EMR-based prediction models developed and deployed in the HIV care continuum: a systematic review
Published in Healthcare & Nursing

Study findings and insights
1. The Role of EMRs in HIV Care
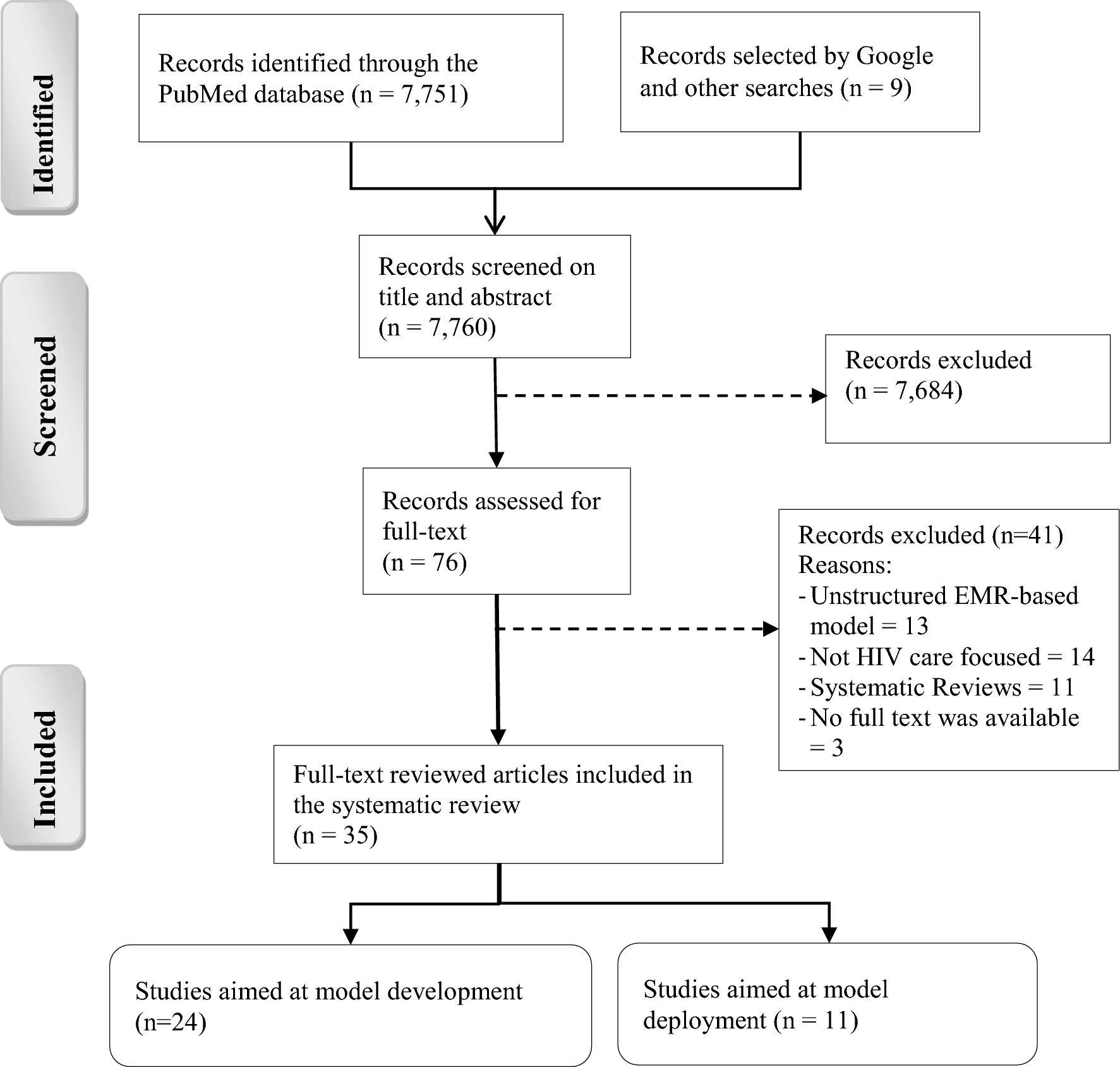
Using electronic medical records (EMRs) to predict patient outcomes is an exciting development in HIV care. EMRs are digital records with information about a patient's medical history, treatments, and test results. By analyzing this data, healthcare providers can identify patterns and predict when patients might be at risk of missing appointments, stopping treatment, or facing other challenges.
2. Benefits of EMR-Based Predictions
This approach has already shown promise. For example, some hospitals have used EMR-based models to increase the number of people being tested for HIV and to ensure those who test positive get connected to care faster. In some cases, EMR tools have helped increase monthly HIV screenings from a few people to hundreds and improve the number of patients staying in care.
