Mapping research evolution in higher education: a scientometric analysis of Brunei Darussalam (1986–2024)
Published in Sustainability and Education

Prolog
When we first set out to explore the evolution of higher education research in Brunei Darussalam, we had a simple yet ambitious goal: to understand how a small nation like Brunei has shaped its academic landscape over nearly four decades. What we didn’t anticipate was just how much we would uncover—not just about the research itself, but also about the collaborative networks, thematic shifts, and emerging trends that define Brunei’s role in global academia. 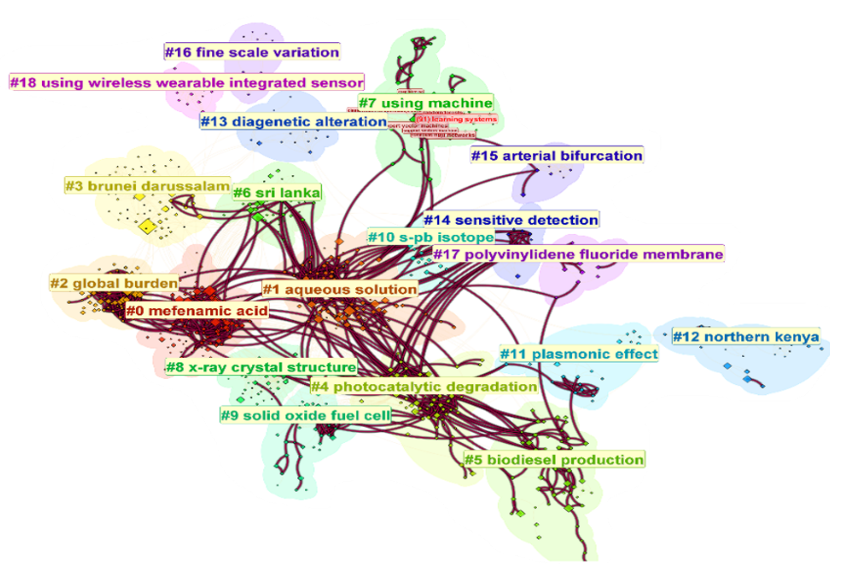
Why This Study?
Brunei might not be the first country that comes to mind when thinking about higher education research, but it has made remarkable progress, especially in fields like sustainability, technology, and public health. As researchers based in Brunei, we often hear about global academic trends, but we wanted to turn the lens inward—what does the data say about our own academic contributions?
Scientometric analysis, a method that applies data analytics to research trends, provided the perfect tool. It allowed us to map out how research in Brunei has evolved since 1986, highlighting key contributors, collaboration patterns, and future opportunities.
The Deep Dive into Data
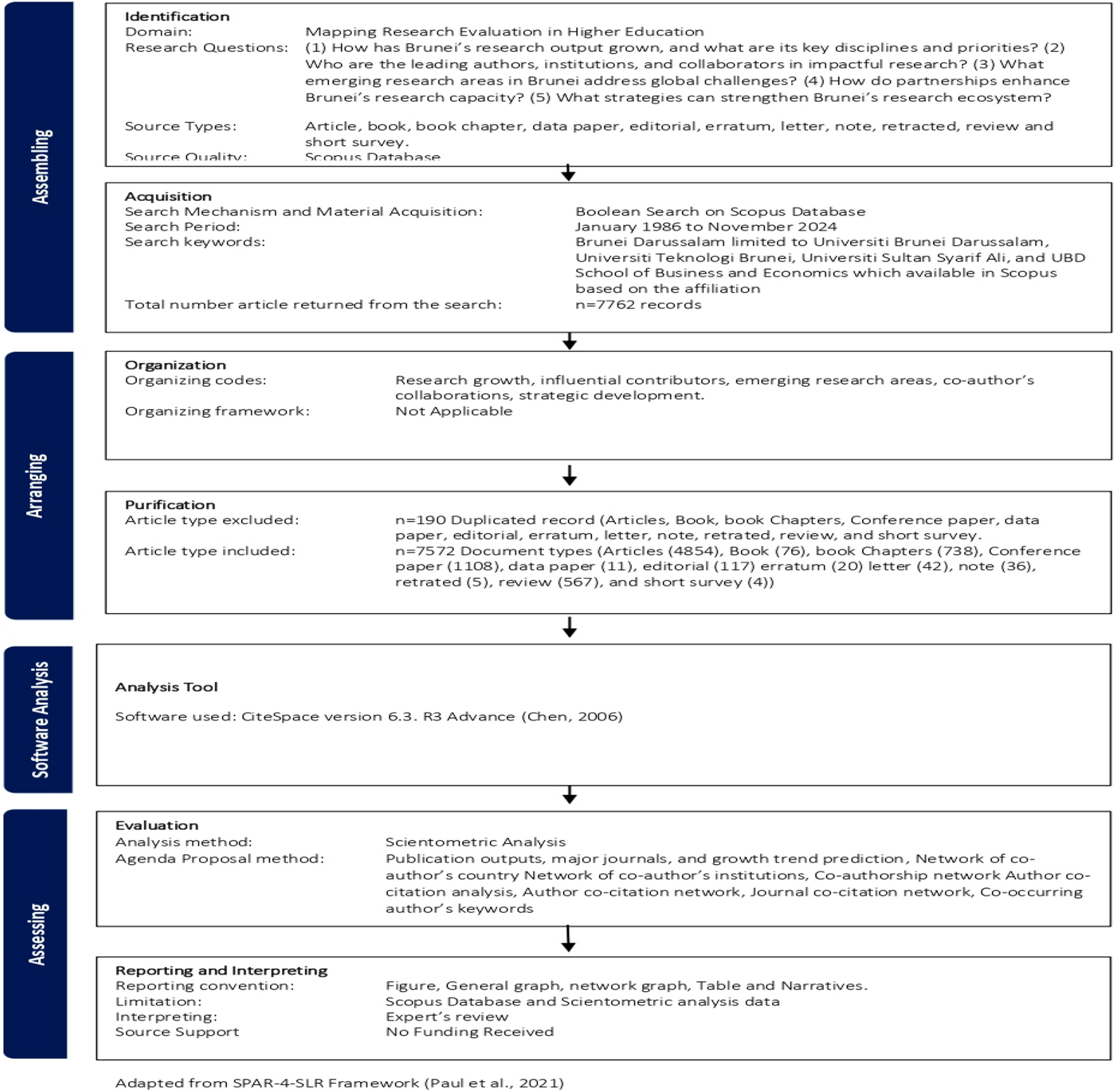
