T3 Talk2Text - A model for near real-time voice transcription in virtual group meetings
Published in Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Computational Sciences, and Education
The Challenge: Capturing Group Discussions for Reflection
Group projects are a cornerstone of modern education, but remote collaboration introduces challenges like unequal participation, miscommunication, and the difficulty of recalling past discussions. While video conferencing tools facilitate real-time interaction, they lack built-in support for documenting conversations. Manual note-taking is cumbersome, and post-meeting transcriptions from recordings are time-consuming.
We asked: How can we provide students and educators with an effortless way to capture and reflect on group discussions in near real-time?
Introducing T3 Talk2Text
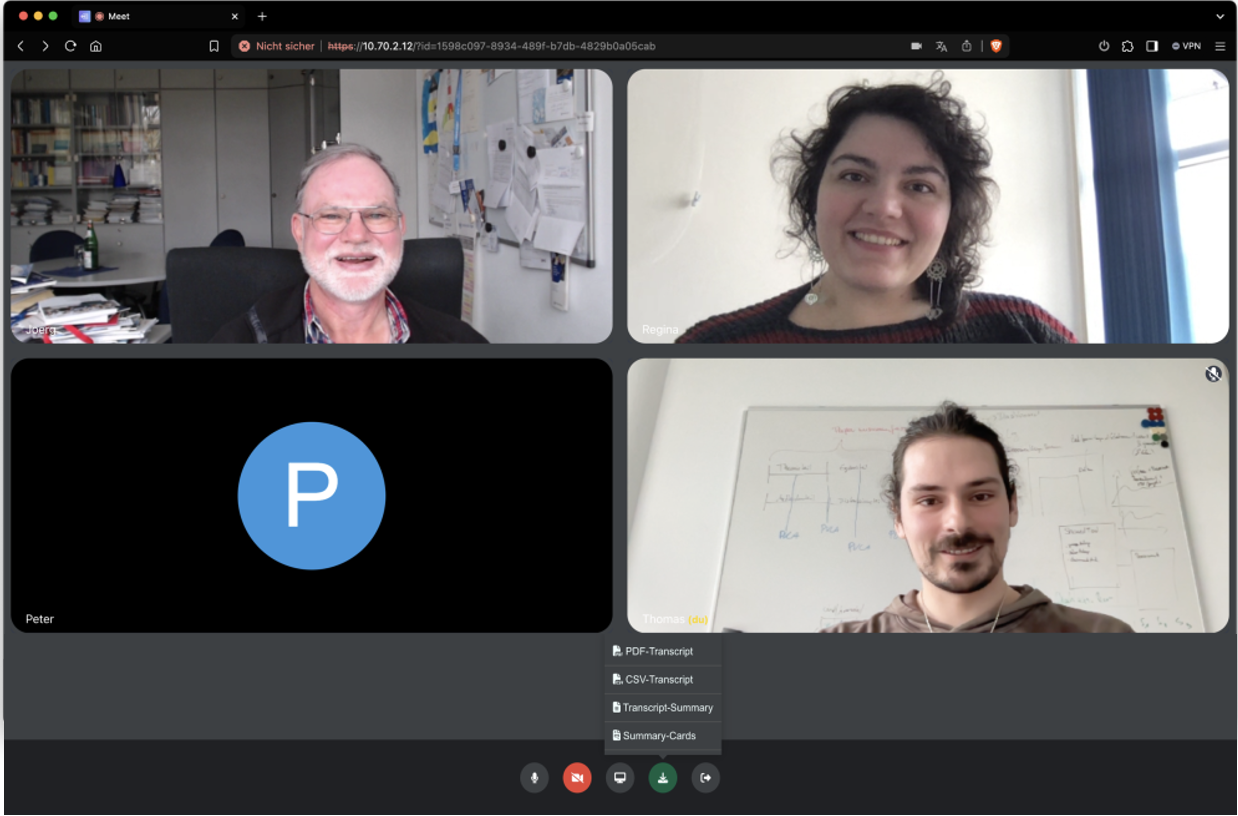
Our solution, T3 Talk2Text, is an open-source web application that integrates:
- WebRTC-based video conferencing (peer-to-peer, no expensive licenses)
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Real-time transcription via OpenAI’s Whisper model
