Unseen Challenges: The Human Stories Behind Waste Management in Shaggar City
Published in Earth & Environment
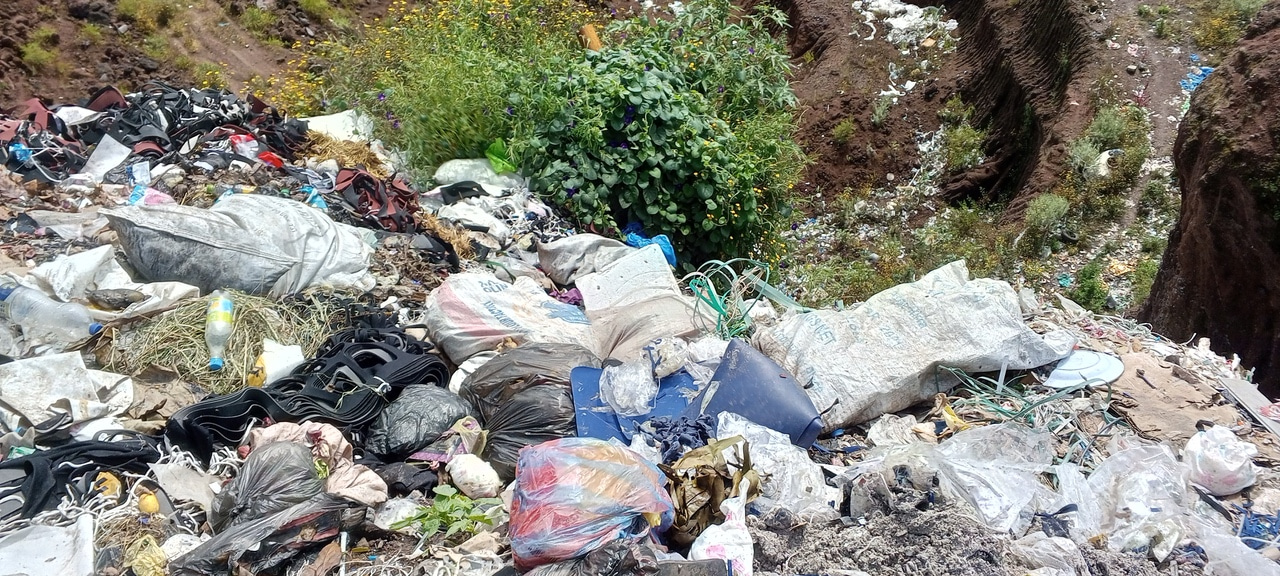

In exploring waste management practices in Shaggar City, Ethiopia, the research shed light on a critical yet underreported issue: the daily struggles and resilience of local communities facing the consequences of inadequate waste management.
The stark reality of waste management in Shaggar City, where communities struggle alongside mounting refuse.
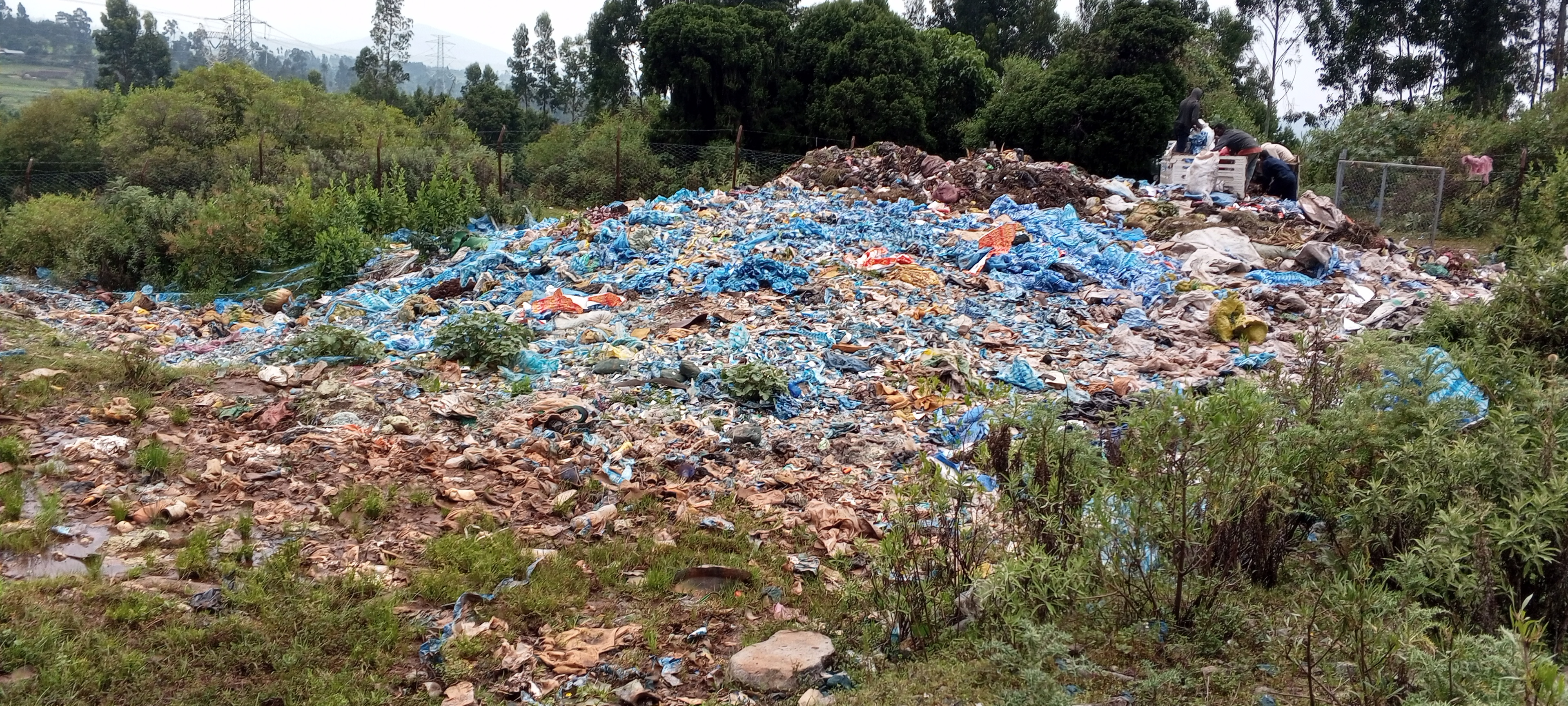