We began by collecting data from Scopus, one of the largest academic databases, focusing on research published by scholars affiliated with Brunei-based institutions. This gave us a massive dataset of 7,572 documents—including journal articles, conference papers, book chapters, and more. To make sense of this information, we turned to CiteSpace, a powerful visualization tool that helps identify research clusters, co-citation networks, and keyword trends over time.
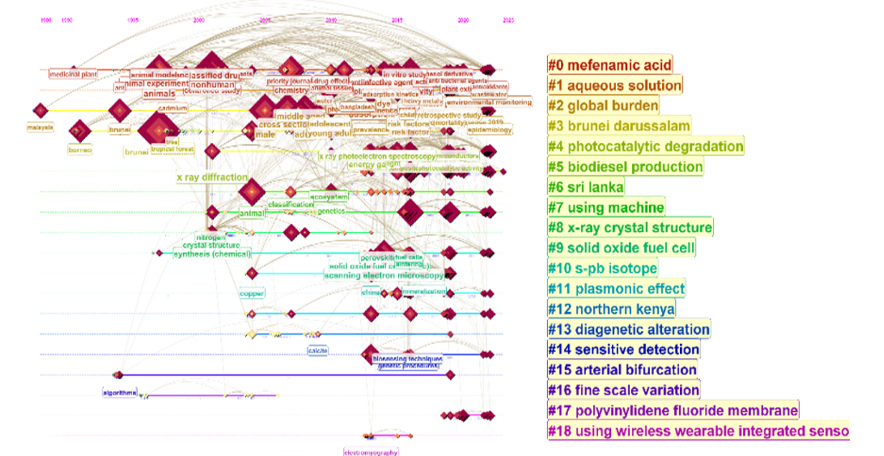
What did we find? A clear shift in research priorities. While earlier studies focused heavily on education and public policy, recent years have seen a surge in interdisciplinary work, particularly in sustainability, artificial intelligence, and nanotechnology. This shift reflects Brunei’s strategic initiatives, like Wawasan 2035, which aims to diversify the economy and promote innovation.
The Power of Collaboration
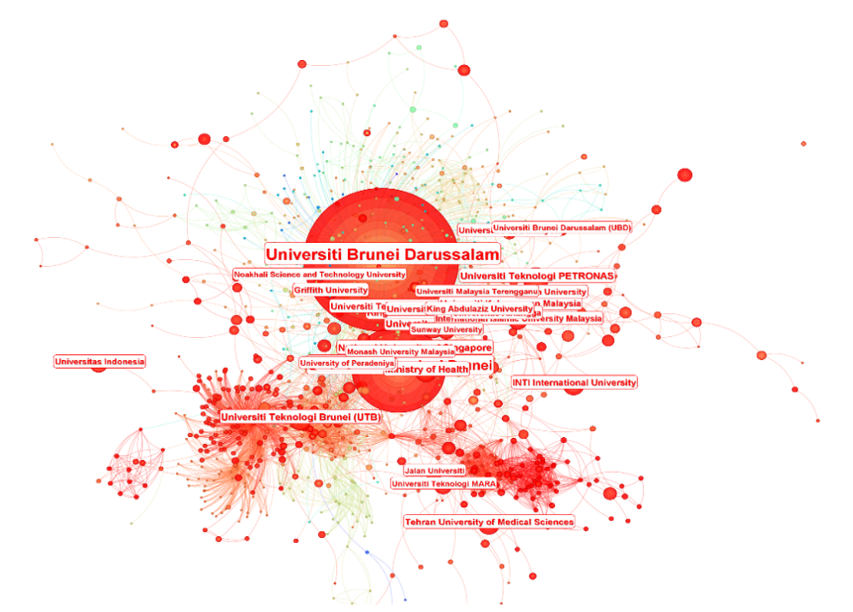
One of the most fascinating insights from our analysis was the role of collaboration—both within Brunei and internationally. Institutions like Universiti Brunei Darussalam (UBD) and Universiti Teknologi Brunei (UTB) have emerged as major research hubs, frequently partnering with universities in Malaysia, Singapore, China, and the UK. These partnerships are crucial because they provide access to broader funding opportunities, expertise, and resources.
