Tamogi-take Mushrooms: The secret to a healthy life through delicious food
Published in Biomedical Research
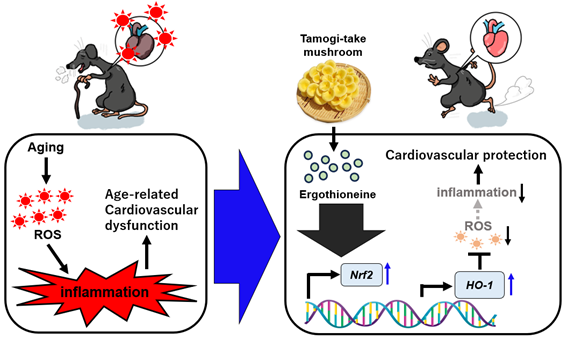
As people age, they often experience a decline in cardiovascular function, reduced vascular flexibility, and diminished exercise tolerance. These changes can significantly impact their ability to maintain an active lifestyle, ultimately affecting overall well-being and quality of life. One of the key contributors to these age-related declines is an increase in oxidative stress, which results from an excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and other oxidative substances. Oxidative stress plays a central role in promoting cellular damage, inflammation, and the progression of aging phenotypes, particularly in the heart and vascular system. Given the growing aging population and the increasing prevalence of age-related cardiovascular diseases, there is a pressing need to identify effective, natural strategies to mitigate these adverse effects and support long-term cardiovascular health.
Tamogi-Take mushrooms (Pleurotus cornucopiae) are a flavorful and highly nutritious variety of mushrooms known for their rich content of ergothioneine (EGT), a naturally occurring antioxidant with strong protective properties. Unlike many other antioxidants, EGT is highly stable under heat, making it an ideal component for inclusion in a variety of meals. Previous studies have highlighted the beneficial effects of EGT on cellular protection against oxidative stress, but our recent research has further demonstrated that continuous intake of Tamogi-Take mushrooms offers significant cardioprotective benefits.
In our recent study, we investigated the effects of long-term Tamogi-Take mushroom consumption in mice, focusing on its impact on oxidative stress, cardiovascular function, and overall exercise capacity. Our findings revealed that regular intake of these mushrooms enhances the production of protective proteins such as NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). These proteins play crucial roles in the body’s defense against oxidative damage by activating antioxidant response pathways and promoting cellular resilience. By upregulating these protective mechanisms, Tamogi-Take mushrooms help safeguard the heart and vascular tissues from age-related deterioration.
Furthermore, our research demonstrated that Tamogi-Take mushroom consumption effectively suppresses the age-related increase in oxidative substances that contribute to chronic inflammation. Inflammation is a key driver of cardiovascular aging, as it exacerbates endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, and myocardial decline. By mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, Tamogi-Take mushrooms help preserve cardiac function and maintain vascular integrity, thereby reducing the risk of age-associated cardiovascular diseases.
Another remarkable finding from our study was the positive impact of Tamogi-Take mushroom intake on exercise tolerance. As people age, their ability to sustain physical activity often declines due to reduced cardiac output and muscle function. However, our research suggests that regular consumption of these mushrooms supports sustained exercise capacity, potentially allowing individuals to maintain an active lifestyle similar to that of their younger years. This effect may be attributed to the combination of antioxidant protection, improved vascular function, and reduced inflammation, all of which contribute to enhanced cardiovascular performance.
From a practical perspective, incorporating Tamogi-Take mushrooms into daily meals is both simple and enjoyable. These mushrooms can be easily added to soups, stir-fries, noodles, and various other dishes, providing a convenient and delicious way to obtain their health benefits. Their mild yet distinctive flavor makes them a versatile ingredient that can complement a wide range of culinary styles.
With the increasing recognition of the importance of dietary interventions in promoting longevity and cardiovascular health, Tamogi-Take mushrooms stand out as a promising natural option. Their ability to modulate oxidative stress, enhance protective protein expression, and maintain cardiovascular function makes them a valuable addition to a heart-healthy diet. Given the strong scientific evidence supporting their benefits, incorporating Tamogi-Take mushrooms into daily nutrition may be a simple yet effective strategy to promote healthy aging and improve overall well-being.
As research continues to uncover the vast potential of functional foods in extending healthspan, Tamogi-Take mushrooms emerge as a particularly compelling option. Whether you are looking to support cardiovascular function, reduce oxidative stress, or simply enhance your diet with a nutritious and flavorful ingredient, these mushrooms offer a powerful yet natural solution. Why not explore the benefits of Tamogi-Take mushrooms and experience their positive impact on health for yourself?
For further information, please refer to our publication:
Sato, M., Torigoe, D., Oike Y, et al. Long-term intake of Tamogi-take mushroom (Pleurotus cornucopiae) mitigates age-related cardiovascular dysfunction and extends healthy life expectancy. npj Aging 11, 1 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41514-024-00191-z
Follow the Topic
-
npj Aging

The mission of this journal is to provide the community with a platform to publish new high-profile insights into all aspects of aging.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Healthy eating and dietary intervention to promote longevity and prevent age-related diseases
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 09, 2026
Sex Differences in Aging Research
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Sep 21, 2026





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in