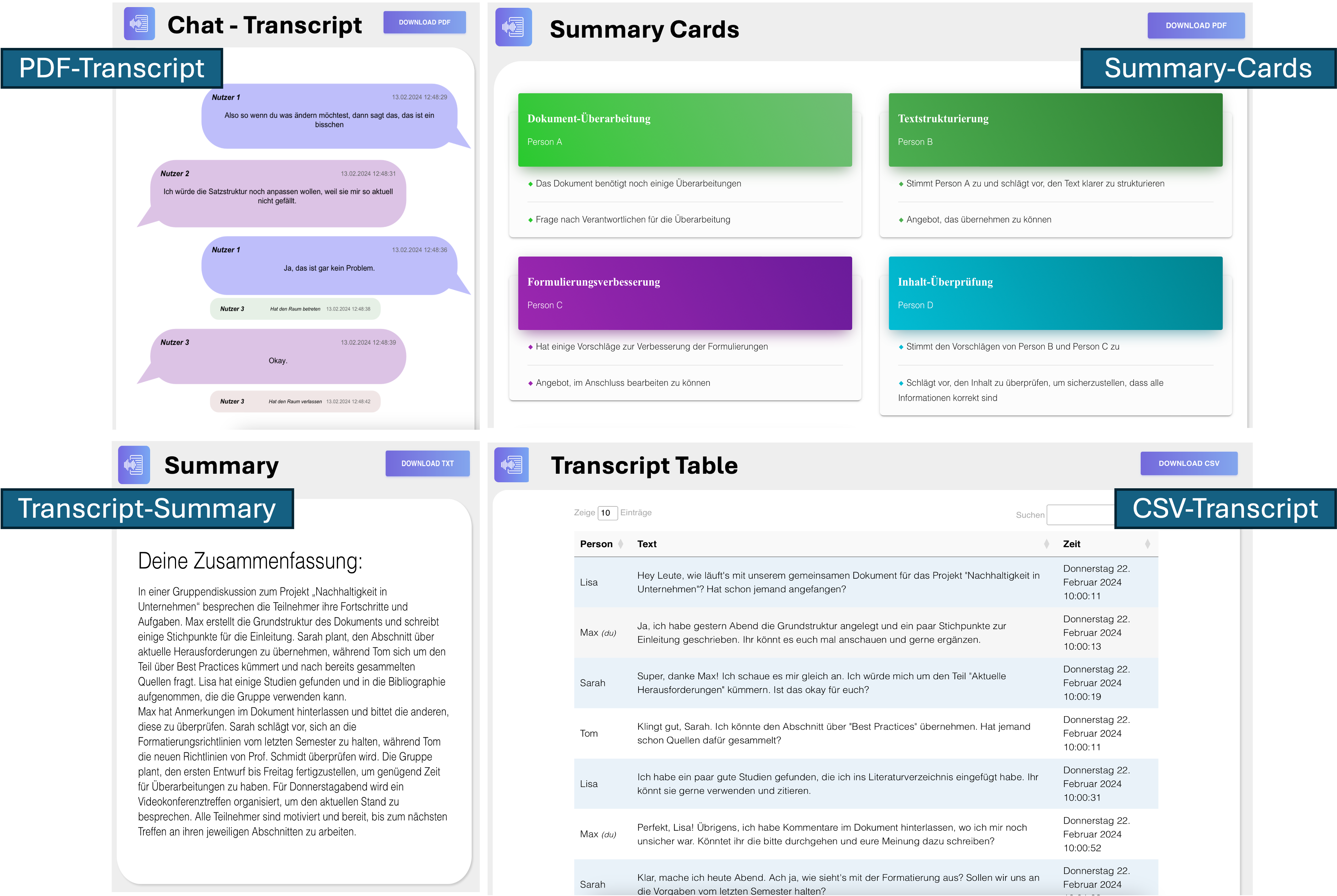
- On-demand summaries (using Llama3 for AI-generated insights)
Unlike commercial tools (e.g., Microsoft Teams), T3 prioritizes privacy (self-hosted), multilingual support, and accessibility (works on any device with a browser).
Key Innovations
-
Voice Activity Detection (VAD) Pipeline
-
Filters background noise and segments speech for accurate ASR input.
-
Achieves 8.04% Word Error Rate (WER) in German—comparable to human transcribers.
-
-
Dynamic Transcript Formats
Users can download transcripts as:-
PDFs (messenger-style, with speaker alignment)
-
CSVs (structured for analysis)
-
AI summaries (condensed key points)
-
-
Scalable Architecture
-
Lightweight SQLite storage for transcripts.
-
Peer-to-peer media streaming reduces server load.
-
Behind the Scenes: Overcoming Technical Hurdles
Challenge 1: Real-Time Processing
WebRTC’s low-latency streams were ideal for video chat but required careful buffering to feed Whisper ASR without delays. Our VAD component ensured only speech segments were processed, optimizing resource use.
