Palaeontology in a pandemic: remote research on dinosaur eggs and embryos
Published in Ecology & Evolution

Like many research scientists, the COVID-19 pandemic threw a wrench into the works of my research plans. My fieldwork has been greatly scaled back these last two years, I’ve been unable to sustain my usual museum research travel, and I have barely started some of the projects that I had originally planned to have finished by now. But the pandemic hasn’t been all-bad. It has also invited some new opportunities.
In May of last year, I was invited by my collaborator Dr. Xing Lida to help describe some dinosaur eggs and embryos, recently collected from Upper Cretaceous red beds (around 72–66 million years old) in southern China. This was not my first collaboration with Chinese colleagues, and I’ve been lucky enough to visit the country on a few occasions to work on some fantastic fossil material there. Unfortunately, the realities of the pandemic lockdowns meant that such travel was now impossible; I would have to work on the fossils from a distance. Not ideal, to say the least, but nonetheless possible, thanks to helpful colleagues, digital photography and videography.
The eggs and their embryonic contents were found as part of a larger clutch that turned up during a construction project in the Ganzhou area of Jiangxi Province. Two of the eggs were acquired by the Yingliang Stone Natural History Museum in Fujian Province, and made available to my colleagues and I for description. The eggs are nearly spherical, about 12 cm in diameter and 660 mL in volume, and thin-shelled (0.4 mm thick). Although not particularly well-preserved, they appear to belong to a fossil eggshell family called Spheroolithidae. These types of eggs are most associated with the duck-billed dinosaurs (or hadrosaurs), a group of large herbivores that lived near the end of the Age of Dinosaurs.
No surprise, then, that the fossil embryos (nicknamed the “Ying Babies”) contained within the eggs are those of a hadrosaur, based on the distinctive shapes of certain skull bones, vertebrae, and limb bones (Figure 1). Hadrosaur embryos had been identified before now, but these new embryos represent likely the best preserved of their kind to date. Unfortunately, it’s difficult to know precisely which species the embryos represent; species-specific diagnostic features often do not manifest until later in life. Still, the squamosal bone at the back of the skull has a distinctive shape reminiscent of only a handful of other hadrosaur species, and might prove helpful in narrowing the possibilities.
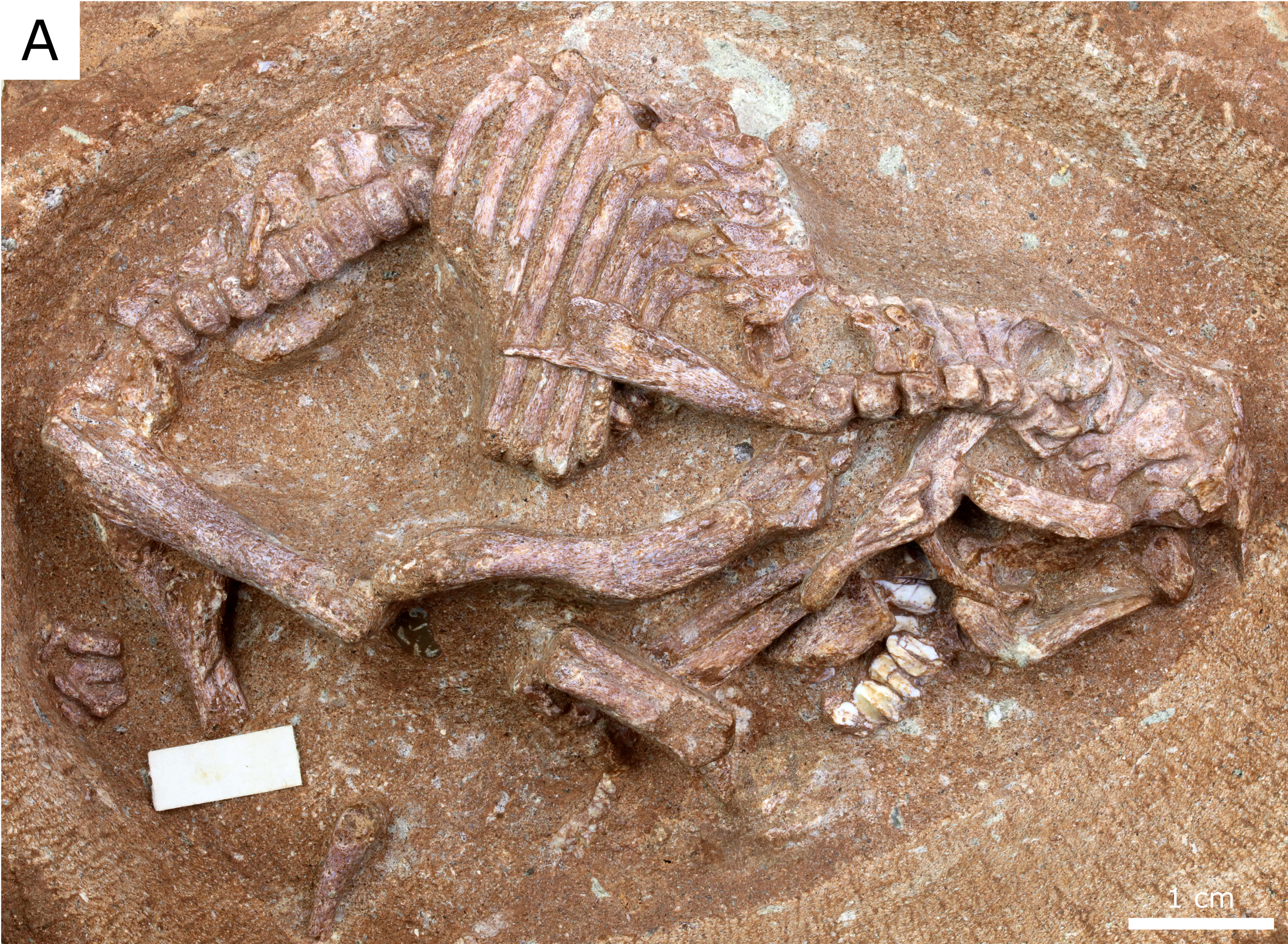

