Advancing prostate cancer research with blood-based biomarkers
Published in Cancer and General & Internal Medicine
Metastatic prostate cancer (PCa) is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates 1. The response of metastatic PCa to the standard treatment options, such as androgen-deprivation therapy or metastasis-directed radiotherapy, is highly diverse, and more efficient tests are urgently warranted for predicting cancer spread and the response of PCa metastases to the treatment 2.
TGF-β1 plays a central role in PCa bone metastasis by promoting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), regulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, and modulating interactions within the bone microenvironment, thereby facilitating tumor cell colonization and survival. Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) enzymes, crucial for cellular detoxification and cancer stem cell regulation, produce retinoic acid (RA) isomers that activate RAR and RXR nuclear receptors, triggering transcription of retinoid-responsive genes 3. TGF-β1 pathway regulates ALDH gene expression and cancer stem cell population 4, whereas RA interacts with TGF-β1 signaling in various cancers, suggesting a complex interplay between retinoid and TGF-β1 pathways 5.
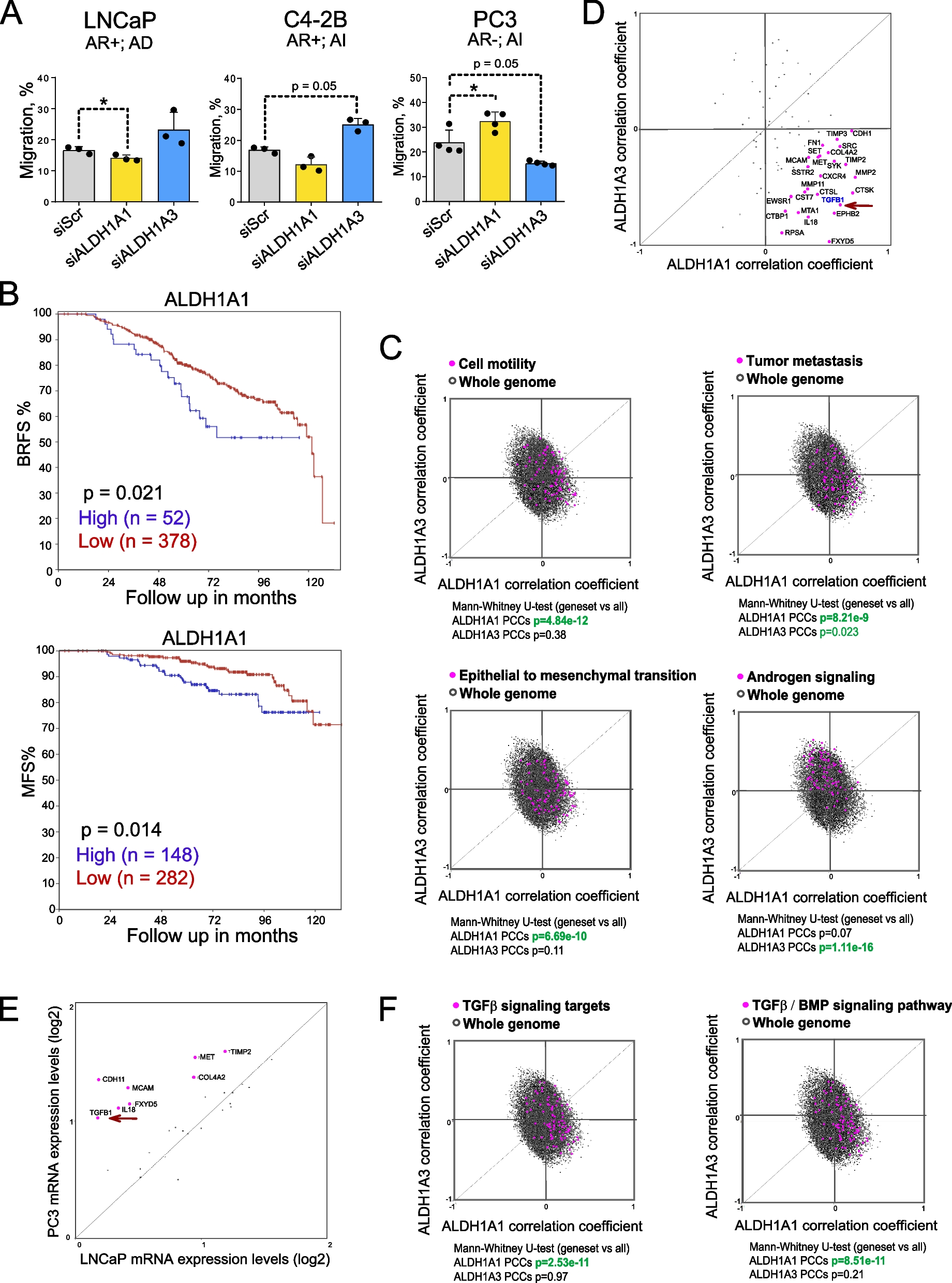
Our study showed that ALDH1A1 and ALDH1A3, the main isoforms contributing to the ALDH activity in PCa cells, differentially regulate cell migration and TGFB1 expression depending on androgen receptor (AR) status. ALDH1A1 positively correlates with TGFB1 expression and promotes migration in androgen-sensitive cells, while ALDH1A3 has an opposing effect. Both ALDH genes regulate TGFB1 gene transcription through the RA-dependent mechanism. TGF-β1 pathway further contributes to the regulation of the MMP11 expression, which is associated with poor clinical outcomes in PCa. Genetic silencing of MMP11 increases tumor cell radiosensitivity, suggesting its role in therapy resistance. Indeed, MMP11 blood plasma levels had a significant association with PSA increase in patients with oligometastatic PCa treated with external beam radiotherapy. Moreover, plasma levels of MMP11 were significantly higher in patients with metastatic PCa compared to those with localized disease. MMP11 demonstrated potential as a blood-based biomarker for metastases, with high specificity (0.93) and sensitivity (0.9). Proteomic profiling identified an ALDH1A1/MMP11-related plasma proteome signature, which correlated with clinical outcomes (Figure 1).
