Geographical variation and associated factors of childhood measles vaccination in Ethiopia: a spatial and multilevel analysis
Published in Biomedical Research, Immunology, and Public Health
Background
In Ethiopia, despite considerable improvement of measles vaccination, measles outbreaks is occurring in most parts of the country. Understanding the neighborhood variation in childhood measles vaccination is crucial for evidence-based decision-making. However, the spatial pattern of measles-containing vaccine (MCV1) and its predictors are poorly understood. Hence, this study aimed to explore the spatial pattern and associated factors of childhood MCV1 coverage.
Methods
An in-depth analysis of the 2016 Ethiopia demographic and health survey data was conducted, and a total of 3722 children nested in 611 enumeration areas were included in the analysis. Global Moran’s I statistic and Poisson-based purely spatial scan statistics were employed to explore spatial patterns and detect spatial clusters of childhood MCV1, respectively. Multilevel logistic regression models were fitted to identify factors associated with
childhood MCV1.
Results
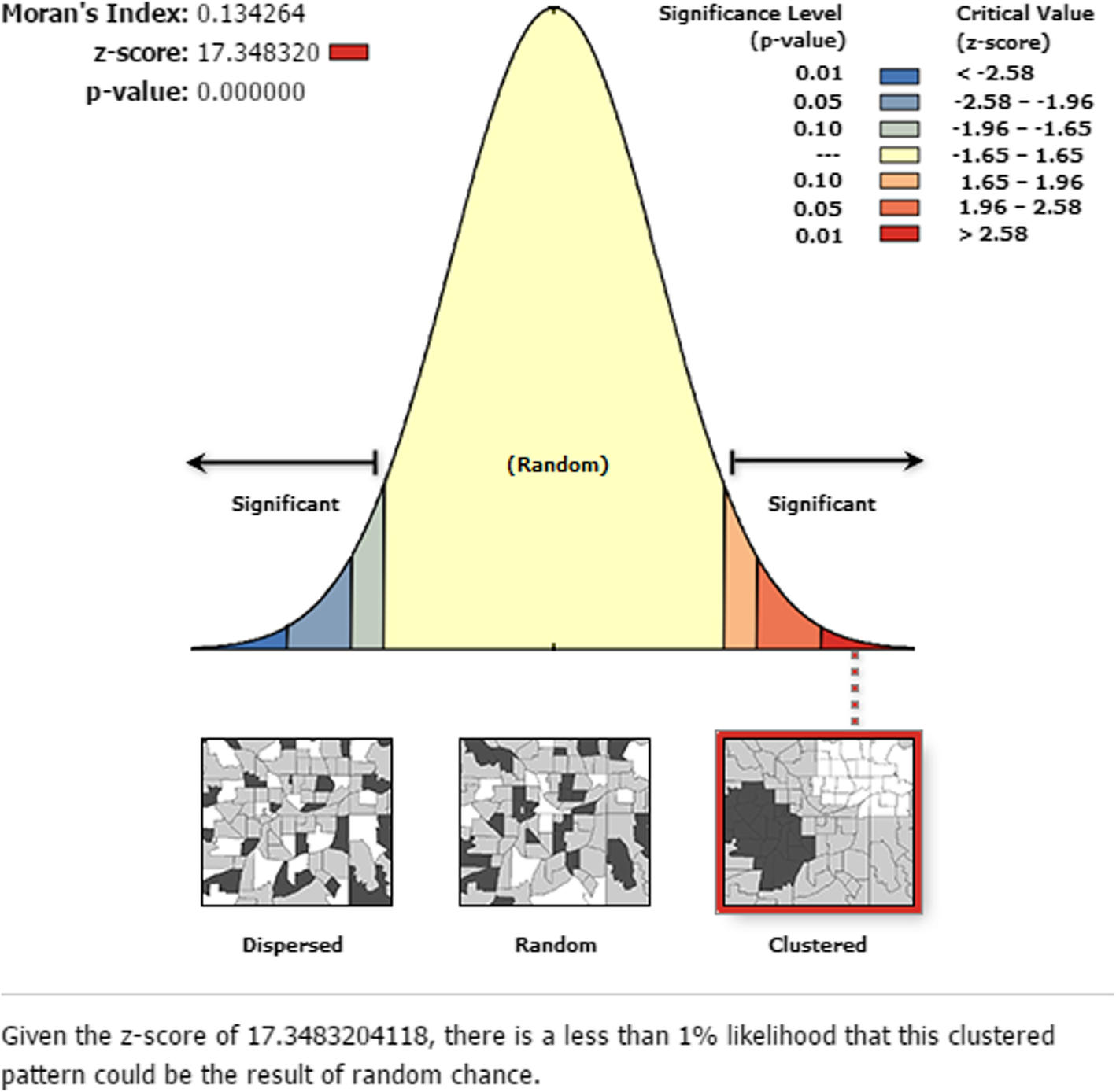
Spatial heterogeneity of childhood MCV1 was observed (Global Moran’s I = 0.13, p-value < 0.0001), and seven significant SaTScan clusters of areas with low MCV1 coverage were detected. The most likely primary SaTScan cluster was detected in the Afar Region, secondary cluster in Somali Region, and tertiary cluster in Gambella Region. In the final model of the multilevel analysis, individual and community level factors accounted for 82% of the variance in the odds of MCV1 vaccination. Child age (AOR = 1.53; 95%CI: 1.25–1.88), pentavalent vaccination first dose (AOR = 9.09; 95%CI: 6.86–12.03) and third dose (AOR = 7.12; 95%CI: 5.51–9.18, secondary and above maternal education (AOR = 1.62; 95%CI: 1.03–2.55) and media exposure were the factors that increased the odds of MCV1 vaccination at the individual level. Children with older maternal age had lower odds of receiving MCV1. Living in
Afar, Oromia, Somali, Gambella and Harari regions were factors associated with lower odds of MCV1 from the community-level factors. Children far from health facilities had higher odds of receiving MCV1 (AOR = 1.31, 95%CI =1.12–1.61).
