Knowledge-based mechanistic modeling accurately predicts disease progression with gefitinib in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
Published in Cancer

Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is associated with a low survival rate at advanced stages. Although the development of targeted therapies has improved outcomes in LUAD patients with identified and specific genetic alterations, such as activating mutations on the epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR), the emergence of tumor resistance eventually occurs in all patients and this is driving the development of new therapies. A large amount of data and knowledge resulting from biological experiments of last decades at different scales (from the molecular level to the population level) and in various conditions (in vitro cultivated cells, animal experiments, human studies) are now publicly available for integration to support new insights and progress. We believe that drug development decision making could benefit from being informed and rationalized by the integration of these heterogeneous data. Knowledge-based mechanistic computational models represent a valuable tool to bridge quantitatively experimental data that are heterogeneous in scale and nature.
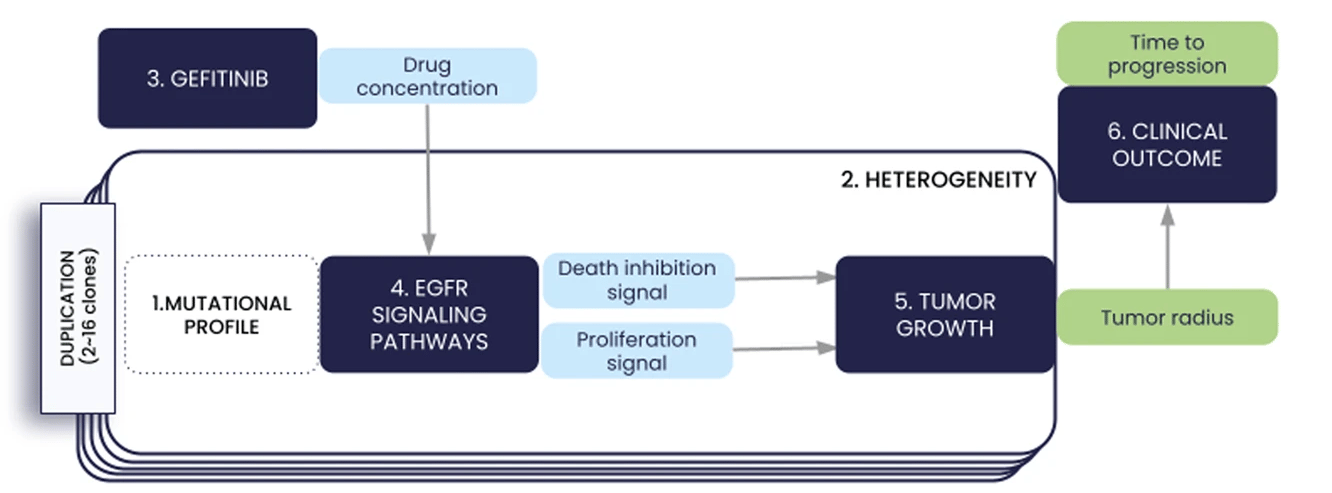
We present in this paper the first iteration of the In Silico EGFR-mutant LUAD (ISELA) model that links LUAD patients’ individual characteristics, including tumor genetic heterogeneity, to tumor size evolution and tumor progression over time under first generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib.
