Helformer: an attention-based deep learning model for cryptocurrency price forecasting
Published in Mathematical & Computational Engineering Applications, Statistics, and Business & Management
🔍 Behind the Scenes: Methodology & Innovation
1. The Helformer Architecture
Helformer integrates three key components to outperform existing models:
-
Series Decomposition: Using Holt-Winters smoothing, we break price data into level, trend, and seasonality components (Fig. 1). This step isolates patterns that traditional Transformers might miss.
-
Multi-Head Attention: Unlike sequential models (e.g., LSTM), Helformer processes all time steps simultaneously, capturing long-range dependencies efficiently.
-
LSTM-Enhanced Encoder: Replacing the standard Feed-Forward Network with an LSTM layer improves temporal feature extraction.
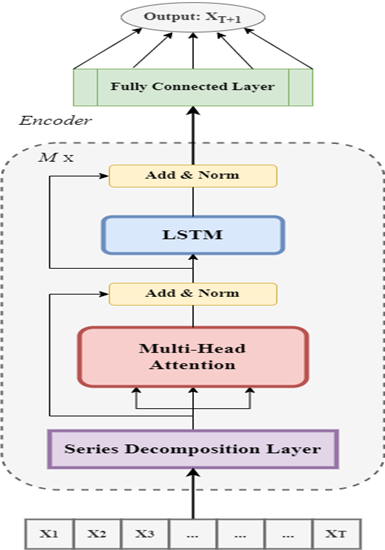
Fig. 1: Helformer architecture.
2. Data & Hyperparameter Tuning
We trained Helformer on Bitcoin (BTC) daily closing prices (2017–2024) and tested its generalization on 15 other cryptocurrencies (e.g., ETH, SOL). To optimize performance, we used Bayesian optimization via Optuna, automating hyperparameter selection (e.g., learning rate, dropout) and pruning underperforming trials early.
3. Evaluation Metrics
Helformer was benchmarked against RNN, LSTM, GRU, and vanilla Transformer models using:
-
Similarity metrics: R², Kling-Gupta Efficiency (KGE), EVS
-
Error metrics: RMSE, MAPE, MAE
-
Trading metrics: Sharpe Ratio, Maximum Drawdown, Volatility, Cumulative returns
💡 Key Findings & Practical Impact
1. Superior Predictive Accuracy
Helformer achieved near-perfect R² (1.0) and MAPE (0.0148%) on BTC test data, outperforming all baseline models (Table 1). Its decomposition step reduced errors by 98% compared to vanilla Transformers.
Table 1: Model Performance Comparison
|
Model |
RMSE |
MAPE |
MAE |
R² |
EVS |
KGE |
|
RNN |
1153.1877 |
1.9122% |
765.7482 |
0.9950 |
0.9951 |
0.9905 |
|
LSTM |
1171.6701 |
1.7681% |
737.1088 |
0.9948 |
0.9949 |
0.9815 |
|
BiLSTM |
1140.4627 |
1.9514% |
766.7234 |
0.9951 |
0.9952 |
0.9901 |
|
GRU |
1151.1653 |
1.7500% |
724.5279 |
0.9950 |
0.9950 |
0.9878 |
|
Transformer |
1218.5600 |
1.9631% |
799.6003 |
0.9944 |
0.9946 |
0.9902 |
|
Helformer |
7.7534 |
0.0148% |
5.9252 |
1 |
1 |
0.9998 |
2. Profitable Trading Strategies
In backtests, a Helformer-based trading strategy yielded 925% excess returns for BTC—tripling the Buy & Hold strategy’s returns (277%)—with lower volatility (Sharpe Ratio: 18.06 vs. 1.85), as shown in Fig. 2.
