
Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (CoNS) species have long been overshadowed by the more notorious Staphylococcus aureus. Prior to molecular methods, the coagulase test was initially used to distinguish the coagulase-positive S. aureus from the staphylococci deemed to be non- or less pathogenic 1. The coagulase enzyme converts fibrinogen to fibrin, thus promoting the clotting of blood plasma2.
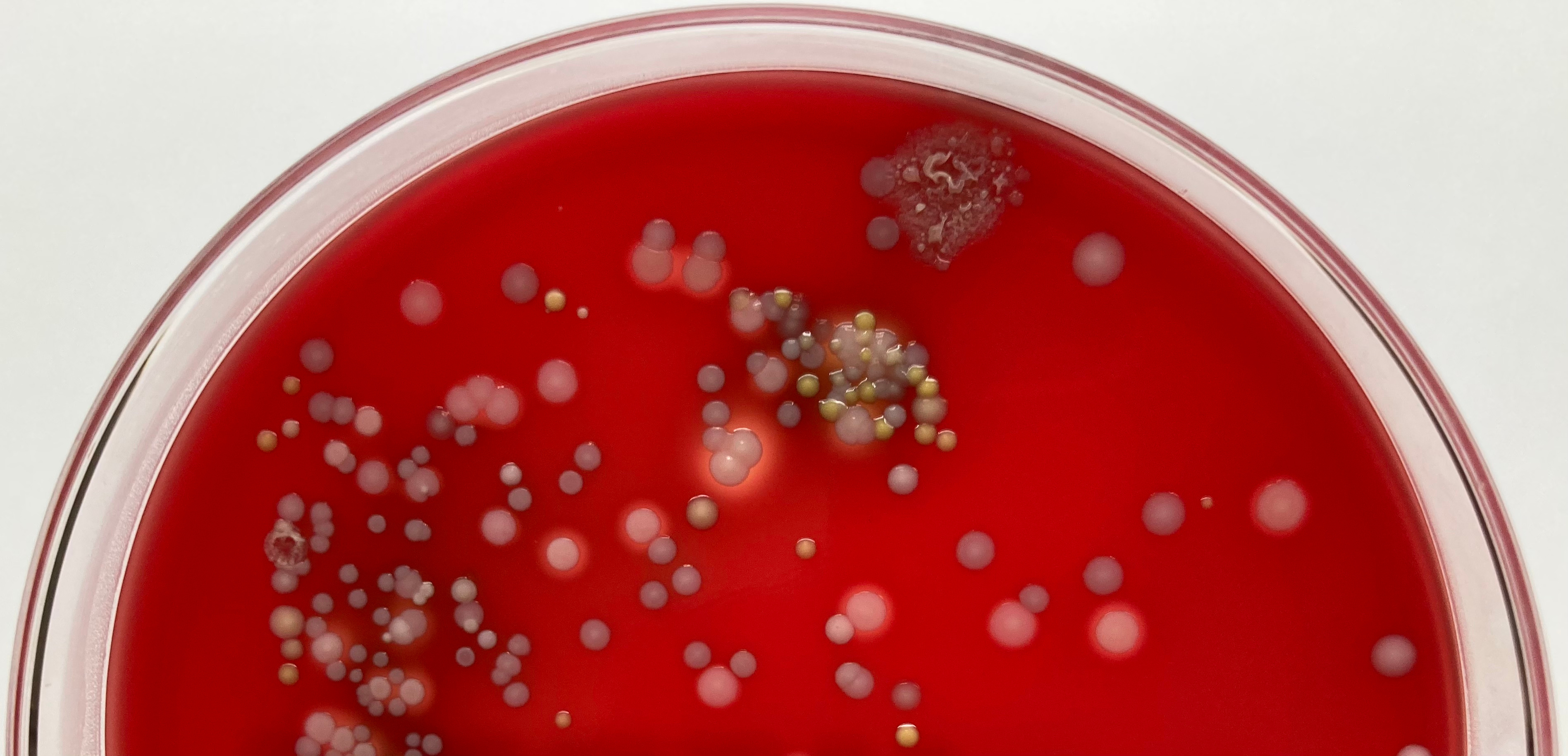
Mixed bacterial colonies on blood agar plate
We have been collaborating with Robert Gibson, Director of the New Hampshire Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory (NHVDL) for the past seven years on Staphylococcus genomics. He and his staff members receive thousands of specimens from pets, farm animals, wildlife, aquatic and zoo animals from the state of New Hampshire and other states in the New England region of the United States. In our culture collection of Staphylococcus isolates from diseased animals (n = 1,034 isolates) sampled from 2017 - 2022, we were pleasantly surprised by the astounding diversity of non-aureus species. There were 28 non-aureus species (898 isolates) and 15 unnamed isolates, based on initial identification using MALDI-TOF. If CoNS are not as clinically important as S. aureus, why do we find so many of them in animal diseases?
We were particularly interested in the evolutionary history of CoNS. A few prior studies reported evidence of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in some CoNS species 3-4 and between S. aureus and the CoNS species S. epidermidis 5, but we hypothesized that HGT is more widespread in CoNS than previously recognized. We sought to investigate genome-wide frequencies and patterns of HGT in 191 genomes representing 15 CoNS species. These were obtained from 10 animal species, most of which came from dogs, cats, and cows. We examined homologous recombination, mobile genetic elements, and shared accessory genes.

