Enhancing Thyroid Cancer Staging with AI
Published in Cancer, Computational Sciences, and General & Internal Medicine

Thyroid cancer is one of the most common cancers in the UK, with approximately 4,000 new cases diagnosed each year. The increasing incidence indicates a growing demand for accurate diagnosis, effective management, and ongoing follow-up care. Precision management of thyroid cancer hinges on two key clinical systems: AJCC (TNM) staging for assessing cancer progression and American Thyroid Association (ATA) risk classification for guiding prognosis and treatment. However, manually extracting and integrating relevant clinical information remains labour-intensive and time-consuming. Our AI model automates this process, reducing clinician preparation time—by nearly 50%—while maintaining high diagnostic accuracy.
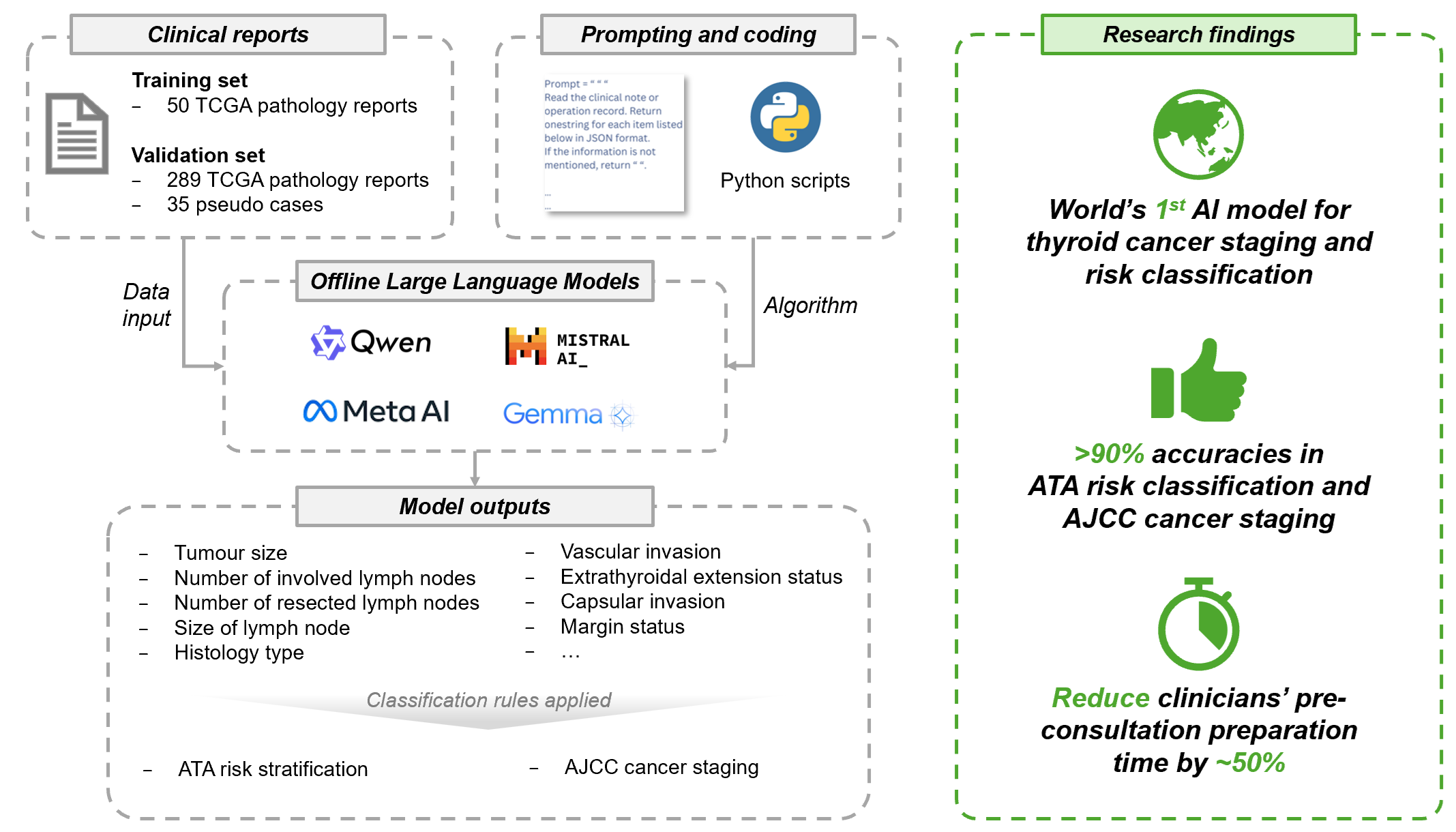
We developed a Named Entity (NE) framework using open-source large language models (LLMs)—Mistral, Llama, Gemma, and Qwen—to parse and analyse free-text pathology and clinical documents. Combined LLM outputs via a majority-vote ensemble achieved 92.9–98.1% accuracy for AJCC staging and 88.5–100% for ATA risk classification.
We further benchmarked this model against the latest released LLMs like DeepSeek-R1, DeepSeek-V3, and GPT-4o, with our offline model performing on par—an essential feature for privacy-focused, deployment in healthcare settings like the NHS.