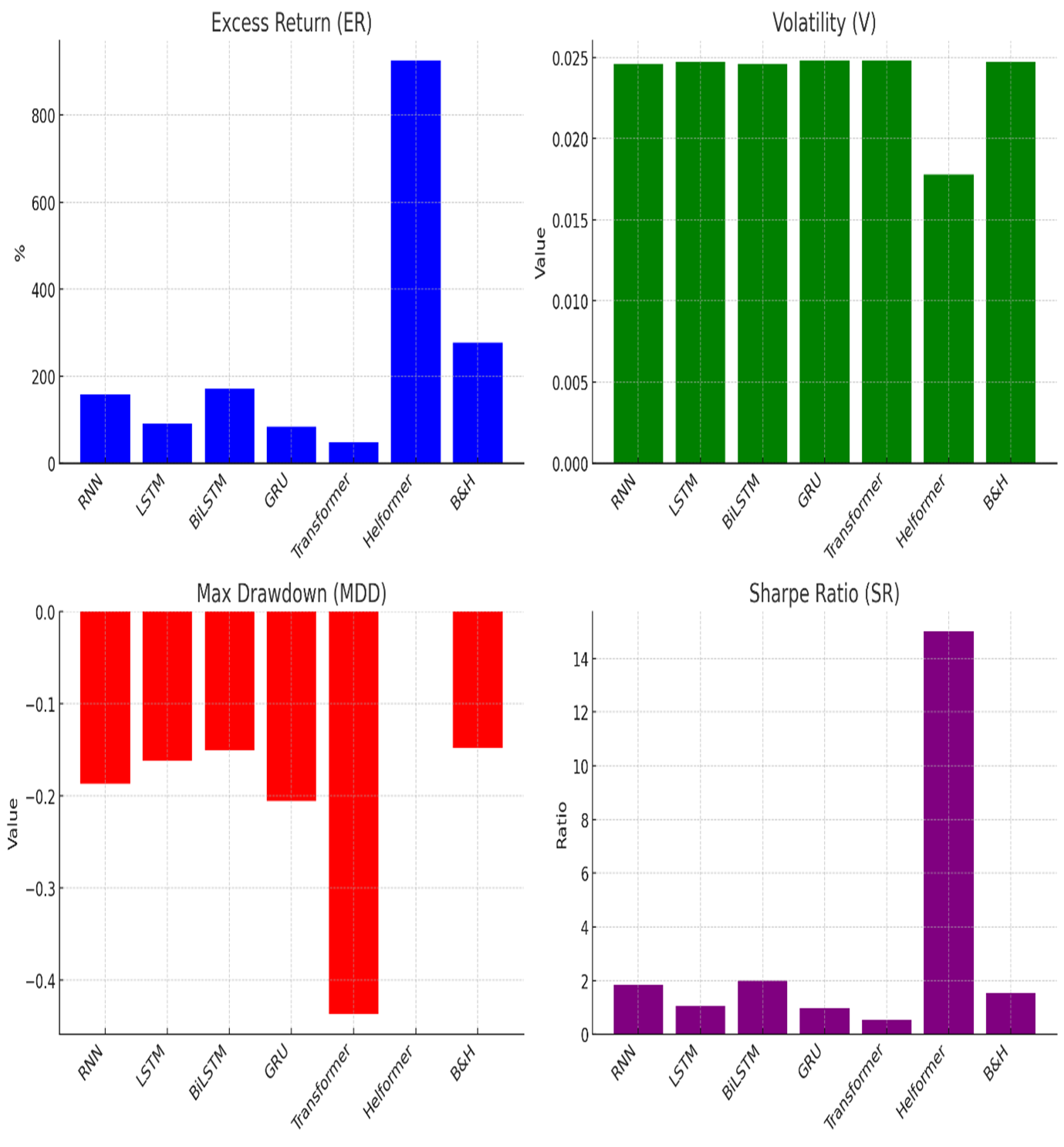 Fig. 2: Trading results.
Fig. 2: Trading results.
3. Cross-Currency Generalization
Helformer’s pre-trained BTC weights transferred seamlessly to other cryptocurrencies, achieving R² > 0.99 for XRP and TRX. This suggests broad applicability without retraining—a boon for investors managing diverse portfolios.
🌍 Relevance to the Community
-
For Researchers: Helformer’s architecture opens avenues for hybrid time-series models in finance, healthcare, and climate forecasting.
-
For Practitioners: The model’s interpretable components (decomposition + attention) make it adaptable to volatile markets beyond crypto.
-
For Policymakers: Reliable price forecasts could inform regulations to stabilize crypto markets and protect investors.
🤝 Acknowledgments & Open Questions
This work wouldn’t have been possible without my brilliant co-authors Oluyinka Adedokun, Joseph Akpan, Morenikeji Kareem, Hammed Akano, and Oludolapo Olanrewaju, or the support of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
We’d love to hear your thoughts!
-
How might Helformer adapt to non-financial time-series data?
-
Could integrating sentiment analysis further improve accuracy?
-
What ethical considerations arise with AI-driven trading?
