Chitosan-based nanomaterials for removal of water pollutants
Published in Chemistry
Explore the Research
 sciencedirect.com
sciencedirect.com
Just a moment...
Skip to main content
Introduction
Water pollution is an escalating global issue, particularly the contamination by heavy metals, dyes, and other harmful substances. Chitosan-based hybrid nanomaterials are emerging as a sustainable, cost-effective solution to address these challenges. This chapter delves into the application of these nanomaterials for the removal of water pollutants, exploring their potential, advantages, and the science behind their effectiveness.
The Science Behind Chitosan
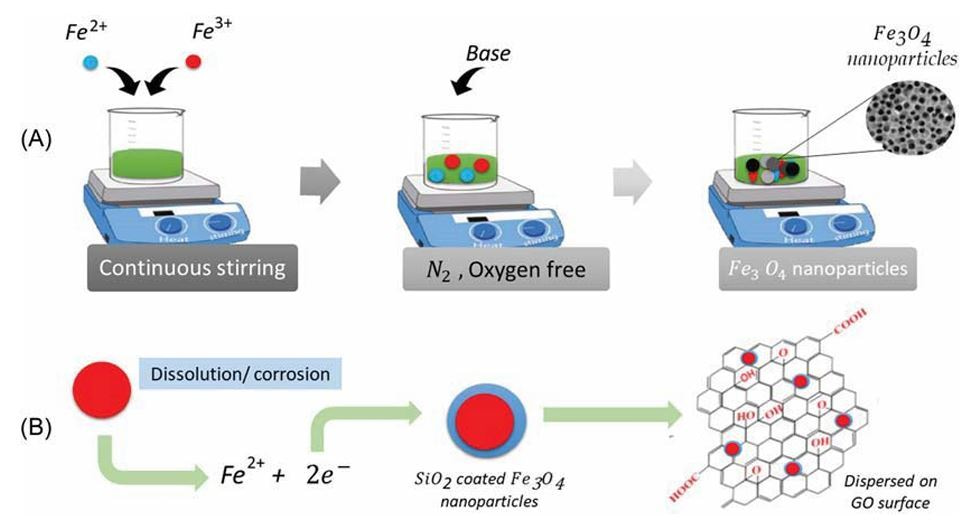
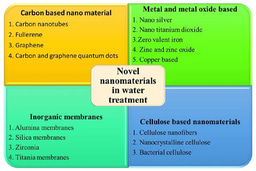
Chitosan, derived from chitin, is a biopolymer that has gained attention due to its biodegradability, biocompatibility, and versatility. Chitosan’s natural properties, including its ability to bind with pollutants like heavy metals and organic compounds, make it an ideal candidate for water treatment applications. The modification of chitosan by combining it with other nanomaterials, such as graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes, and magnetic particles, enhances its adsorption capacity, stability, and functionality.
Key Applications of Chitosan-Based Hybrid Nanomaterials
-
Heavy Metal Removal
Chitosan-based nanomaterials are highly effective in removing toxic metals like lead, cadmium, and arsenic from water. Their ability to form strong bonds with metal ions allows them to adsorb these contaminants efficiently. The modifications introduced into chitosan-based hybrids improve their surface area and chemical reactivity, further enhancing the removal process. -
Dye and Organic Pollutant Removal
Synthetic dyes used in textiles and other industries are a significant source of water pollution. Chitosan-based hybrid nanomaterials can adsorb a wide range of organic pollutants, including dyes and pharmaceutical residues. By modifying chitosan with nanoparticles like silver or activated carbon, the adsorption efficiency is significantly increased. -
Magnetic Nanomaterials for Easier Recovery
Magnetic chitosan composites are gaining popularity due to their ease of recovery from water. These materials can be easily separated from contaminated water using a magnetic field, making them highly efficient and reusable. This approach not only offers a solution to water pollution but also contributes to the sustainability of the material. -
Environmental Benefits
One of the most significant advantages of using chitosan-based nanomaterials is their eco-friendliness. Unlike conventional chemical treatments, these nanomaterials are biodegradable and non-toxic, ensuring that they do not pose a risk to the environment after use. The development of such green technologies is essential for long-term environmental sustainability.
Challenges and Future Directions
While chitosan-based hybrid nanomaterials hold significant promise, there are challenges that need to be addressed. The efficiency of these materials can vary depending on factors such as the type of pollutant, environmental conditions, and the degree of chitosan modification. Further research is needed to optimize their performance, reduce production costs, and explore large-scale applications.
What’s Next?
The potential of chitosan-based nanomaterials in water treatment is vast, but there is still much to discover. Researchers are exploring new methods to enhance the material's properties, making them more effective for industrial-scale applications. The continued development of chitosan-based hybrids could lead to groundbreaking advancements in environmental remediation.
What are your thoughts on the future of chitosan-based nanomaterials for water treatment? How do you think we can improve these materials to tackle emerging water pollution challenges?
Let’s continue the conversation and explore how we can leverage these innovative solutions to address global water pollution.
Read the full chapter here: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-21891-0.00016-0
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
Excited to share our chapter on chitosan-based nanomaterials for the removal of water pollutants! 🌍💧 In this work, we explore how hybrid chitosan composites can effectively tackle contaminants like heavy metals and dyes—offering a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for water treatment. We delve into advancements like magnetic recovery, enhanced adsorption capacity, and real-world applications. Looking forward to your thoughts and discussions on how we can further innovate in green water remediation!
📘 Read more: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-21891-0.00016-0