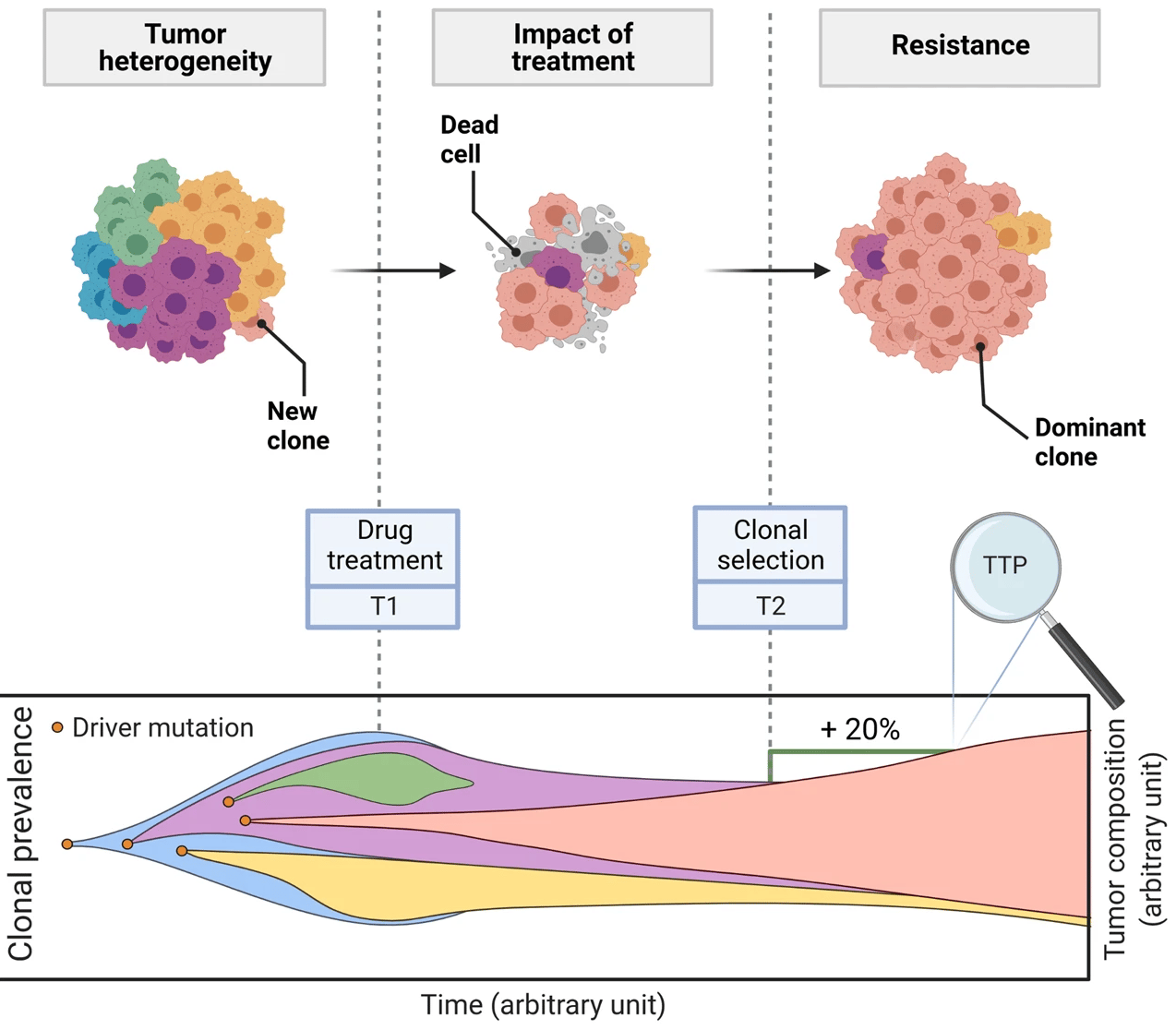
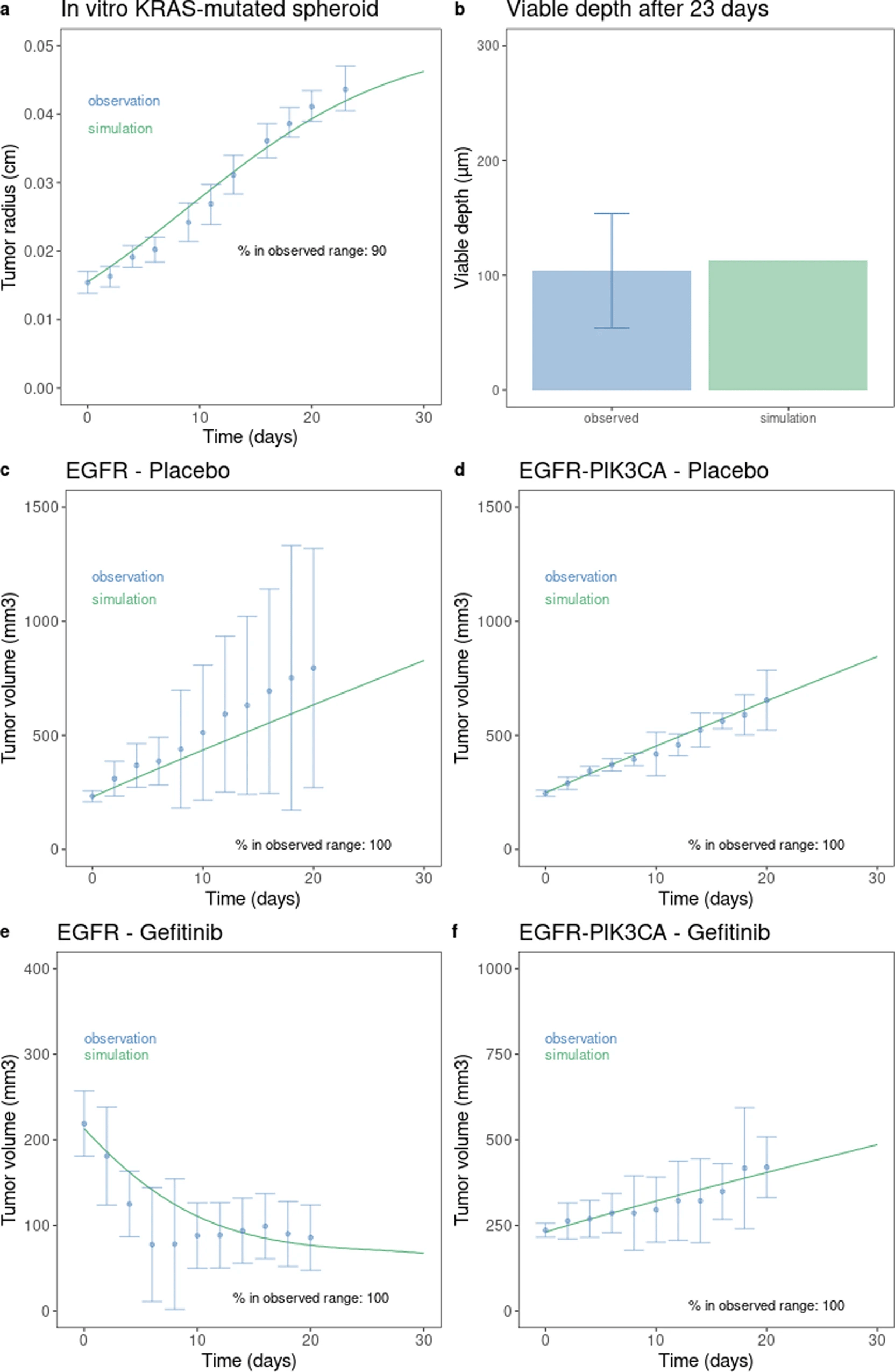
This is a translational mechanistic model which gathers extensive knowledge on LUAD and was calibrated on multiple scales, including in vitro, human tumor xenograft mouse and human, reproducing more than 90% of the experimental data identified (10.1007/s10441-022-09445-3).
