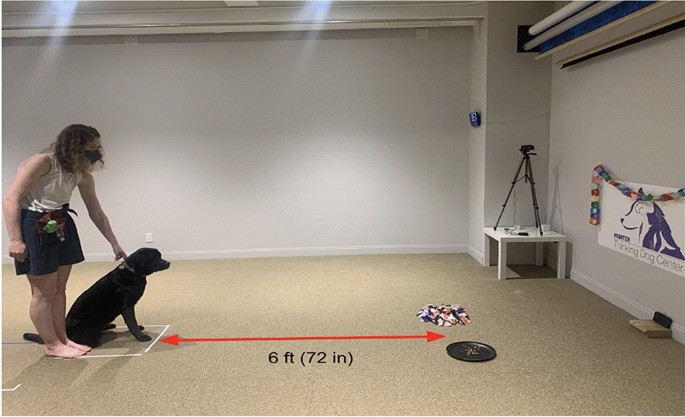
To test this, we adopted a community science approach by providing dog owners with a snuffle mat and a plate and asking them to record their dog's behavior when simultaneously offered both feeding options with identical amounts of food. Due to the applied nature of enrichment in dogs, we thought a community science paradigm would allow owners to have an active involvement in understanding their dog's feeding behavior. Since there is also a link between contrafreeloading and exploratory behavior (7), we provided owners with a Fi Smart Dog Collar (https://tryfi.com/) to track activity levels.
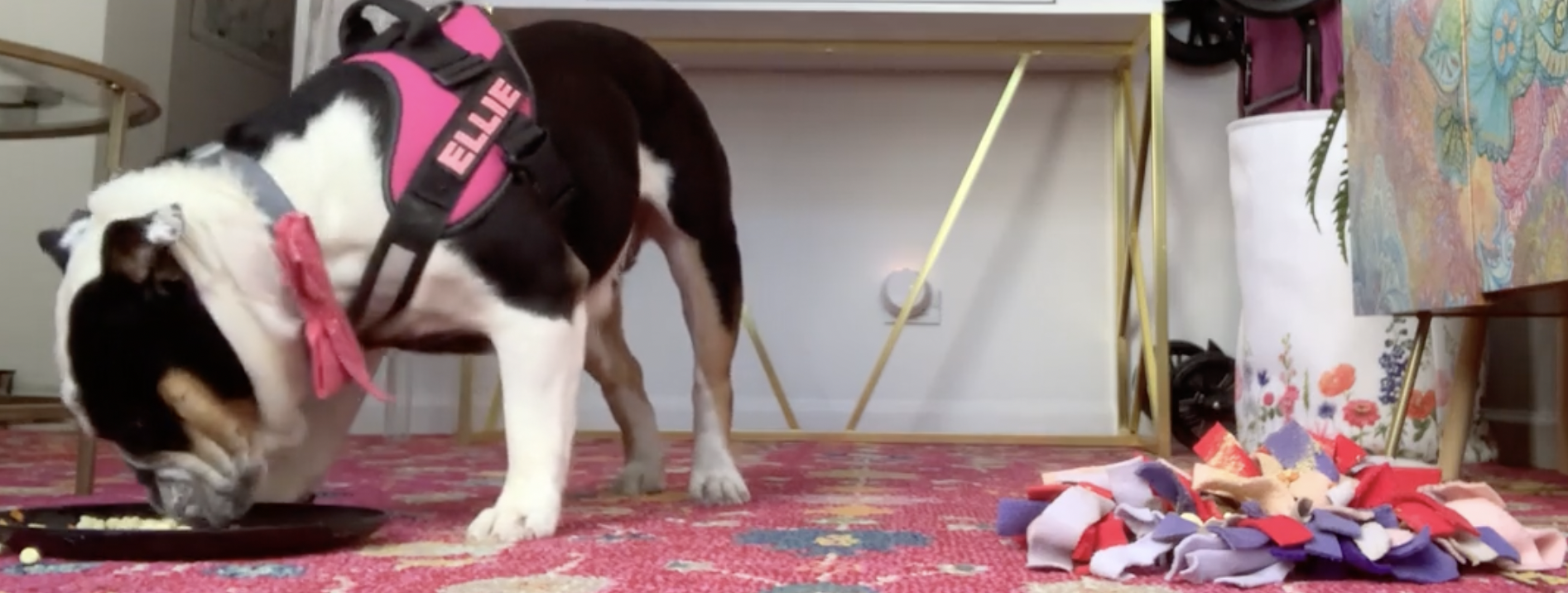

After looking at many options for a snuffle mat, we decided to make our own snuffle mats out of anti-fatigue rubber floor mats. We made this decision based on our desire to have the free food and snuffle mat similar sizes. To make the "snuffle" part of the snuffle mat, we went to the craft store and bought remnants of fleece fabric. We cut the fabric into smaller pieces and wove the fabric through the holes of the fatigue mat to create a feeder that mimics natural foraging behavior.

