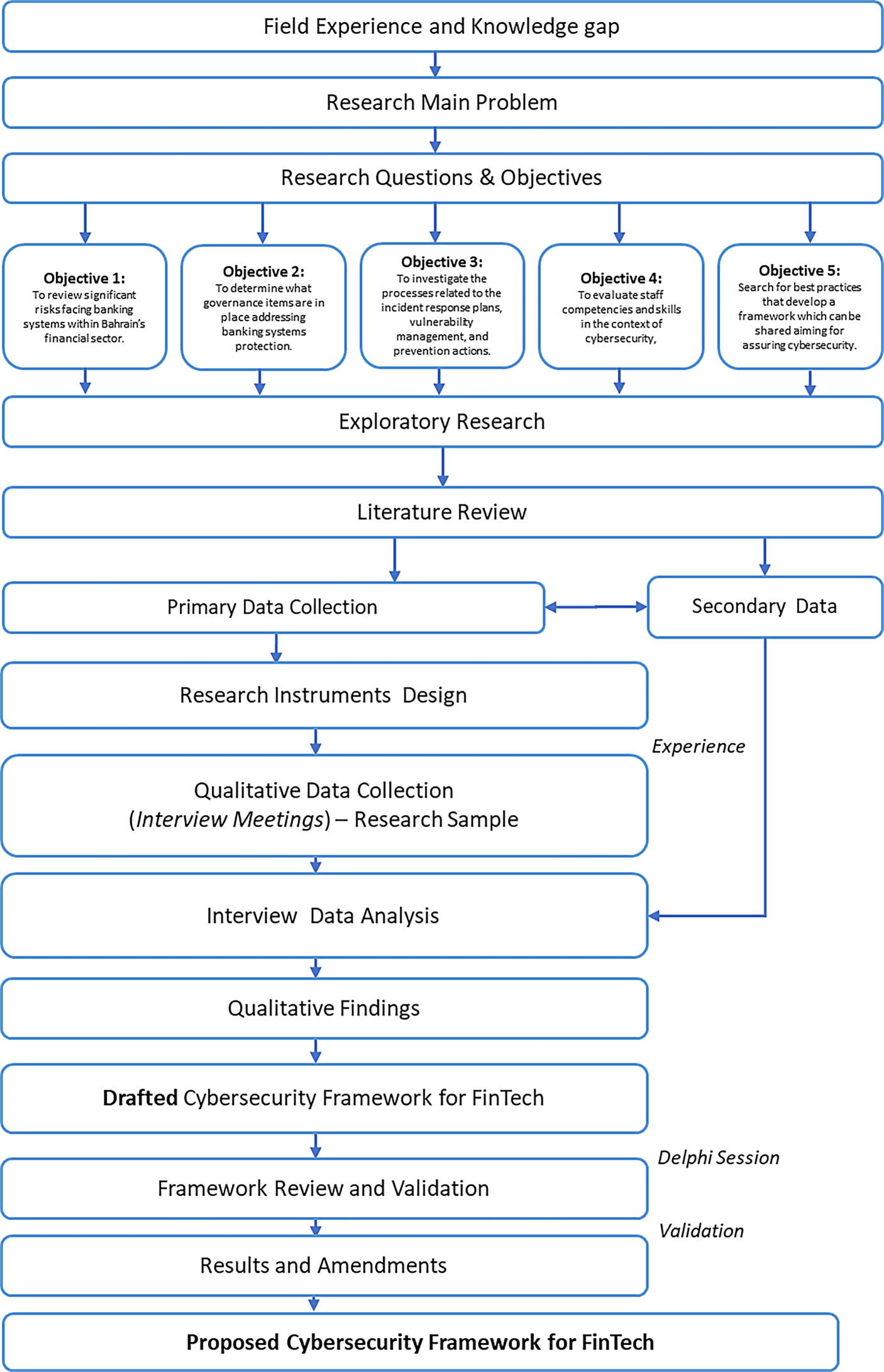
"Development of Cybersecurity Framework for FinTech Innovations: Bahrain as a Case Study"
Published in Arts & Humanities, Business & Management, and Economics

Overview
The authors, Salah AlBenJasim, Haifa Takruri, Rabab Al-Zaidi, and Tooska Dargahi, embarked on this research to bridge the significant gap in existing literature regarding tailored cybersecurity frameworks for FinTech, which are uniquely positioned within the broader context of financial services vulnerabilities.