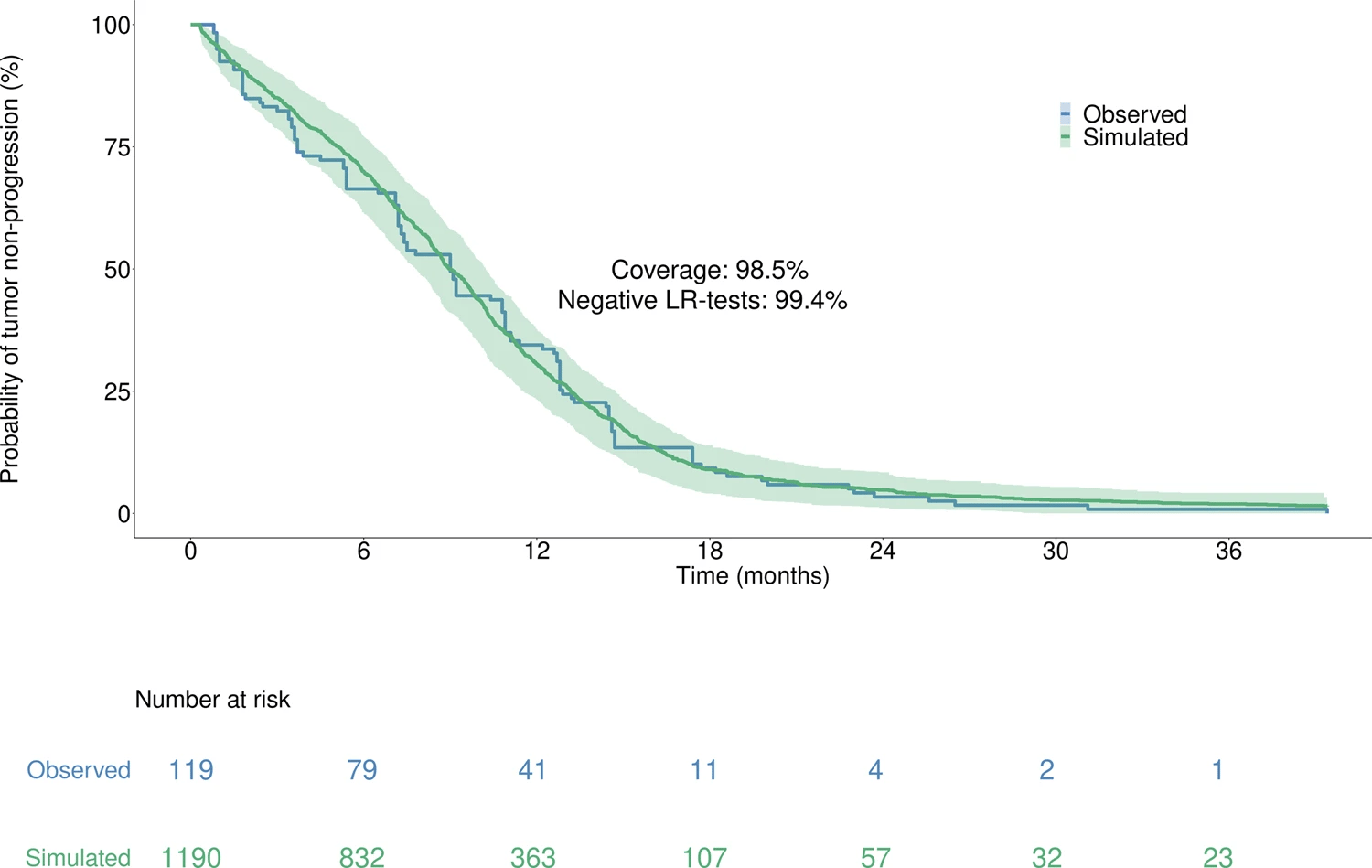
Moreover, with 98.5% coverage and 99.4% negative logrank tests, the model accurately reproduced the time to progression from the Lux-Lung 7 clinical trial, which was unused in calibration, thus supporting the model high predictive value.
To go further and to use the validated model to identify the key parameters that impact the change in tumor size and the resulting time to progression, we performed a sensitivity analysis on all individual virtual patients characteristics. Both analyses on tumor radius and TTP consistently identified the immune system (2 parameters), neoangiogenesis (1 parameter), tumor initial size (2 parameters), initial size of the resistant subclone (1 parameter), as well as 1 parameter encompassing the impact of implicit mutations on cell proliferation cancer hallmark as critically impactful on both outputs of interest.