Challenge 2: Multilingual Support
Whisper’s multilingual capabilities let T3 adapt to diverse classrooms, though future work will explore fine-tuning for non-native accents.
Challenge 3: Privacy-First Design
All data stays on institutional servers, and temporary audio files are deleted post-transcription, which is critical for GDPR compliance.
Impact and Future Directions
Initial tests with student groups showed T3 seamlessly integrated into discussions without disrupting collaboration. Educators highlighted its potential for:
-
Identifying participation gaps (via speaker-labeled transcripts).
-
Conflict resolution (revisiting past dialogue).
-
Research (analyzing communication patterns across courses).
Next steps include:
-
Deploying Whisper Large Turbo for faster, even more accurate transcriptions.
-
Longitudinal studies in university courses to measure learning outcomes.
Try It Out!
T3 is open-source and available for institutions to adapt. We welcome collaborations to explore its use in classrooms and beyond.
Read the full paper: The Paper
Code repository: Github
Contact: Thomas.Kasakowskij@fernuni-hagen.de
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Education

An international, peer-reviewed open access journal that publishes original work in all areas of education, serving the community as a broad-scope journal for academic trends and future developments in the field.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Empowering Education through AI: Opportunities, Challenges and Risk Governance
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of education as a double-edged sword. On one hand, it holds great promise for empowering teaching, learning, assessment, and educational management by making them more efficient, accurate, adaptive, and responsive. On the other hand, the increasing integration of AI in education elicits significant pedagogical, ethical, social, and policy concerns, such as reduced learner agency, algorithmic control, academic misconduct, and exacerbated educational disparities. Without proper risk governance, the AI technologies intended to empower education may end up disrupting the educational processes and wreaking chaos on educational development. This calls for coordinated efforts from policymakers, researchers, and practitioners worldwide to ensure the legitimate, appropriate, responsible, and ethical use of AI in education.
Against this backdrop, this Collection aims to promote critical inquiry into the intricate and multifaceted features of AI use in education. We particularly welcome interdisciplinary perspectives that explicate how policymakers, researchers, educators, and learners can participate in and collaborate to leverage the transformative power of AI while mitigating the potential risks within different educational scenarios and across diversified cultural contexts. Potential topics include (but are not limited to):
1. Social, ethical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioural terrains of AI use in education
2. Human-AI collaboration in teaching, learning, assessment, and educational management
3. Learner agency, self-regulation, and AI-empowered learning
4. Teacher professional development in AI-empowered education
5. AI literacy for educators and learners
6. Educational equity and academic integrity in the AI era
7. Policy innovation and risk governance for AI use in various educational settings
8. Cross-cultural perspectives on AI use and governance in education
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 4
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence (AI); Human-AI collaboration; AI-empowered education; policy innovation; risk governance; educational equity; academic integrity
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 26, 2026
Empowering Education: Interdisciplinary Convergence and Skill Ecosystem Reconstruction for a Sustainable Future
In an era of unprecedented environmental and societal challenges, education systems must transform to empower students as catalysts for sustainable futures. This Collection advances sustainability education beyond environmental awareness, focusing on developing critical competencies—systems thinking, ethical decision-making, and innovative problem-solving—essential for building resilient societies.
We call for systemic reimagining of education across all levels and disciplines, particularly highlighting:
• Cross-curricular integration of sustainability principles in STEM and vocational training
• Pedagogical innovations that bridge theory-practice gaps
• Industry-education synergies for green skills development
• Digital transformation of sustainability learning
Key Research Domains
Contributions should address critical intersections of sustainability and education, including but not limited to:
• Curriculum innovation for actionable sustainability knowledge
• Evidence-based pedagogical strategies fostering sustainability literacy
• Vocational education redesign for green economy readiness
• Industry partnerships enhancing real-world learning
• Digital technologies (AI, data analytics) in sustainability education
• Assessment frameworks for sustainability competencies
• Teacher professional development models
• Global citizenship and ethical responsibility cultivation
Transformative Objectives
By examining how curricula, teaching strategies, and learning environments can embed sustainability principles, this Special Issue aims to:
• Equip learners with values-driven leadership capabilities
• Develop scalable solutions for environmental, social, and economic challenges
• Catalyze education’s role in achieving global sustainability goals
We invite submissions offering actionable insights and transformative frameworks to prepare students for thriving in a rapidly evolving world.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 31, 2026






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in