Conclusion
A clustered pattern of areas with low childhood MCV1 coverage was observed in Ethiopia. Both individual and community level factors were significant predictors of childhood MCV1. Hence, it is good to give priority for the areas with low childhood MCV1 coverage, and to consider the identified factors for vaccination interventions.
Keywords
Measles, Vaccination, Spatial, Multilevel, Ethiopia
Follow the Topic
-
BMC Public Health

An open access, peer-reviewed journal that considers articles on the epidemiology of disease and the understanding of all aspects of public health.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Cancer in older adolescents and young adults
BMC Public Health is calling for submissions to our Collection on Cancer in older adolescents and young adults.
Cancer in older adolescents and young adults presents unique epidemiological challenges, with distinct patterns of incidence, risk factors and outcomes compared to other age groups. This Collection aims to enhance our understanding of cancers that affect these populations, such as gastrointestinal, endometrial, colorectal, cervical and breast cancers, some of which are HPV- or obesity-related. We invite research that explores disparities in cancer outcomes and advances evidence-based strategies for prevention, early detection, and management. For the purposes of this collection, we define older adolescents and young adults as being between 15 to 39 years old.
Topics of interest related to cancer in older adolescents and young adults include but are not limited to:
• Recent and longer-term trends in the incidence and mortality of different types of cancer
• Role of infectious, environmental, and lifestyle factors in cancer development
• Impact of obesity at age of diagnosis or prior obesity (such as during childhood) on subsequent cancer risk and outcomes
• Disparities in outcomes by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status
• Innovations in cancer prevention, screening, and early detection
• Long-term survivorship and quality of life among cancer survivors
• Policy implications for cancer prevention and control in younger populations
This collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 3 Good Health & Well-Being.
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 26, 2026
Monitoring, preventing, and managing type 2 diabetes
BMC Public Health is calling for submissions to our Collection on Monitoring, preventing, and managing diabetes at the population level. With rates of type 2 diabetes rising globally, especially in low- and middle-income countries and underserved communities, prevention strategies are critical. As the disease progresses people with diabetes are at increased risk of complications such as cardiovascular and kidney diseases, neuropathy and visual loss.
This Collection seeks submissions that explore population-level approaches to monitoring rates of diabetes, preventing or delaying the development of type 2 diabetes, and system-wide efforts to improve the management of the disease and reduce rates of complications, with a focus on improving health outcomes and reducing healthcare burdens.
Submissions are encouraged on primary prevention initiatives and culturally adapted, community-level interventions to reduce the risk of diabetes. Research aimed at improving systems for monitoring rates of diabetes and its complications through routinely-collected health data, or for improving management by enhancing patient engagement with healthcare systems or better identifying those in need, are encouraged. Research on diabetes education and support systems is also welcomed, with a focus on empowering individuals to adopt and sustain healthier lifestyles and avoid known causes of diabetes.
Additional topics of interest include (but are not limited to):
Access to healthcare and diabetes management
The impact of food insecurity on diabetes outcomes
Community-based interventions for low-income populations
Interventions to reduce exposure to environmental causes of diabetes
Financial barriers to diabetes medication and treatment
Housing instability, employment status and type 2 diabetes
Health literacy, poverty, and diabetes management
Policies to reduce poverty-related health disparities in diabetes
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 3: Good Health & Well-Being.
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jul 16, 2026



Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in