NephroQuiz: a fishy rash.
Published in General & Internal Medicine
A 51-year-old man presented for evaluation of a newly developed rash (xerosis with hyperpigmented scaly lesions on his arms, legs, abdomen, and back). Skin biopsy showed hyperkeratosis with non-necrotising granulomas. He had no medical history, did not report any nausea, vomiting, chest pain, dyspnea, or urinary symptoms. On examination his blood pressure was 125/75 mmHg, pulse rate was 85 beats per minute, and his oxygen saturation was 96%.
Laboratory investigations showed creatinine 6.27 mg/dL (normal range 0.67–1.17; a baseline measurement 2 months before he presented was 0.9), sodium 137 mmol/L (normal range 136–145), potassium 3.8 mmol/L (normal range 3.5–5.1), bicarbonate 22 mmol/L (normal range 22–29), calcium 15.1 mg/dL (normal range 8.6–10.2), albumin 4.3 g/dL (normal range 3.5–5.2), ionized calcium 1.91 mmol/L (normal range 1.17–1.38), parathyroid hormone (PTH) 9.1 pg/mL (normal range 18.4–80.1), PTH-related protein 3.4 pmol/L (normal range 0.0–2.3), 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 97.3 pg/mL (normal range 19.9–79.3), and angiotensin-converting enzyme 120 U/L (normal range 16–85).
Urinalysis was positive for proteinuria with a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 0.92. Further serology workup showed the following: negative hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and HIV serologies, normal C3 and C4, undetectable antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), anti-double stranded DNA antibodies titer of <1:10 (normal <1:10), negative antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs), serine protease 3 antibodies (PR3-ANCAs) titer of 0 AU/mL (normal 0–19), myeloperoxidase antibodies (MPO) titer of 0 AU/mL (normal 0–19), and phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) antibody titer of <1:10 (normal <1:10).
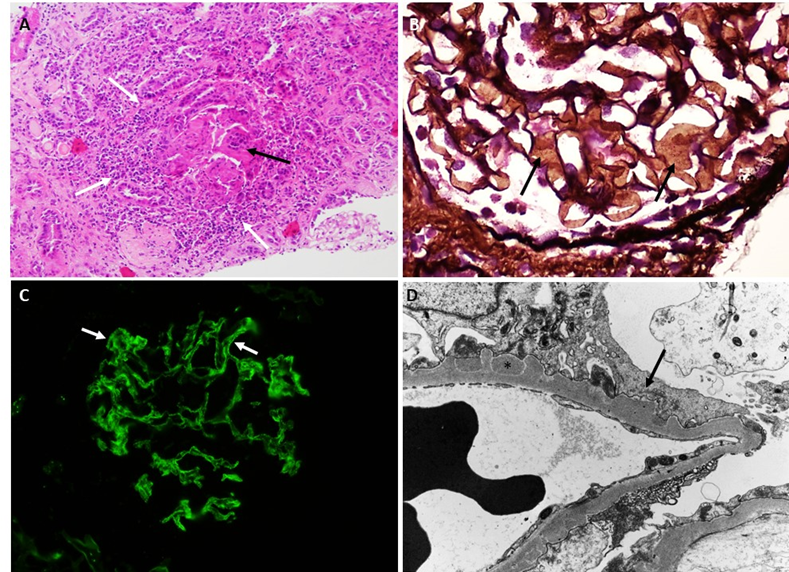
Kidney biopsy (shown above) was performed with: light microscopy hematoxylin and eosin stain (A), light microscopy periodic acid methenamine silver stain (B), IgG Immunofluorescence microscopy (C), electron microscopy (D).
The correct answer and explanation will be revealed once you select an answer in the multiple choice question above.
Click here to read the original case report. We encourage discussion of the case and questions in the comments.
Follow the Topic
-
BMC Nephrology

This is an open access journal publishing original peer-reviewed research articles in all aspects of the prevention, diagnosis and management of kidney and associated disorders, as well as related molecular genetics, pathophysiology, and epidemiology.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Robotic surgery: clinical application in nephrology
BMC Nephrology is calling for submissions to our Collection on Robotic surgery: clinical application in nephrology.
Robotic surgery has emerged as a transformative approach in the field of nephrology, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision and control. With the advent of advanced robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, urologists are now able to tackle intricate renal surgeries that were previously deemed challenging with traditional methods. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications in nephrology are expanding, paving the way for innovative surgical practices.
The integration of robotic surgery into nephrology is of critical importance as it addresses the increasing demand for effective and less invasive treatment options for renal diseases. Recent advancements in robotic technology have led to improved dexterity and visualization during surgery, allowing for greater surgical accuracy. The continuous development in this field not only promises enhanced surgical outcomes but also positions robotic surgery as a key player in the future of renal care.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
Applications of da Vinci surgery in nephrology
Innovations in robotic microsurgery
High-tech surgery techniques in renal procedures
Future directions in robotics in medicine
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 22, 2026
Novel therapies for glomerular diseases
BMC Nephrology invites submissions to our Collection on Novel therapies for glomerular diseases.
Glomerular diseases encompass a diverse group of disorders that affect the kidney's filtering units, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. These conditions, which include focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, minimal change disease, and IgA nephropathy, have traditionally posed challenges in terms of effective treatment options. Recent advancements in our understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and the introduction of novel therapeutic modalities, such as targeted biologics and small molecules, present new avenues for intervention. This Collection invites contributions that explore these innovative therapies and their potential to transform the management of glomerular diseases.
Advances in clinical research have led to promising developments, including the successful completion of several clinical trials that evaluate the efficacy of new agents. These therapies not only aim to improve patient outcomes but also focus on personalized treatment approaches that consider individual patient characteristics. By fostering collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and industry partners, we can enhance our understanding and management of these complex conditions. Continued research in this field has the potential to yield groundbreaking discoveries that could redefine treatment paradigms for glomerular diseases.
Topics of interest for this Collection include, but are not limited to:
Novel therapeutic agents in glomerular diseases
Clinical trials of innovative treatments
Impact of new therapies on patient outcomes
Personalized treatment approaches for glomerular disorders
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being and SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
All manuscripts submitted to this journal, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in