We invited owners to our lab in Manhattan to meet their dogs and show them how to conduct the study on their own at home. All owners were provided a "goody bag" with all supplies and instructions. As a thank you to the owners, all participants were able to keep the supplies (e.g. snuffle mat, tray and Fi Collar) after the study ended. In order to allow owners to ask us an questions with ease, we created a Facebook group for owners to ask any lingering questions that came up after their lab visit. We also invited owners to introduce their dogs to the group to provide a sense of community.
Once dogs completed the study, owners were sent a certificate of participation. We invited owners to send us photos of their dogs posing with their certificates.
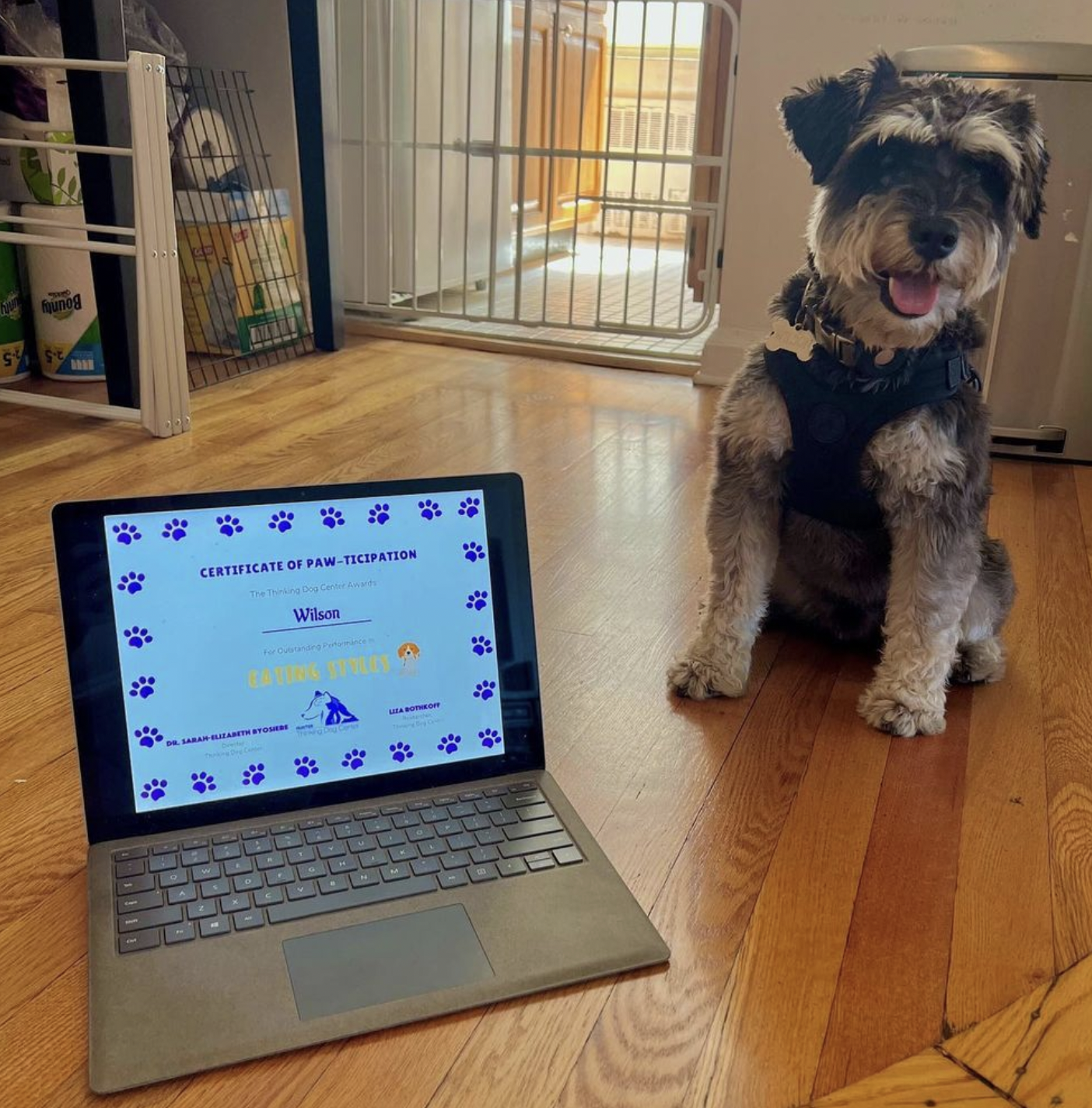

We thank all of the dogs and their owners for their participation!
References
- Inglis, I. R., Forkman, B. & Lazarus, J. Free food or earned food? A review and fuzzy model of contrafreeloading. Anim. Behav. 53, 1171–1191 (1997).
- Jensen, G. D. Preference for bar pressing over ‘freeloading’ as a function of number of rewarded presses. J. Exp. Psychol. 65, 451–454 (1963).
- Osborne, S. R. The free food (contrafreeloading) phenomenon: A review and analysis. Anim. Learn. Behav. 5, 221–235 (1977).
- de Jonge, F. H., Tilly, S.-L., Baars, A. M. & Spruijt, B. M. On the rewarding nature of appetitive feeding behaviour in pigs (Sus scrofa): Do domesticated pigs contrafreeload? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 114, 359–372 (2008).
- Sasson‐Yenor, J. & Powell, D. M. Assessment of contrafreeloading preferences in giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis). Zoo Biol. 38, 414–423 (2019).
- Delgado, M. M., Han, B. S. G. & Bain, M. J. Domestic cats (Felis catus) prefer freely available food over food that requires effort. Anim. Cogn. (2021). doi:10.1007/s10071-021-01530-3
-
Bean, Mason, G. J., & Bateson. Contrafreeloading in starlings: Testing the information hypothesis. Behaviour. 136, 1267–1282 (1999).
Follow the Topic
-
Scientific Reports

An open access journal publishing original research from across all areas of the natural sciences, psychology, medicine and engineering.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Reproductive Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 30, 2026
Women’s Health
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in