What’s most interesting about the eggs (and the embryos they contain) is their size relative to those of more specialized hadrosaurs (called hadrosaurids) from the Upper Cretaceous rocks of North America. Hadrosaurids come in two varieties: the lambeosaurines that bore elaborate, hollow crests on their skulls, and the hadrosaurines that lacked such crests. It is traditionally understood that hadrosaurines laid smaller eggs than lambeosaurines (900 mL vs. 4,000 mL, respectively), and consequently produced smaller hatchlings. More than that, hadrosaurine hatchlings are thought to have been less developed, particularly in the formation of the limb bones, compared to lambeosaurines. Thus, hadrosaurine hatchlings are thought to have been altricial, having spent a long time in the nest post-hatching while their limb bones finished forming; the larger lambeosaurine hatchlings were, by contrast, precocial and ready to join the herd at once. The question that naturally arises for the evolutionary biologist concerns the ancestral condition: Were hadrosaurids ancestrally altricial or precocial as hatchlings? The eggs and embryos my coauthors and I describe are both small and from a more primitive lineage of hadrosaurs, suggesting that altriciality was the original condition for hadrosaurids.
Throughout the pandemic, I have frequently joined the chorus in complaining about the move to online work. The endless Zoom meetings, the IT issues that go neglected, and the eye strain from staring at a screen all day have all taken their toll. Still, I wonder how much more my research might have suffered had this pandemic hit 15 or 20 years ago. Certainly, I wouldn’t have been able to collaborate with my colleagues from the other side of the world on such marvelous fossils. I’ll try to bear it in mind the next time I feel sorry for myself because I can’t have any genuine crispy duck.
Follow the Topic
-
BMC Ecology and Evolution

An open access, peer-reviewed journal interested in all aspects of ecological and evolutionary biology.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Bioacoustics and soundscape ecology
BMC Ecology and Evolution welcomes submissions to its new Collection on Bioacoustics and soundscape ecology. By studying how animals use sound and how noise impacts them, you can learn a lot about the well-being of an ecosystem and the animals living there. In support of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 13: Climate action, 14: Life below water and 15: Life on land, the Collection will consider research on:
The use of sound for communication
The evolution of acoustic signals
The use of bioacoustics for taxonomy and systematics
The use of sound for biodiversity monitoring
The impacts of noise on animal development, behavior, sound production and reception
The effect of anthropogenic noise on the physiology, behavior and ecology of animals
Innovative technologies and methods to collect and analyze acoustic data to study animals and the health of ecosystems
Reviews and commentary articles are welcome following consultation with the Editor
(Jennifer.harman@springernature.com).
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 27, 2026
Ecology of soils
BMC Ecology and Evolution invites researchers to submit their work on soil ecosystems and their implications for environmental sustainability. Soils are living, dynamic systems that support a vast array of organisms, from tiny microbes to plants and animals. They play a vital role in keeping our planet healthy by recycling nutrients, storing carbon, and helping regulate water and climate. Understanding how soil life functions and adapts is essential for tackling major environmental challenges like climate change, habitat loss, and soil degradation.
This collection of articles aims to showcase the latest research in soil ecology, emphasizing the interactions among soil organisms, biogeochemical processes, and ecosystem functions across various landscapes. We invite submissions that explore the following topics:
•Microbial and faunal diversity in soils: Patterns, drivers, and functional roles of bacteria, fungi, protists, and invertebrates
•Soil biogeochemistry and ecosystem functioning: Nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and soil health in both natural and managed ecosystems
•Soil-plant interactions: Rhizosphere processes, plant-microbe symbioses, and their effects on vegetation dynamics
•Land use and climate change impacts on soil communities: Responses of soil biodiversity and functions to agricultural intensification, urbanization, pollution, and climate shifts
•Soil metagenomics, phylogenetics, and functional ecology: Advances in molecular approaches for studying soil microbial and faunal communities
•Conservation and restoration of soil ecosystems: Strategies for maintaining soil biodiversity and ecosystem services in degraded landscapes
All manuscripts submitted to BMC Ecology and Evolution, including those submitted to collections and special issues, are assessed in line with our editorial policies and the journal’s peer review process. Reviewers and editors are required to declare competing interests and can be excluded from the peer review process if a competing interest exists.
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 15: Life on Land.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 02, 2026





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in