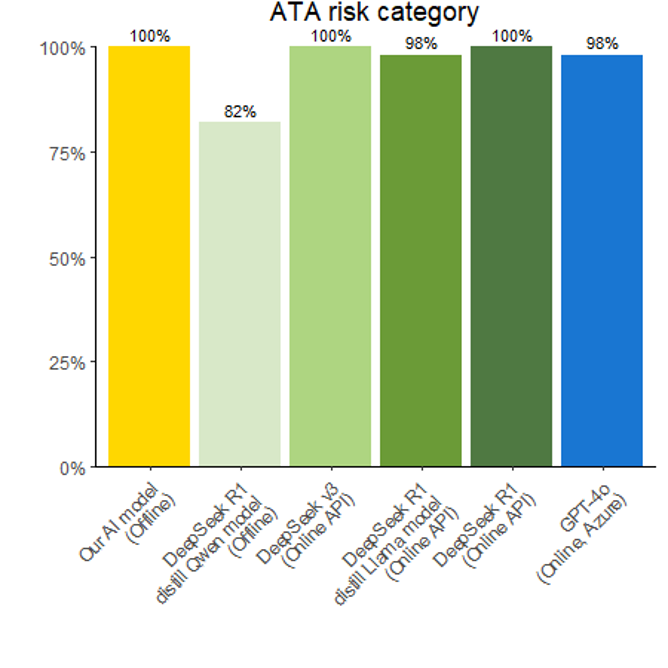
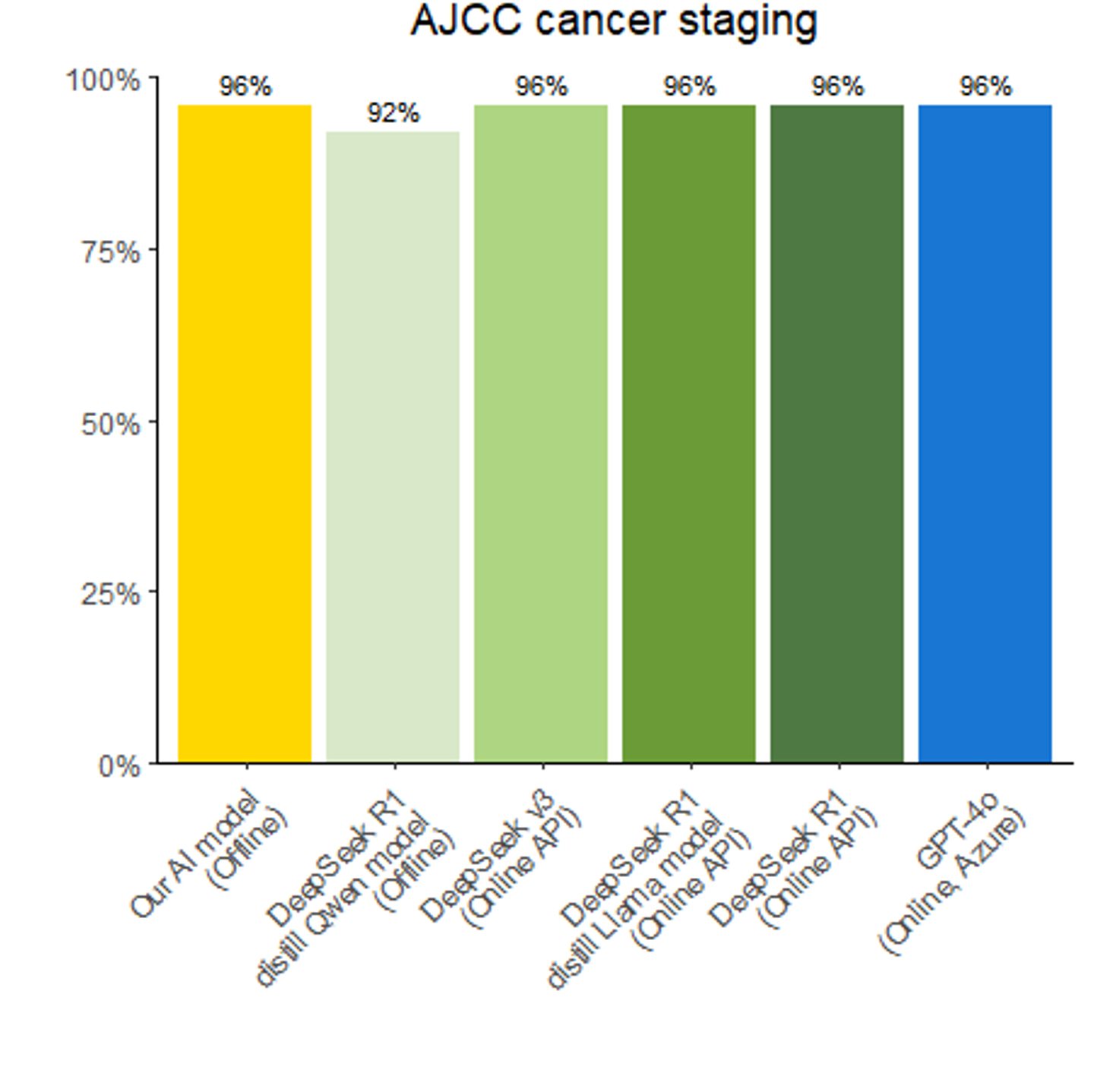
As thyroid cancer diagnoses continue to rise, our next step is evaluating the model on large-scale real-world data to support deployment in clinical practice, beginning with NHS hospitals. We believe this work can significantly reduce the cognitive and time burden on clinicians, freeing up time for meaningful interaction and counselling with patients and enhancing quality of care. A significant advantage of this model is its offline capability, which would allow local deployment without the need to share or upload sensitive patient information, thereby providing maximum patient privacy.
We're excited about the potential this AI model has for real-world impact and welcome collaboration with healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers interested in bringing AI to the clinical frontline.
Follow the Topic
-
npj Digital Medicine

An online open-access journal dedicated to publishing research in all aspects of digital medicine, including the clinical application and implementation of digital and mobile technologies, virtual healthcare, and novel applications of artificial intelligence and informatics.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Digital Health Equity and Access
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 03, 2026
Evaluating the Real-World Clinical Performance of AI
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 03, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in