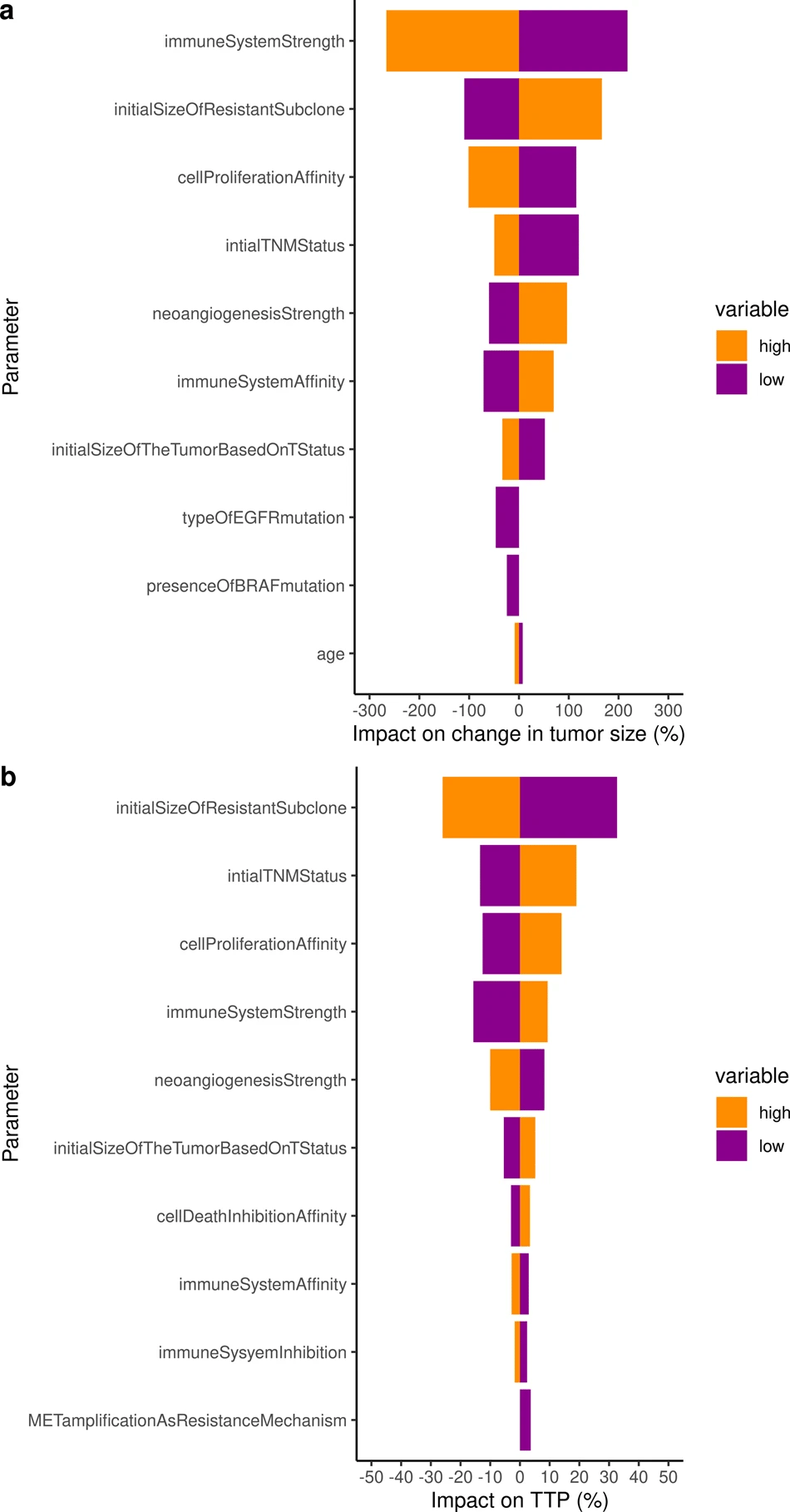
The ISELA model presented in this paper is a predictive and reliable mechanistic model of tumor growth evolution for patients treated with gefitinib with TTP as primary outcome.
We believe that in silico approaches such as the one presented in this article provide tools to overcome frequent issues related to clinical trials: they notably ensure the clinical equipoise by enrolling the exact same virtual patients in control and investigational arms. As a consequence, in silico models supporting drug development can ease the development of new drugs improving the medical care of patients diseases such as LUAD
Follow the Topic
-
npj Systems Biology and Applications

An online Open Access journal dedicated to publishing the premier research that takes a systems-oriented approach and encourages studies that integrate, or aid the integration of, data, analyses and insight from molecules to organisms and broader systems.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Systems mechanobiology
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 28, 2026
Fostering Cross-Disciplinary Modeling in Biology and Medicine
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 15, 2026



Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in