Prompt Engineering in Consistency and Reliability with the Evidence-Based Guideline for LLMs
Published in Computational Sciences and General & Internal Medicine

Initial Research Idea:
Ever since ChatGPT was introduced, we have gradually felt the charm of Large Language Models (LLMs) in our daily learning and life. Through reading literature and exploration, we found that LLMs have shown notable capabilities in various aspects of the medical field, and that prompt engineering can enable us to better utilize Large Language Models (LLMs). However, we noticed in our regular use and reading studies that LLMs always generate different answers to the same question, even if they are identical, which is quite concerning in the application of medical fields. Additionally, the application of LLMs in sub-specialties and specific diseases was still in the exploratory stage at the beginning of this study. Combining our expertise and the disease Osteoarthritis (OA), which affects a large number of patients, we further explored the application prospects of LLMs based on evidence-based guidelines and prompt engineering.
Initial Research:
We initially explored GPT-4 through manual input and data collection and published a preprint at: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3336823/v1. It was also submitted to npj Digital Medicine. The study found that the application of prompt engineering could improve the performance of GPT-4 in medicine. The reliability of GPT-4 in answering medical questions is not clear, and further research is necessary.

Review and Revision:
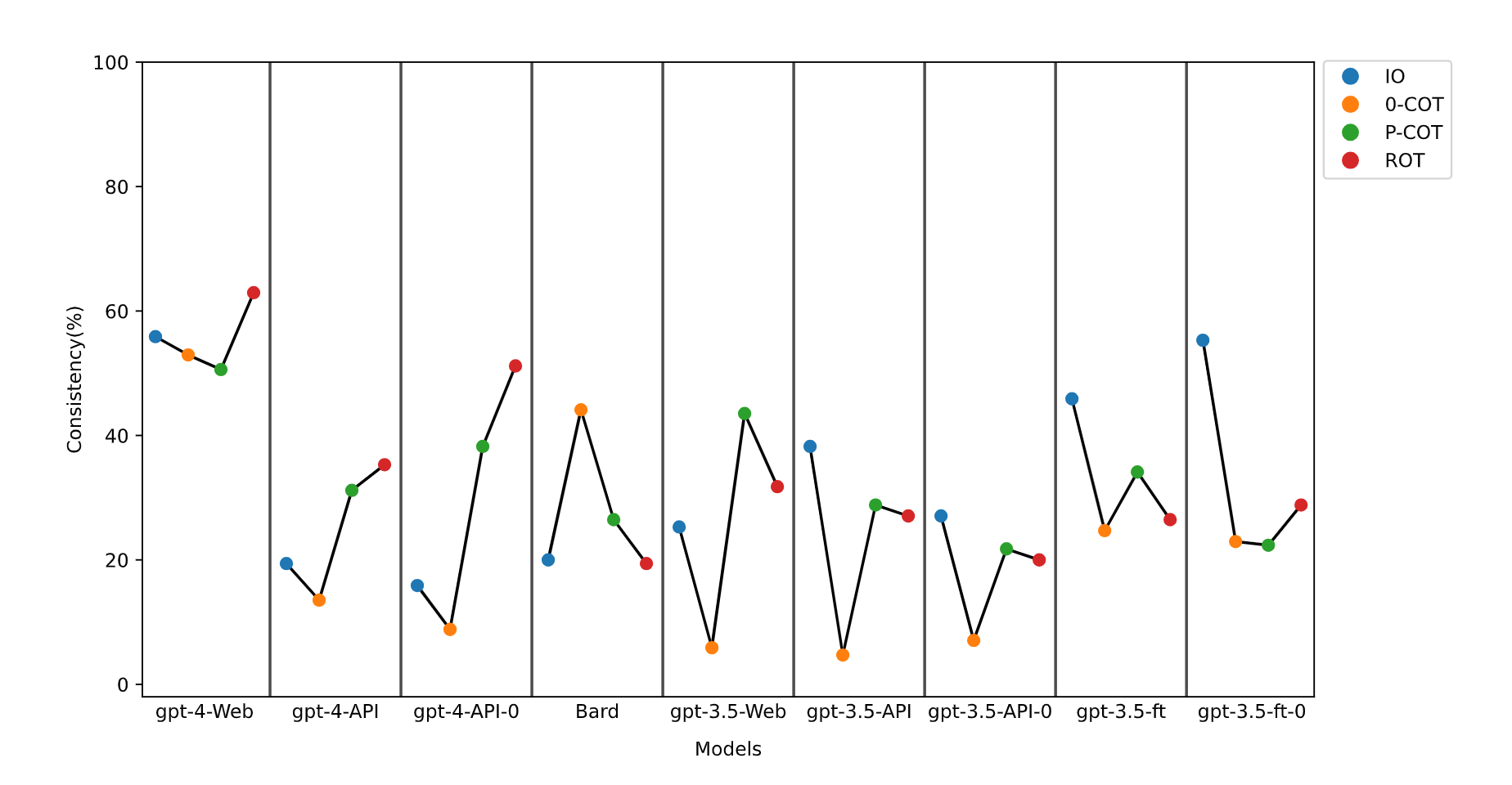
The reviewers' comments were profound and instructive. Based on these comments, we further explored the application changes of prompt engineering in different models, different model parameters, and after fine-tuning. We discovered that different prompts had variable effects across various models, and gpt-4-Web with ROT prompting had the highest consistency. An appropriate prompt may improve the accuracy of responses to professional medical questions. Moreover, it is advisable to pose the input questions multiple times to gather more comprehensive insights, as responses may vary with each inquiry. In the future of AI healthcare involving LLMs, prompt engineering will serve as a crucial bridge in communication between LLMs and patients, as well as between LLMs and doctors.
Future Research:
The exploration of prompt engineering in the application of LLMs in medicine is preliminary. Apart from prompt engineering, agents, fine-tuning, and RAG are all important means to assist the application of LLMs. We will explore the combination of these technical methods in future research and participate in the development and clinical validation of medical LLMs.
Follow the Topic
-
npj Digital Medicine

An online open-access journal dedicated to publishing research in all aspects of digital medicine, including the clinical application and implementation of digital and mobile technologies, virtual healthcare, and novel applications of artificial intelligence and informatics.
Your space to connect: The Primary immunodeficiency disorders Hub
A new Communities’ space to connect, collaborate, and explore research on Clinical Medicine, Immunology, and Diseases!
Continue reading announcementRelated Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Digital Health Equity and Access
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 03, 2026
Evaluating the Real-World Clinical Performance of AI
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 03, 2026




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in