An end-to-end workflow to study newly synthesized mRNA following rapid protein depletion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Published in Chemistry, Protocols & Methods, and Cell & Molecular Biology
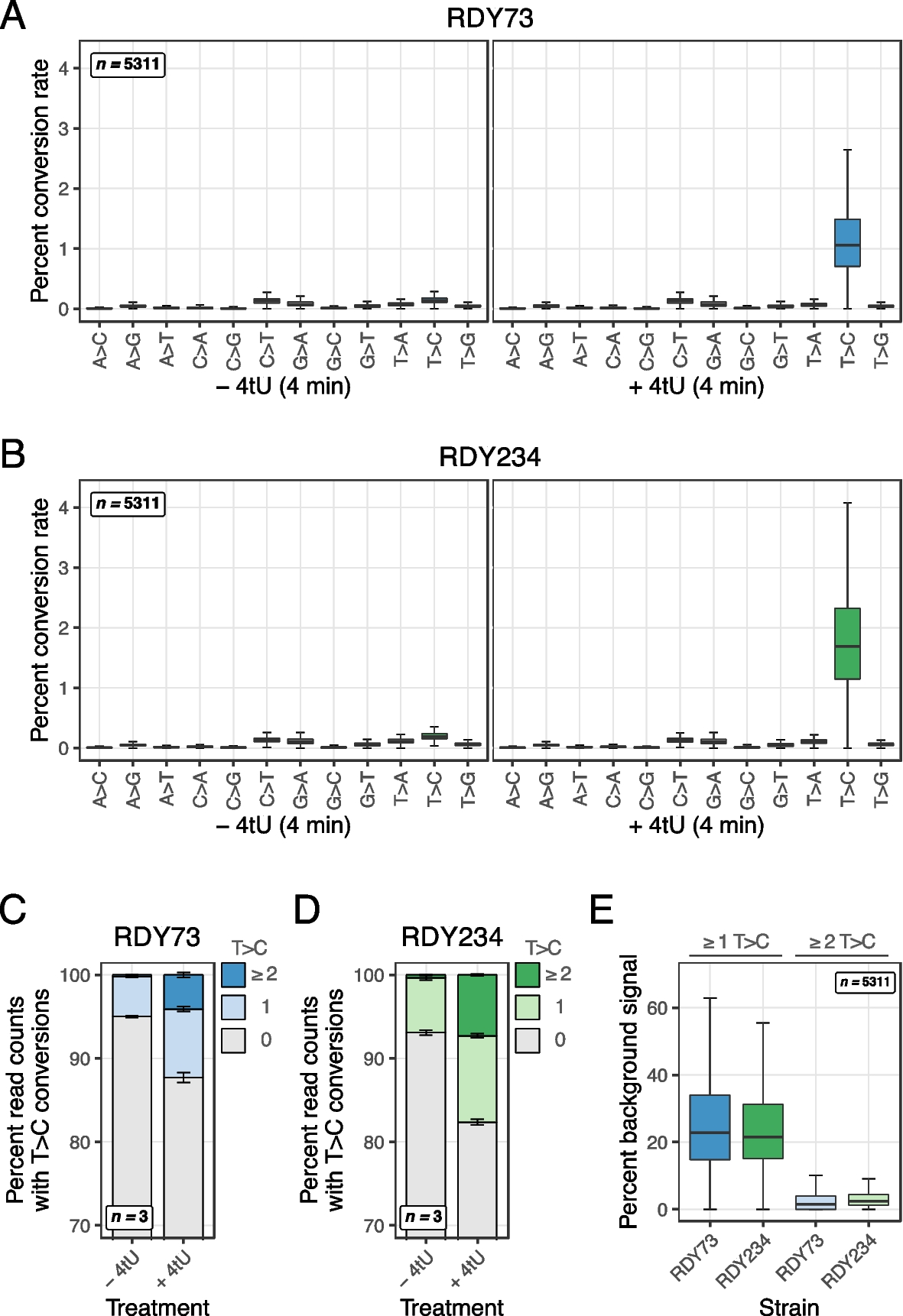
Join Gabriel Gasque, Head of Outreach at protocols.io, as he interviews John Ridenour and Rafal Donczew, the authors of a recently published protocol in BMC Methods, presenting an end-to-end workflow to deplete proteins of interest and measure newly synthesized RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Get ready for exclusive insights, behind-the-scenes secrets, and a glimpse into the future of their innovative work.
Follow the Topic
-
BMC Methods

An open-access, peer-reviewed journal that focuses on publishing lab protocols and methodology papers in the natural sciences; including biology, chemistry, physics, computational and biomedical sciences.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Enzyme engineering
Enzyme engineering is the process of customizing enzymes to improve characteristics by altering or modifying their amino acid sequences. The general approaches in enzyme engineering include directed evolution, rational and semi-rational design, DNA shuffling, structure base design, random mutagenesis, and cell surface display.
Recent advances have demonstrated that engineered enzymes can be applied across a wide range of sectors—including healthcare, food and agriculture, environmental management, renewable fuels, and pharmaceuticals—as efficient and selective biological catalysts.
Emerging technologies such as machine learning-assisted enzyme modeling, high-throughput screening, and the development of novel biocatalytic pathways are also accelerating progress in the field. These innovations are enabling more sustainable and precise approaches in both research and application.
Ongoing research in enzyme engineering holds the promise of discovering entirely new biocatalysts while fine-tuning existing ones for highly specific tasks. As enzyme engineering continues to evolve through interdisciplinary collaboration, the future points toward the development of tailored enzymes for specialized applications across health, industry, agriculture, and environmental management.
Topics of interest for this Collection include:
Advances in directed evolution techniques
Engineered enzymes in medical and diagnostic applications
Enzyme applications in food and agricultural systems
Biocatalysis for pharmaceutical synthesis
Sustainable practices and green chemistry through enzyme engineering
Enzyme innovations in waste valorization and environmental management
Applications of engineered enzymes in biofuels and renewable energy
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Apr 23, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in