Co-author Stephanie S.R. Souza with Fred
Our results showed that frequent but structured patterns of HGT exist within and between CoNS species shaped by their overlapping ecological niches (animal hosts) and geographical proximity. We found frequent transfer partners as well as certain lineages and species that are frequent donors or frequent recipients of exogenous DNA, regardless of the identify of their animal hosts. They are also major reservoirs of diverse phages, plasmids and mobilizable genes encoding antimicrobial resistance, heavy metal resistance, and virulence. These findings underscore the importance of CoNS not only in maintaining animal health but also in understanding the evolutionary history of the genus Staphylococcus.
My research group and I feel especially fortunate that we have a strong collaboration with NHVDL Director Robert Gibson. Our paper is testament to what academic institutions and veterinary diagnostic laboratories can achieve together. We showed that the application of genomic methods should not be limited to human clinical settings. Antimicrobial resistance and other genetic material can traverse recognized boundaries of bacterial species as well as across different ecological niches. Whole genome sequencing across the One Health continuum is imperative to the development of effective surveillance, diagnostic, and treatment options for CoNS infections. Lastly, we hope our findings will encourage more in-depth studies of CoNS and sampling of more diverse animal species. There are likely many more Staphylococcus species yet to be discovered. Exciting times ahead!

Senior author Cheryl Andam with Sparky
Full details of our findings are described in https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-023-04877-0
References cited:
1 Cadness-Graves B. et al. Slide test for coagulase-positive staphylococci. Lancet 2,736–738 (1943).
2 McAdow M. et al. Staphylococcus aureus secretes coagulase and von Willebrand factor binding protein to modify the coagulation cascade and establish host infections. Journal of Innate Immunology 4, 141–148 (2012).
3 Sun Z. et al. Determining the genetic characteristics of resistance and virulence of the "Epidermidis Cluster Group" through pan-genome analysis. Frontiers in Cellular Infection and Microbiology 10, 274 (2020).
4 Zong Z. et al. Diversity of SCCmec elements in methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci clinical isolates. PLoS One 6, e20191 (2011).
5 Méric G. et al. Ecological overlap and horizontal gene transfer in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Genome Biology and Evolution 7,1313-1328 (2015).
Follow the Topic
-
Communications Biology

An open access journal from Nature Portfolio publishing high-quality research, reviews and commentary in all areas of the biological sciences, representing significant advances and bringing new biological insight to a specialized area of research.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
From RNA Detection to Molecular Mechanisms
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 05, 2026
Signalling Pathways of Innate Immunity
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: May 31, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in