Yet, challenges remain. Despite increasing research output, Brunei’s representation in high-impact international journals still lags behind other Southeast Asian countries. This raises an important question: How can small academic ecosystems like Brunei's gain greater visibility on the global stage?
The Unexpected Discoveries
Every research project has moments of surprise, and ours was no different. While we expected to see sustainability as a dominant theme—given Brunei’s rich biodiversity and environmental focus—we were intrigued by the rise of research in artificial intelligence and nanotechnology. These emerging fields have the potential to position Brunei as a leader in niche areas, especially in applications related to renewable energy, healthcare, and smart technologies.
Another unexpected trend? The increasing use of blended learning and digital education research, particularly during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. This highlights how global crises shape research priorities, sometimes in unpredictable ways.
Challenges Along the Way
Of course, no study comes without its hurdles. One of our biggest challenges was ensuring our data was as comprehensive as possible. Scopus, while an excellent resource, tends to favor indexed journals, meaning that some locally published research may have been overlooked. To address this, we had to carefully design our search parameters to ensure we captured the full breadth of Brunei’s research output.
Another challenge was making sense of the visual networks produced by CiteSpace. Scientometric maps can look like a web of interconnected nodes and lines, and interpreting them required a combination of technical expertise and contextual understanding. Thankfully, our team worked closely to cross-check findings and ensure we weren’t just seeing patterns in the data, but understanding what they meant for the future of research in Brunei.
Looking Ahead
So, what’s next? Our study has laid the groundwork for future research into how Brunei can strengthen its academic footprint internationally. Key takeaways include:
- Investing in interdisciplinary research that bridges fields like AI, sustainability, and public health.
- Strengthening international collaborations to boost global visibility.
- Encouraging more publications in high-impact journals to enhance research influence.
- Leveraging digital tools to modernize education and research methodologies.
This journey has shown us that small academic ecosystems can make a big impact, especially when they align their research priorities with global challenges. Brunei has the potential to become a knowledge hub in Southeast Asia, and with strategic efforts, its research contributions will only continue to grow.
Final Thoughts
Writing this paper was more than just an academic exercise—it was an opportunity to reflect on how research shapes national development and how collaborations drive innovation. We hope this study will spark further discussions about the role of small but ambitious academic communities in global research.
For fellow researchers exploring scientometric analysis or working in small research ecosystems, our advice is simple: Be curious, embrace collaboration, and let the data guide you. You never know what insights you’ll uncover!
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Sustainability

A multi-disciplinary, open access, community-focussed journal publishing results from across all fields relevant to sustainability research whilst supporting policy developments that address all 17 of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What are SDG Topics?
An introduction to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Topics and their role in highlighting sustainable development research.
Continue reading announcementRelated Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Artificial Intelligence and Digital Innovation in Advancing Sustainable Development Goals
This Collection is expected to explore the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital innovation in improving progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). We aim to highlight interdisciplinary research, technological breakthroughs, and practical applications that leverage AI-driven tools, data science, and digital systems to tackle global challenges such as poverty, climate change, healthcare, education, and sustainable infrastructure. This Collection provides a platform for advancing responsible and inclusive innovation by closely bridging technology and sustainability.
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 9, SDG 11, SDG 12, SDG 13 & SDG 16
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Digital Innovation, Sustainable Development Goals, Smart Technologies, Data Science, Climate Action, Ethical AI, Smart Cities, Digital Transformation.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 01, 2026
Advancing Sustainable Development: The Role of Circular Economy Practices, Green Innovation and Corporate Responsibility
Achieving sustainable development, as envisioned in the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda, requires transformative solutions to reconcile economic growth with environmental and social imperatives. Circular economy practices, green innovations, and corporate responsibility stand out as critical drivers in this effort—reducing resource depletion, fostering innovation, and embedding accountability into global systems. Yet, their combined potential to accelerate progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) remains underexplored. This Collection aims to unravel these synergies, offering actionable insights for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners committed to a sustainable future.
Keywords: Sustainable Development, Circular Economy Practices, Green Innovation, Corporate Responsibility, Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Development.
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 7, SDG 12, SDG 13 and SDG 17.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Apr 01, 2026
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in