The research, “Waste Management Practices and Perceptions among Firms and Communities in Shaggar City, Ethiopia,” reveals a troubling reality: waste treatment and disposal practices are woefully inadequate, leading to severe environmental and public health challenges.
Residents living near massive landfills or disposal sites face ignored challenges. Just beyond the farmer's home, a chaotic mix of decomposing organic matter and discarded plastics forms a toxic environment. Each day, they navigate this challenging landscape, ensuring their children stay away from hazardous materials while yearning for a better future.
Many community members resist confronting the environmental health risks that permeate their lives due to the glaring lack of awareness and resources. Extensive open dumping and improper waste disposal practices exacerbate these risks, leading to respiratory illnesses and waterborne diseases among vulnerable populations.
Through interviews with community leaders and government officials, researchers learned that many local folks are either uninformed about the dangers of industrial waste or excluded from conversations about waste management practices. Local industries often distance themselves from the communities they affect, prioritizing production over environmental responsibility. Our findings revealed that approximately 72.7% of surveyed firms cited a lack of collaboration as a significant barrier to implementing sustainable waste practices. For many, waste management is not just an environmental issue; it's a daily struggle for survival.
Notably, our study indicates that while 63.7% of firms engaged in innovative practices, many do not perceive their innovations as environmentally impactful. Collaboration between industries and communities is crucial. By fostering partnerships, industries can better understand community concerns and the environmental responsibilities they owe to their neighbors.
The environmental protection authority needs to focus on creating multistakeholder partnerships. Bringing together firms, community representatives, and governmental bodies can bridge the gap that exacerbates waste management issues and enhance overall environmental performance.
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Environment

This is a transdisciplinary, open-access journal that provides a leading platform for the rapid dissemination of knowledge and advances covering the research and innovation that is taking place across the environmental sector.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Environmental Pollutants: Origins, Pathways, Impacts, and Sustainable Solutions
Pollution is a critical threat to ecosystems, human health, and the planet’s future. From industrial waste in China to microplastics in the Mediterranean and PFAS contamination in the U.S., pollutants spread across air, water, and soil, harming wildlife and communities worldwide. Understanding how these contaminants move, transform, and impact the environment is key to designing effective solutions.
This collection brings together cutting-edge research on pollution sources, environmental behavior, risks, and innovative cleanup strategies—covering everything from heavy metals in mining regions to pharmaceutical waste in urban waterways. We highlight advances in environmental science, green technology, and policy to tackle both long-standing and emerging threats like e-waste and AI-driven monitoring. The topics include, but are not limited to, the following:
• Pollution Origins: Industrial, agricultural, and urban sources, including legacy and emerging contaminants.
• Environmental Pathways: How pollutants travel through air, water, soil, and food chains.
• Risks and Impacts: Effects on biodiversity and human health, from local hotspots to global crises.
• Cleanup and Prevention: Nature-based solutions (like wetland restoration) and high-tech innovations (such as catalytic oxidation).
• Policy and Tools: Smart regulations, predictive modeling, and new detection methods.
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to: SDG 11
Keywords:PFAS, Heavy metals, Microplastics, Emerging Contaminants, Emission sources, Environmental forensics, Ecological indicators, Pollution sources, Contaminant transport, Ecological risk assessment, Pollutant fate and transformation, Bioaccumulation, Ecological restoration, Remediation technologies, Sustainable pollution management
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 01, 2026
Socio-ecological Systems and Climate Resilience
Climate change poses a significant threat to both biophysical systems and societal communities. Climate resilience is embedded within socio-ecological systems (SES), where social actors and the ecological units they manage are interdependent as part of their livelihoods. Achieving climate resilience requires adjustments to social structures, political and economic systems, power dynamics, worldviews, cultures, values, and ideologies in order to create a sustainable, climate-resilient society. Additionally, there is a need to bridge emerging technology (e.g., AI) with social innovation to enhance the capacity for real-time, data-driven decision-making, foster community-resilient responses to climate impacts, and ultimately reshape climate adaptation policies and practices.
The Collection invites the submission of interdisciplinary and policy-oriented research with innovative systems approaches and emerging methodologies for decision-making and co-designing climate solutions. We encourage contributions from a wide range of fields, including environmental science, sociology, human geography, environmental economics, environmental public health and public policy, etc. We seek research that focuses on the interconnectedness between human societies and natural ecological systems, the impacts of climate change on human well-being, community adaptive capacity, innovative governance solutions, knowledge co-production (with an emphasis on local and indigenous knowledge for climate adaptation), climate equity, local and global collaboration efforts, and the role of technology and education in enhancing climate resilience.
Manuscripts presenting empirical studies, theoretical frameworks, policy analysis, and case studies that contribute both to theoretical advancements and practical applications are encouraged.
Keywords:Socio-Ecological Resilience, Climate Governance, Technological And Social Innovation, Indigenous Knowledge Systems, Sustainability Transition, Human And Ecological Well-Being
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in