MicroRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases: from molecular mechanisms to clinical biomarkers, detection methods and therapeutic strategies—advances and challenges
Published in Neuroscience, Cell & Molecular Biology, and Biomedical Research
From Molecules to Medicine: How MicroRNAs Could Transform Neurodegenerative Disease Diagnosis and Therapy
Published: October 06, 2025
🔗 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-025-08419-w
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are among the most challenging medical conditions of our time. Despite decades of research, most patients are still diagnosed only after irreversible neuronal loss has occurred. Early and accurate detection remains the key to effective intervention but current diagnostic tools, such as imaging and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests, are expensive, invasive, and not suitable for large-scale screening.
In our recent review published in Neurological Sciences, we explored an emerging solution that may change this landscape: microRNAs (miRNAs); small, noncoding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression and reflect the molecular state of cells and tissues.
Click Here to Access full Article
Why MicroRNAs Matter
MiRNAs act as fine-tuners of gene networks involved in synaptic function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis, all of which play central roles in neurodegeneration.
Their remarkable stability in biofluids such as blood, plasma, serum, and CSF makes them promising non-invasive biomarkers. More than 2,600 human miRNAs have been identified, collectively influencing over half of all protein-coding genes, a scale that underlines their diagnostic and therapeutic potential.
Mapping the Path from Mechanism to Clinic
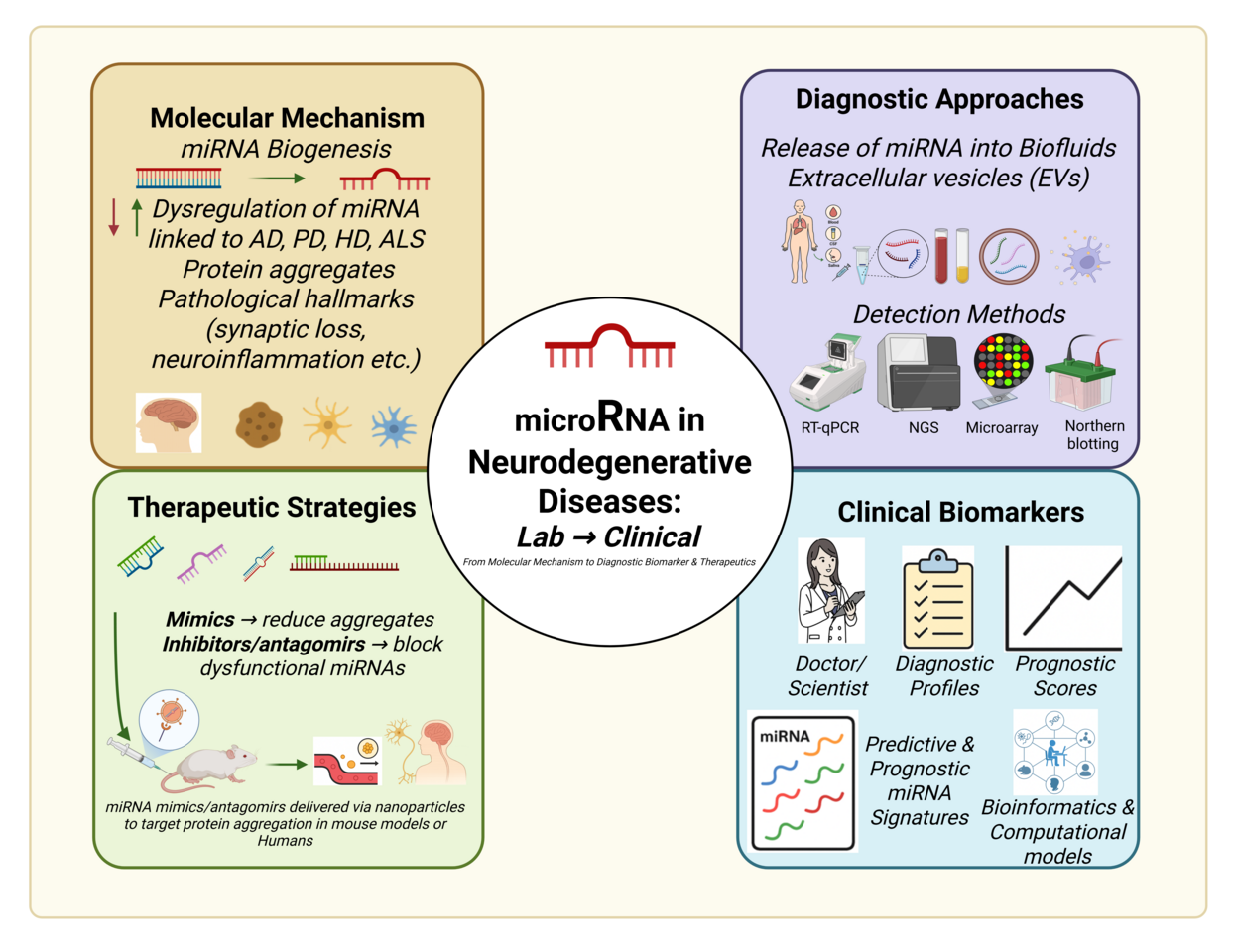
Our review, “MicroRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases: from molecular mechanisms to clinical biomarkers, detection methods and therapeutic strategies—advances and challenges,” provides a comprehensive synthesis across four dimensions:
-
Molecular Insights: How dysregulated miRNAs contribute to hallmark mechanisms in NDDs, from amyloid-β accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease to α-synuclein aggregation in Parkinson’s disease.
-
Detection Technologies: A comparative overview of RT-qPCR, next-generation sequencing (NGS), microarrays, and emerging biosensor-based and point-of-care (POC) platforms, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and clinical readiness.
-
Therapeutic Strategies: Advances in miRNA mimics, antagomirs, sponges, and delivery systems (including viral vectors, lipid nanoparticles, and exosomes) aimed at restoring normal gene regulation.
-