Taken together, the study highlights the interplay between ALDH genes, TGF-β1, and MMP11 in PCa progression and metastasis. ALDH1A1-driven RA signaling promotes TGFB1 expression, which in turn regulates MMP11, contributing to metastatic dissemination and therapy resistance. Plasma MMP11 levels emerged as a promising prognostic biomarker for metastatic PCa. Our research marks a significant step in understanding PCa progression and highlights the potential of blood-based biomarkers like MMP11 for early detection of metastatic disease and personalized treatment strategies.
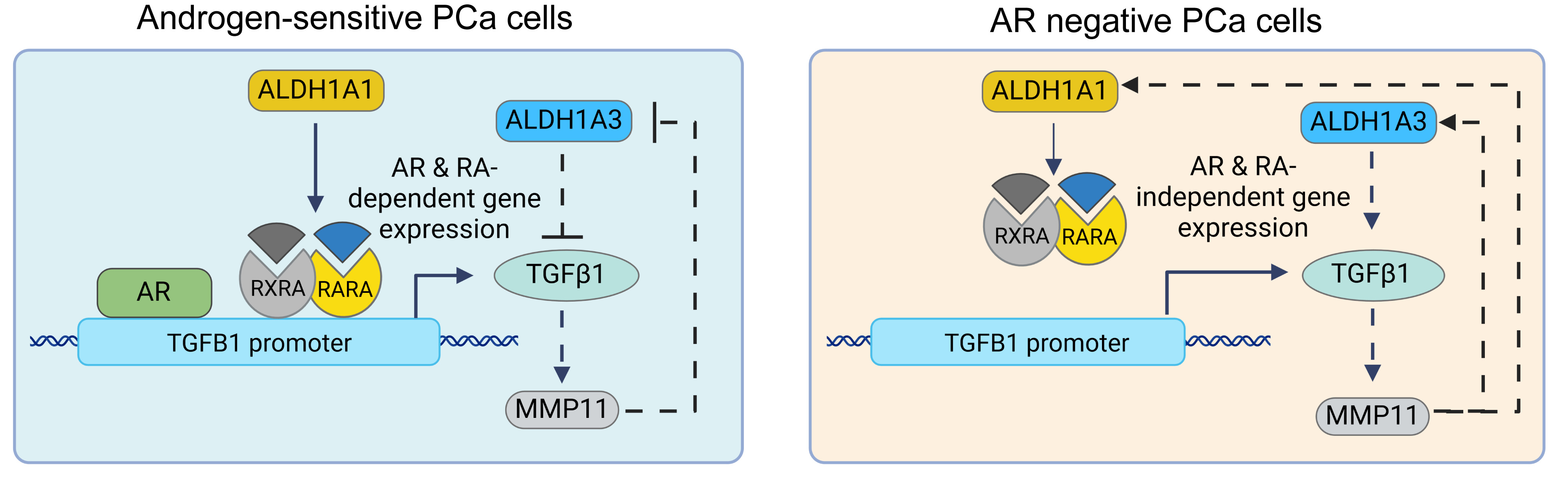
Figure 1. ALDH1A1 regulates TGFB1 expression in androgen-sensitive cells through AR- and RA-dependent mechanisms. In contrast, the interplay between TGF-β1 and MMP11 is present in the androgen-sensitive and castration-resistant models of PCa.

Lead authors of the study (from left to right): Anna Dubrovska, Ielizaveta Gorodetska.
References:
- Katzenwadel, A., and Wolf, P. (2015). Androgen deprivation of prostate cancer: Leading to a therapeutic dead end. Cancer Letters 367, 12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.021.
- Bubendorf, L., Schöpfer, A., Wagner, U., Sauter, G., Moch, H., Willi, N., Gasser, T.C., and Mihatsch, M.J. (2000). Metastatic patterns of prostate cancer: an autopsy study of 1,589 patients. Hum Pathol 31, 578–583. https://doi.org/10.1053/hp.2000.6698.
- Gorodetska, I., Offermann, A., Püschel, J., Lukiyanchuk, V., Gaete, D., Kurzyukova, A., Freytag, V., Haider, M.-T., Fjeldbo, C.S., Di Gaetano, S., et al. (2024). ALDH1A1 drives prostate cancer metastases and radioresistance by interplay with AR- and RAR-dependent transcription. Theranostics 14, 714–737. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.88057.
- Bellomo, C., Caja, L., and Moustakas, A. (2016). Transforming growth factor β as regulator of cancer stemness and metastasis. Br J Cancer 115, 761–769. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.255.
- Ni, X., Hu, G., and Cai, X. (2019). The success and the challenge of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of cancer. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59, S71–S80. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1509201.
Follow the Topic
-
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research

Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research is an online peer-reviewed journal that publishes original research papers, reviews and commentaries in cancer research, from bench to bedside.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Breaking cancer DRUG RESISTANCE: Looking for an interdisciplinary effort solving an unmet clinical need in oncology
All submissions in this collection undergo the journal’s standard peer review process.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Apr 30, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in