Disparity between global drought hazard and awareness
Published in Earth & Environment
Explore the Research

Disparity between global drought hazard and awareness - npj Clean Water
npj Clean Water - Disparity between global drought hazard and awareness
Natural disasters have threatened to human beings and the ecosystem. Among the various natural disasters, drought is one of the most insidious and costliest, adversely affecting the global economy and livelihoods. Unlike sudden disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes, drought is a slow-onset phenomenon that gradually intensifies. This prolonged nature of drought often results in the shortage of drinking water and the disruption of local economies.
The Slow Onset and Impact of Drought
Drought creeps in gradually, often going unnoticed until it reaches a critical stage. This slow progression makes drought particularly challenging to manage and mitigate. Initially, the effects of drought might be low rainfall, lower water levels in rivers and lakes, and a slight decrease in agricultural yields. However, as drought conditions persist, the situation can escalate, causing severe water shortages, crop failures, and ultimately, the migration of people from drought-stricken areas in search of better living conditions.
When the prolonged nature of drought is recognized by affected communities, significant damage may already have occurred. The delayed awareness often hampers timely interventions, making it difficult to implement effective mitigation strategies. This challenge is further compounded by the fact that droughts can vary in intensity and duration, making it difficult to predict their onset and ultimate impact. As a result, communities in drought-prone areas may find themselves unprepared for the long-term consequences, resulting in a cycle of vulnerability and hardship.
Global Awareness of Drought
In recent years, there has been the need to edvance global understanding of drought and its impacts. This study examines global awareness of drought in three dimensions: local, remote, and global awareness. Local awareness refers to seeking information from the internet on drought conditions within a specific country. Remote awareness refers to the recognition of drought hazards in areas that are not under drought conditions. Global awareness involves the awareness of drought by individuals or communities that are geographically distant from the affected area.
One of the key findings of this study is that while the incidence of drought has not significantly changed over the past decade, there has been a remarkable increase in global awareness of drought. This heightened awareness is evident in the growing interest in drought-related information, particularly online. The advent of the internet and social media has made it easier for people to access information about drought, regardless of their location. This has contributed to a broader understanding of the issue and a recognition of the need for global action to address drought and its effects.
The Role of Long-Lasting Droughts in Enhancing Awareness
Long-lasting droughts have played a crucial role in enhancing both local- and global-level awareness of the issue. When a drought persists over an extended period, its impacts become visible and severe. Water shortage becomes pronounced, agricultural production declines and the risk of wildfires increases. These adverse effects make it difficult for the public to ignore the reality of drought, prompting greater attention and concern.
At the local level, communities directly affected by long-lasting droughts are forced to confront the challenges posed by the water shortage. Farmers may struggle to irrigate their crops, leading to reduced yields and financial losses. Households may face water rationing, impacting daily life and hygiene. As the drought persists, the economic and social pressures can cause a heightened sense of urgency, driving effort to find solutions and adapt to the changing conditions.
The Influence of Economic Factors on Drought Awareness
The study also highlights the role of economic factors in shaping awareness of drought (Figure 1). Specifically, it was found that nations with high gross domestic product (GDP) per capita tend to have a great remote-level awareness of drought. This suggests that countries with high GDP per capita, which may not be directly affected by drought, are nonetheless more responsive to the issue and more likely to seek information about it.
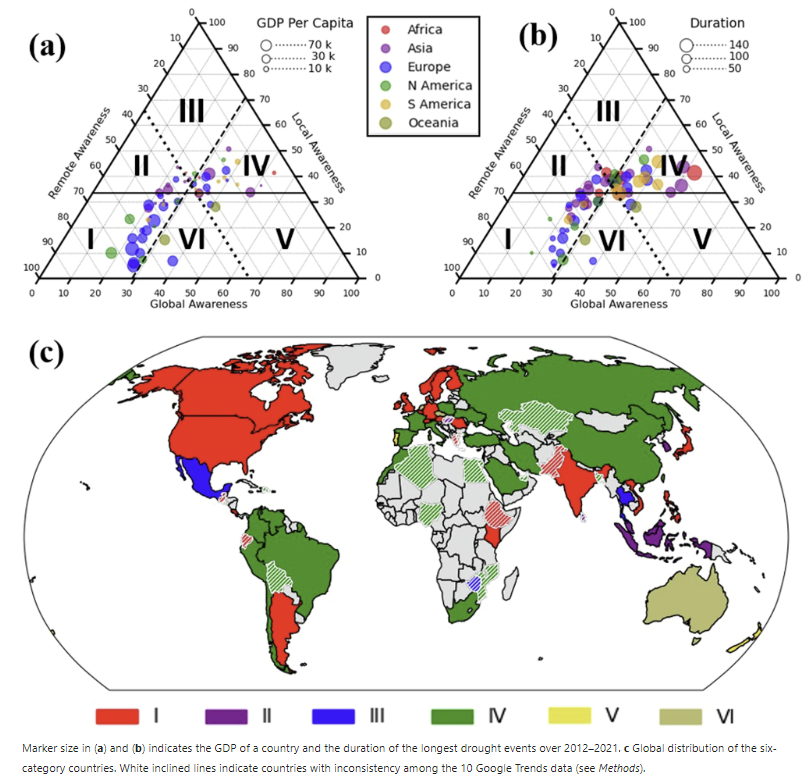
Figure 1. Roles of drought severity and GDP on drought awareness in multi-dimensions.
There are several reasons for this correlation between economic prosperity and drought awareness. Countries with high GDP per capita often have a great access to information and technology, making it easy for people to stay informed about global issues. In addition, higher levels of education in these regions may contribute to a greater understanding of the causes and consequences of drought. Furthermore, the economic interests of countries with high GDP per capita may be tied to those affected by drought, particularly in terms of agricultural production and trade. As a result, there is a vested interest in staying informed about drought conditions and their potential impact on the global economy.
Global Disparities in Drought Hazard and Awareness
Despite the increase in global awareness of drought, there are still significant disparities between nations in terms of both the hazard posed by drought and the level of awareness. Some developing countries are more vulnerable to the impacts of drought due to factors such as poverty, lack of infrastructure, and limited access to resources. In these areas, the ability to respond to and mitigate the effects of drought is often constrained, causing great suffering and economic losses.
In contrast, countries with high GDP per capita, particularly in Europe and North America, are better equipped to manage the impacts of drought. These regions often have more advanced infrastructure, greater access to technology, and more robust social safety nets. As a result, they are better able to cope with the challenges posed by drought, even if they are not directly affected by it.
The study underscores the continuing role of developed nations in enhancing global awareness of an emerging drought. These developed countries have been at the forefront of efforts to raise awareness of drought and its impacts, both within their borders and globally. Through initiatives such as research funding, international cooperation, and public awareness campaigns.
Follow the Topic
-
npj Clean Water

This journal publishes high-quality papers which report cutting-edge science, technology, application, policy and societal issues that contribute towards a more sustainable supply of clean water.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence Innovations for Resilient and Sustainable Clean Water: Novel Methodologies and Case Studies
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026
Advances in Smart Water Systems: From Source to Tap and Beyond
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in