🔗 Access the full paper: SpringerLink | ReadCube
Follow the Topic
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
2025 Australasian Data Science and Machine Learning (AusDM25) Special Issue
The Australasian Data Science and Machine Learning (AusDM) Conference has firmly established itself as the premier Australasian meeting point for both practitioners and researchers in Data Science, Data Analytics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning—including cutting-edge areas such as Deep Learning and Generative AI. Since its inception in 2002, the AusDM conference series has provided a leading forum for presenting, disseminating, and discussing the latest research advances spanning algorithms, software, systems, and practical applications across diverse industries.
Continuing this tradition, AusDM 2025 aims to foster cross-disciplinary knowledge exchange, highlight emerging research directions, and promote collaboration across academia, government, and industry.
This Special Issue cordially invites authors of accepted AusDM 2025 conference papers to submit extended versions of their work. Topics of interest include, but are not limited to, the following areas of Data Science and Machine Learning:
Foundational Techniques in Machine Learning and AI
Supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and self-supervised learning Deep learning and representation learning Reinforcement learning and federated learning Transfer learning, meta-learning, few-shot and continual learning Multitask and multimodal learning Generative models (GANs, diffusion models) Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) Zero-shot learning and prompt-based learning
Learning from Diverse and Complex Data
Analytics over structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data Text, time-series, graph, spatial, spatio-temporal, and network data Web, social media, multimedia, IoT, and sensor data Sequential, temporal, and dynamic data modelling
Data-Centric AI and Data Engineering
Data preprocessing, cleaning, integration, matching, and linkage Privacy-preserving and secure data mining Data-centric AI pipelines and dataset curation Computational aspects of data mining and large-scale data management
Scalable and Real-Time Data Analytics
Big data analytics and scalable Machine Learning Parallel and distributed learning algorithms Data stream mining and real-time analytics Edge, cloud, and IoT-enabled Machine Learning systems
Interactive and Visual Analytics
Visual analytics and explainability through visualisation Human-in-the-loop machine learning Interactive data exploration and decision support
Responsible, Causal, and Explainable AI
Explainable and interpretable Machine Learning Fairness, accountability, transparency, and ethics in AI Causal inference and causal machine learning Robustness, generalization, and uncertainty quantification
Applied Data Science and Machine Learning Across Domains
Applications in business, finance, education, agriculture, urban planning, healthcare, sports, social sciences, cybersecurity, arts, and humanities Domain-specific AI systems in biomedical informatics, environmental science, astronomy, engineering, and beyond Industrial case studies and data-driven product innovation
Submission Requirements
Submitted journal manuscripts must include at least 30% new content beyond the conference version. All submissions will undergo a rigorous peer-review process in accordance with the journal’s standards.Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Apr 30, 2026
LLM-Augmented Multimodal Data Fusion for Large-Scale Data Analysis
The rapid growth of multimodal data—such as text, images, sensor streams, graphs, and structured records—has made cross-modal integration critical for modern large-scale data analysis. However, the heterogeneous nature of multimodal sources and the limitations of conventional fusion techniques hinder effective semantic alignment, representation learning, and scalable analytics.
Although large language models (LLMs) offer strong capabilities in reasoning, abstraction, and cross-domain understanding, current data pipelines still lack efficient mechanisms to incorporate LLM-driven semantics into multimodal fusion workflows. This thematic series aims to bridge this gap by exploring innovative approaches that leverage LLMs to enhance multimodal data fusion and enable more powerful, comprehensive data-driven insights.
This collection focuses on advancing LLM-Augmented Multimodal Data Fusion for Large-Scale Data Analysis, encouraging research on:
LLM-enhanced representation learning Semantic alignment across heterogeneous modalities Generative or retrieval-assisted fusion strategies Scalable system designs for real-world applications The goal is to promote new analytical paradigms where LLM-driven intelligence reshapes multimodal integration and utilization in complex scientific and industrial ecosystems.The topics include, but are not limited to:
LLM-augmented cross-modal semantic alignment for large-scale analytics
Generative and retrieval-assisted fusion for multimodal data integration
Representation learning for heterogeneous and multi-source data fusion
Knowledge grounding and reasoning across diverse data modalities
Scalable fusion architectures for large-volume multimodal datasets
Foundation-model-assisted modality completion and data annotation
Graph–text–sensor fusion for scientific and engineering data analysis
Temporal–spatial multimodal fusion for real-world big data applications
Self-supervised learning for multimodal representation and alignment
Benchmarking, datasets, and evaluation protocols for multimodal fusion
Efficient fusion mechanisms for high-dimensional industrial and IoT data
Domain-specific multimodal fusion applications for data-driven intelligence
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Aug 31, 2026