Key Findings
The research identified several key findings that underscore the unique cybersecurity landscape in Bahrain:
-
Increased Cyber Threats: The study emphasizes that FinTech companies are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals, leading to a surge in phishing attacks, data breaches, and ransomware incidents. The statistics shared in the paper, such as the rise in data breaches in the financial sector, highlight the urgency of addressing these threats.
-
Existing Framework Limitations: The authors found that existing cybersecurity frameworks predominantly cater to traditional financial institutions and fail to address the specific and evolving needs of FinTech companies. This lack of targeted frameworks poses a risk to the FinTech ecosystem in Bahrain.
-
Proposed Framework: The authors successfully proposed an adaptable cybersecurity framework tailored to the FinTech sector. This new framework is designed to mitigate specific risks and vulnerabilities identified during the research, thus providing a robust foundation for enhancing cybersecurity resilience in Bahrain's FinTech environment.
-
Expert Validation: The framework's feasibility and relevance were evaluated through panel discussions and Delphi sessions with industry experts. Their positive feedback affirms the potential impact of the proposed solutions.
Challenges Encountered
Throughout the research process, the authors faced several challenges:
-
Complexity of the Topic: Cybersecurity is a dynamically evolving field, and keeping pace with new threats and vulnerabilities was a significant challenge. The rapid technological advancements in FinTech further complicated this process.
-
Data Collection: Gathering data through interviews with stakeholders in a highly sensitive area like cybersecurity proved challenging. Gaining the trust of potential participants and ensuring confidentiality were vital for meaningful data collection.
-
Adapting Research to Local Context: Since the research focused on Bahrain, the authors had to account for local regulations, market conditions, and cultural factors, which required careful consideration in developing a relevant framework.
Successes Achieved
Despite the challenges, several successes emerged during the study:
-
Collaborative Data Gathering: Managing to conduct in-depth interviews with key stakeholders from banks, FinTech firms, and regulators was a significant achievement, providing valuable insights that shaped the research findings.
-
Framework Development: The successful formulation of a tailored cybersecurity framework represents a notable contribution to the field. This framework not only addresses the unique risks faced by FinTech companies in Bahrain but also serves as a model that could be adapted by other nations with similar economic profiles.
-
Impact on Policy Development: The research has the potential to influence policymakers in Bahrain to consider more nuanced regulatory measures that reflect the unique cybersecurity challenges faced by the FinTech sector.
Personal Anecdotes
Reflecting on the collaborative nature of this research, team discussions often sparked lively debates about the balance between innovation and security in FinTech. A memorable moment was during one of the Delphi sessions, where an expert shared a personal experience of a cyber breach, which brought the often abstract statistics to life and reinforced the need for a robust framework. This anecdote resonated with the team’s commitment to producing research that has real-world implications.
Implications for Future Research
The findings from this study underscore several avenues for future research:
-
Global Application: While the focus was on Bahrain, researchers can explore the applicability of the proposed framework in other GCC countries or regions where FinTech is emerging.
-
Longitudinal Studies: Additional research could assess the ongoing efficacy of the proposed framework over time, examining its adaptability to evolving cyber threats.
-
Broader Stakeholder Engagement: Future studies might expand to include a wider range of stakeholders, including consumers and technology partners, to develop an even more comprehensive view of the FinTech cybersecurity landscape.
Follow the Topic
-
International Cybersecurity Law Review

This is a journal publishing articles on global developments in cybersecurity, data security, technology, law, and regulation.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in