Revolutionizing 3D Genome Analysis: AI Unveils the Optimal Resolution for Hi-C Data Integration – A New AI-Powered Method for Automatically Determining the Best Bin Size –
Published in Computational Sciences

Summary for General Readers
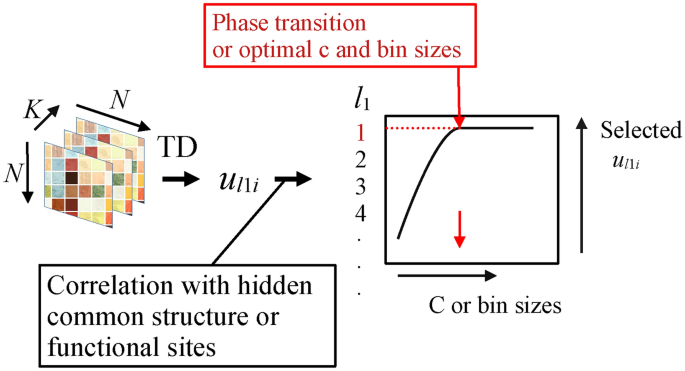
This study introduces a new AI-powered computational method for analyzing Hi-C data, which is used to study the 3D structure of DNA. When analyzing Hi-C data, determining the optimal bin size (resolution) is crucial—if the bin size is too large, important details may be lost, while if it is too small, noise can obscure meaningful patterns. This becomes even more challenging when integrating multiple Hi-C datasets, as a common optimal bin size must be found for all datasets.
The researchers developed a novel approach using tensor decomposition-based unsupervised feature extraction (TD-based FE). This AI-driven method can automatically determine the best bin size by detecting phase transition-like phenomena, without requiring any manual parameter tuning.
Key Findings
- The proposed method was tested on two Hi-C datasets (GSE260760 and GSE255264).
- It successfully identified the optimal bin sizes: 1,000,000 base pairs (bp) for GSE260760 and 150,000 bp for GSE255264.
- Compared to traditional methods, TD-based FE showed a higher correlation with functional genomic sites such as CTCF binding sites and topologically associating domains (TADs).
- This approach outperformed simple averaging techniques commonly used in Hi-C analysis.
Conclusion
This research presents a breakthrough in genomic data analysis by providing an automated, AI-driven method to determine the optimal resolution for integrating multiple Hi-C datasets. This innovation has the potential to enhance the accuracy of chromatin interaction studies and advance genomic and medical research, ultimately contributing to a deeper understanding of gene regulation and disease mechanisms.
Follow the Topic
-
Scientific Reports

An open access journal publishing original research from across all areas of the natural sciences, psychology, medicine and engineering.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Reproductive Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 30, 2026
Women’s Health
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in