3. Challenges of Implementing EMR Models
However, there are still challenges to making these models work well. For instance, missing information in a patient’s record can lead to biased predictions. Also, most of the current studies have been done in high-income countries, so it’s not yet clear how well these models will work in other settings.
4. Future Potential of EMR-Based Tools
Despite these hurdles, the potential of EMR-based prediction models is significant. With ongoing improvements and wider testing, these tools could transform HIV care, making it more personalized and efficient. By understanding when and where patients need the most support, healthcare providers can help more people stay engaged in their treatment, reduce the spread of HIV, and ultimately improve the quality of life for those living with the virus.
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Health Systems

This journal takes a multidisciplinary approach to address systems-level research and discussions relating to health systems, services and informatics, reflecting health outcomes, including from business and health policy perspectives.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Building Resilient Health Systems and Outbreak Preparedness in Africa: Policy, Governance, and Technological Innovation
Achieving timely prevention, detection, and response to infectious disease threats, while maintaining equitable access to essential services—depends on robust, well-governed health systems. In Africa’s diverse contexts, strengthening these systems requires integrated policy frameworks, adaptive management practices, and innovative technologies that address gaps in surveillance, workforce capacity, supply chains, and community engagement.
This Article Collection examines multidisciplinary strategies to enhance health system resilience and epidemic preparedness across the continent. We focus on:
- Policy and Governance: Crafting adaptive national and subnational policies, financing models, and regulatory environments that incentivize rapid outbreak response and sustain routine care.
- Health System Management: Optimizing human resources for health, supply-chain logistics, and facility-level coordination to maintain continuity of care during emergencies.
- Digital Health & Informatics: Deploying electronic surveillance platforms, mobile health (mHealth) tools, and data-analytics dashboards for real-time monitoring, early warning, and evidence-based decision-making.
- Surveillance & Laboratory Networks: Expanding laboratory capacity, sample-transport systems, and integrated One Health approaches to detect zoonoses and emerging pathogens.
- Community Engagement & Risk Communication: Leveraging regional partnerships, local governance, and culturally tailored messaging to build trust and promote preventive behaviors.
- Operational Research & Evaluation: Implementing outbreak simulations, performance metrics, and rapid-cycle evaluations to refine interventions and inform scalable best practices.
We welcome submissions that generate practical, scalable solutions for African health systems. By uniting insights from policymakers, health managers, informaticians, and frontline practitioners, this Collection aims to inform evidence-driven investments, strengthen preparedness capacities, and improve health outcomes across the continent.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 01, 2026
Improving Domestic resource mobilisation to support health financing transition in Sub-Saharan Africa
It is generally acknowledged that recent improvements in health outcomes in Africa have been attributed to the increase in development assistance for health, especially over the past three decades. With development assistance for health in Sub-Saharan Africa on the decline, increased domestic resource mobilization for health will be needed to sustain progress or even avoid disruptions, given recent and likely future declines in external support.
There is also a general recognition that bridging the funding gap in the face of declining donor aid funding will depend crucially on governments in Africa increasing domestic funding and planning transitions towards greater domestic health spending. Arguably, recent events in the global health financing architecture have only added impetus to a situation that has been unfolding for several years. Despite high-level political and policy statements, domestic financing remains very low in many African countries.
Thus, one question that confronts national health authorities and health financing policy experts is, are there plausible scenarios over the short and medium term to transition towards increased domestic financing in anticipation of declining development assistance for health, with minimal disruptions to the progress made so far? Rather than focusing on aspirational targets, such as the share of total government spending allocated to the health sector, it is essential to examine how well countries are performing, given their level of income and other spending drivers. Bringing new evidence on the potential of African countries to increase domestic resources for health into one collection would greatly add value to the debate.
This collection will feature empirical papers that will hopefully examine the extent to which countries can increase domestic resources for health. The scope of empirical papers covers the following pertinent dimensions of health financing, including revenue mobilization, risk pooling, and strategic purchasing:
(a) Quantifying the potential for domestic resource mobilization for health
(b) Modelling future health spending and costs in the short to medium term, incorporating scenarios about anticipated changes in external health financing.
(c) Estimating the efficiency or effectiveness of health spending.
(d) Evaluating the impact of strategic purchasing on health system performance
(e) Description and evaluation of levels and patterns of development assistance for health in sub-Saharan Africa.
(f) Evaluation of effective strategies that countries are implementing to increase domestic financing for health.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Aug 26, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in