Translational Barriers: Critical issues such as reproducibility, standardization of extraction and normalization protocols, off-target effects, and regulatory pathways that must be addressed before miRNA tools can reach the clinic.
From Promise to Practice
The review emphasizes that miRNA-based diagnostics and therapeutics are no longer theoretical, several have reached preclinical and early clinical testing. However, achieving real-world impact will require coordinated action in a few key areas:
-
Standardization: Harmonized protocols for miRNA extraction, quantification, and data normalization.
-
Validation: Large, multicenter studies to confirm diagnostic performance across diverse populations.
-
Integration: Combining miRNA data with other omics layers and applying machine learning for improved patient stratification and predictive modeling.
-
Safe Delivery: Developing targeted, biocompatible carriers that can efficiently cross the blood–brain barrier without immune toxicity.
Looking Ahead
MiRNAs exemplify the next generation of precision medicine biomarkers; sensitive, dynamic, and mechanistically relevant.
By bridging molecular biology, bioengineering, and clinical research, we can transform them from powerful research tools into routine clinical diagnostics and therapies for neurodegenerative diseases.
I hope this review contributes to that interdisciplinary dialogue and encourages collaboration among neuroscientists, clinicians, bioengineers, and data scientists.
Read the full article here:
👉 Azam, H.M.H., Mumtaz, M., Rödiger, S. et al. MicroRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases: from molecular mechanisms to clinical biomarkers, detection methods and therapeutic strategies—advances and challenges. Neurological Sciences (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-025-08419-w
👉 Azam, H.M.H., Rößling RI, Geithe C, Khan MM, Dinter F, Hanack K, Prüß H, Husse B, Roggenbuck D, Schierack P, Rödiger S. MicroRNA biomarkers as next-generation diagnostic tools for neurodegenerative diseases: a comprehensive review. Front Mol Neurosci (2024). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2024.1386735
Share this Article: https://rdcu.be/eJJJ3
Have thoughts or related work?
Share your insights or experiences in developing miRNA-based diagnostics or therapies; I would love to connect and discuss how we can collectively accelerate translation to clinical application.
Follow the Topic
-
Neurological Sciences

Neurological Sciences is intended to provide a medium for the communication of results and ideas in the field of neuroscience. The journal welcomes contributions in both the basic and clinical aspects of the neurosciences.
Your space to connect: The Psychedelics Hub
A new Communities’ space to connect, collaborate, and explore research on Psychotherapy, Clinical Psychology, and Neuroscience!
Continue reading announcement
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in