Advanced Nanomedicines for Treating Refractory Inflammation‑Related Diseases
Published in Materials and Biomedical Research
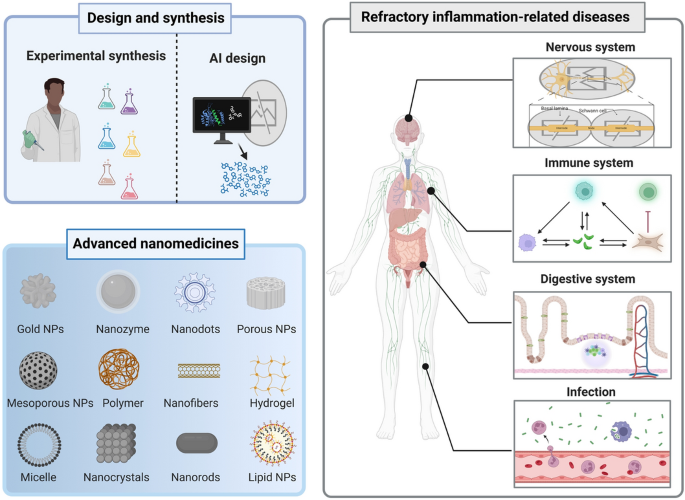
As chronic inflammation underlies diabetes, neuro-degeneration, cardiovascular failure and even cancer, the limits of small-molecule anti-inflammatories become ever clearer. Now researchers from Naval Medical University & Shanghai University, led by Prof. Yu Chen, Prof. Jishun Yang and Prof. Meiqi Chang, have delivered a 55-page roadmap on “smart” nanomedicines that scavenge ROS, re-programme immunity and restore tissue homeostasis. The work, published in Nano-Micro Letters, outlines design rules, AI-assisted screening and scalable synthesis that could fast-track next-generation anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Why Advanced Nanomedicines Matter
- ROS Precision Control:Nanozymes, metallic & carbon NPs switch between •OH generation for anti-infection and instant H2O2/O2− scavenging to protect neurons or cardiomyocytes.
- Multi-Modal Targeting:Stimuli-responsive coatings (pH, enzyme, NIR, US) + cell-membrane camouflage guide drugs to inflamed colon, arthritic joint or ischaemic brain while sparing healthy tissue.
- Manufacturing Ready:Green biosynthesis, self-assembly and high-throughput AI/ML pipelines cut cost > 50 % vs conventional liposomes and are compatible with GMP-grade microfluidics.
Innovative Design and Features
- Hard Nanomaterials: CeO2, MnOx, Cu–Pt and Prussian-blue nanozymes exhibit SOD/CAT/POD/GPx-like cascades; 2-D MXenes deliver 59 % photothermal conversion for on-demand ROS modulation.
- Soft Nanomaterials: PLGA-PEG polymersomes, exosomes and nanocellulose provide elasticity < 20 MPa, ECM-mimetic fibres and renal-clearable 25 nm carriers that cross the BBB or cartilage barrier.
- Computational Nanomedicine: Energy-level & adsorption-energy principles allow 10 000-fold virtual screening of MOF, MOFene and single-atom libraries; ML-PBPK models predict tumour or plaque delivery within 2-fold of in-vivo values.
- Safety Toolkit: Multi-scale tox schemes (C. elegans → zebrafish → human organoids/organ-on-chip) plus high-content imaging define safe dose windows and guide surface de-charge strategies.
Applications and Future Outlook
- Wound & Infection: Ag-ZnO, GO-PEI/NO and Pt@V2C nanoplatforms eradicate MRSA biofilms and accelerate diabetic wound closure in 8 days versus 14 days for standard care.
- IBD & Arthritis: Oral YMD@MPDA (yeast-cell-wall/ROS-scavenging) and intra-articular PtCuOx/CeO2 nanozymes suppress NF-κB, M1→M2 switch and protect cartilage in DSS-colitis and OA models.
- Neuro-inflammation: MSC-magnetite, Q@CeBG and 2-D V2C ensembles cut infarct volume by 60 % in stroke, improve AD memory scores and are translatable via intranasal or focused-US delivery.
- Challenges and Opportunities: Key hurdles remain—batch-to-batch membrane-protein fidelity of biomimetic cloaks, long-term biodegradation of metal oxides, and harmonised regulatory tox assays. Future work will integrate closed-loop AI optimisation, large-animal GLP studies and point-of-care nanozyme diagnostics to accelerate clinical translation.
This comprehensive review provides a blueprint linking material innovation, computational design and multi-organ disease biology to create safe, potent and cost-effective anti-inflammatory nanotherapies.
Stay tuned for more breakthroughs from Professor Chen’s and Professor Yang’s teams at Shanghai University and Naval Medical Center!
Follow the Topic
-
Nano-Micro Letters

Nano-Micro Letters is a peer-reviewed, international, interdisciplinary and open-access journal that focus on science, experiments, engineering, technologies and applications of nano- or microscale structure and system in physics, chemistry, biology, material science, and pharmacy.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in