Ruxolitinib discontinuation syndrome: incidence, risk factors and management in 251 patients with myelofibrosis
Published in Cancer

Ruxolitinib is the first JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor (JAKi) approved for the treatment of splenomegaly and symptoms related to myelofibrosis (MF). In the early phase I/II study of RUX in MF, most patients experienced relapse of symptoms and splenomegaly after discontinuation, and life-threatening adverse events (AEs) occurred in 11% of patients. Further cases of severe AEs attributed to RUX discontinuation have been subsequently described, despite a careful stepwise reduction of RUX. These events, attributed to an acute rebound of cytokine storm, were defined as RUX discontinuation syndrome (RDS) and typically present within 3 weeks from RUX discontinuation.
With this study, we aimed to investigate modalities of RUX discontinuation, incidence, timing, and severity of RDS and outcome and risk factors associated with RDS in a real-world context.
In 2016 we established a clinical network to collect information about RUX therapy in MF, now including 21 hematology centers and 700 RUX-treated MF patients, coordinated by our Hematology Institute in Bologna.

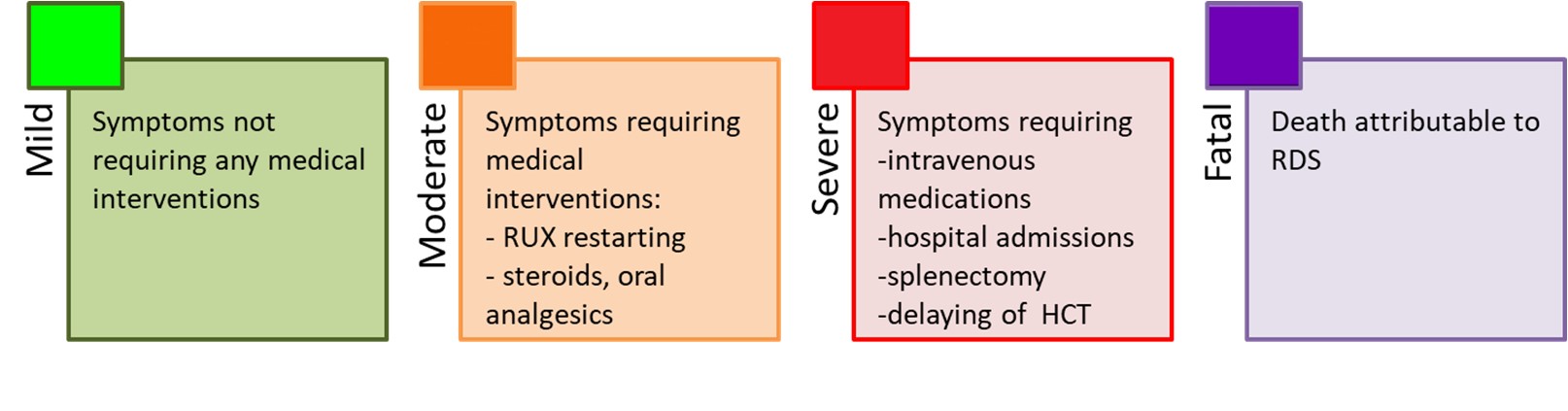
We conducted a specific survey to obtain data on timing and modalities of RUX discontinuation, and subsequent outcome. RDS included all symptoms that presented within 21 days from RUX discontinuation and that we attributed to RUX discontinuation. Based on previous definition, we graded RDS as follows :
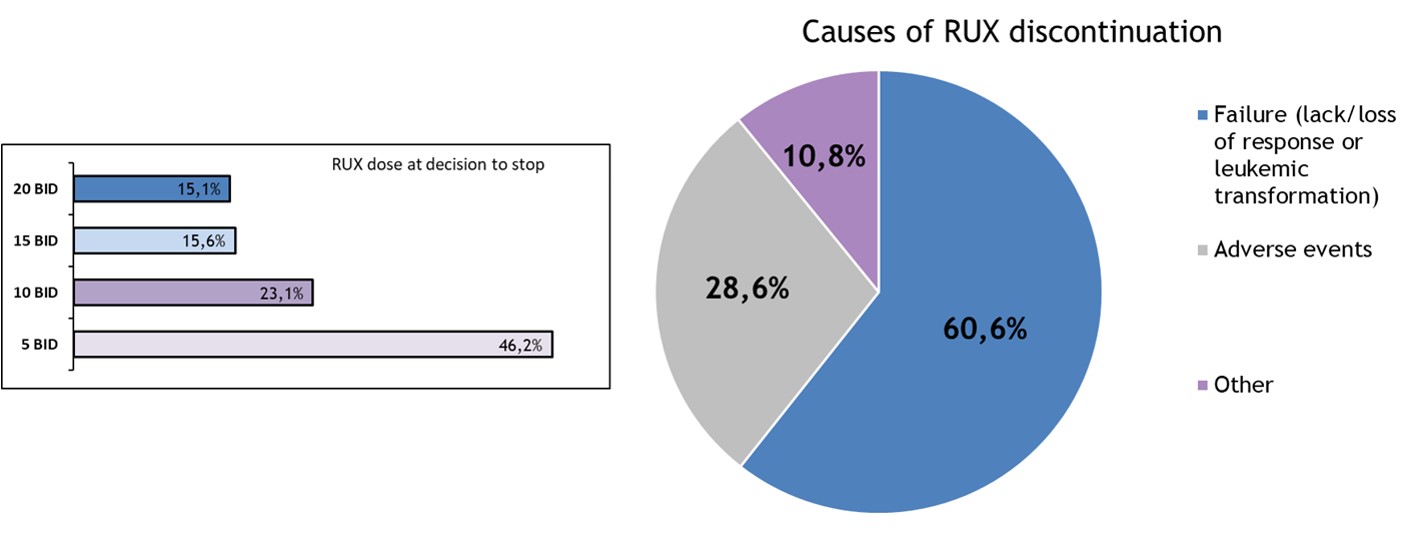
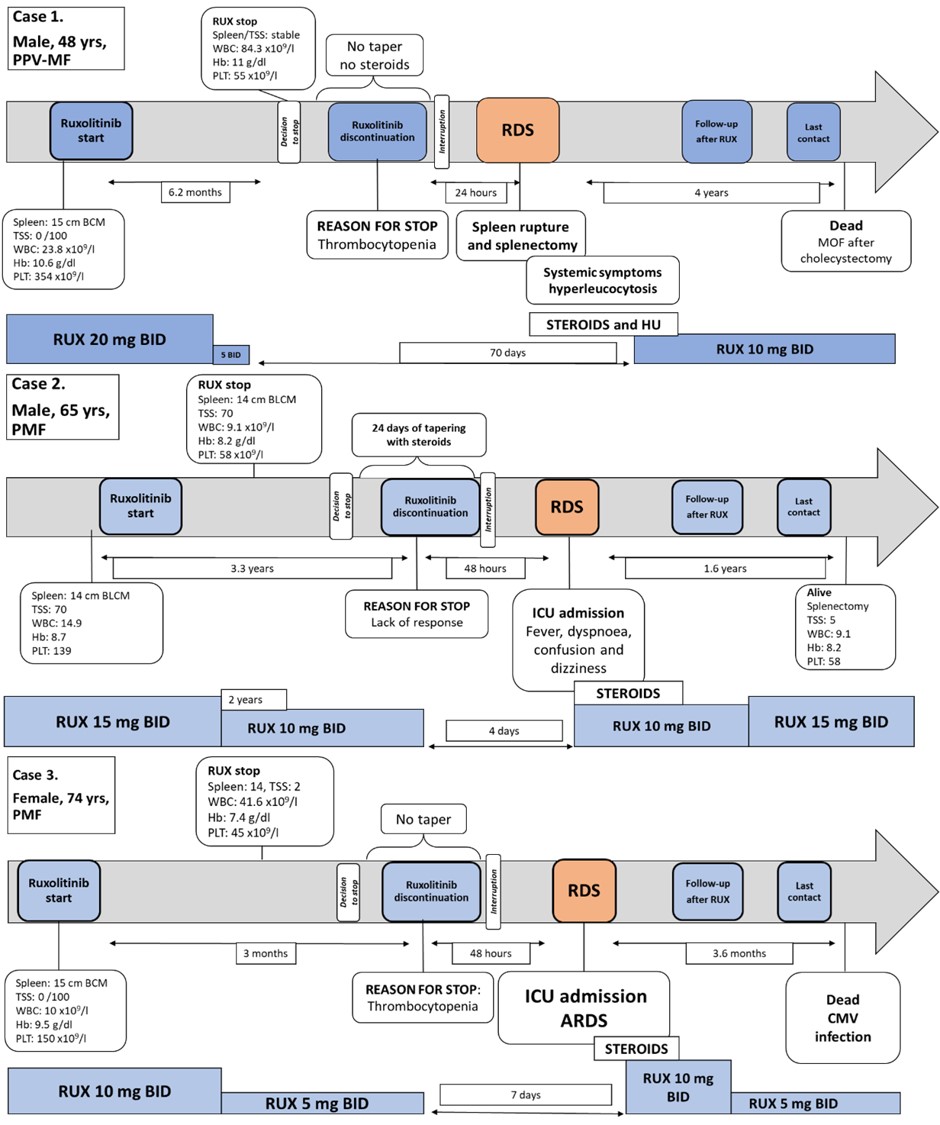
After a median time on RUX of 36.1 months, 251 patients discontinued RUX and were evaluable for RDS. Daily dose at RUX stop and causes of discontinuation are detailed below.
RUX was abruptly discontinued in 162 patients while RUX dose was first gradually decreased in 89 patients. RUX tapering pattern was very variable among Centers.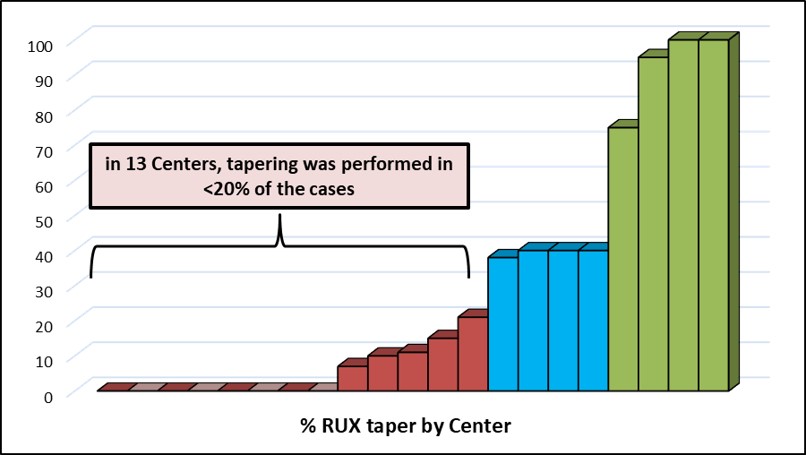
We observed an RDS in 34 (13.5%) patients after a median of 7 days from RUX stop. RDS was mild in 61.8% and moderate in 29.4% of the 34 patients.
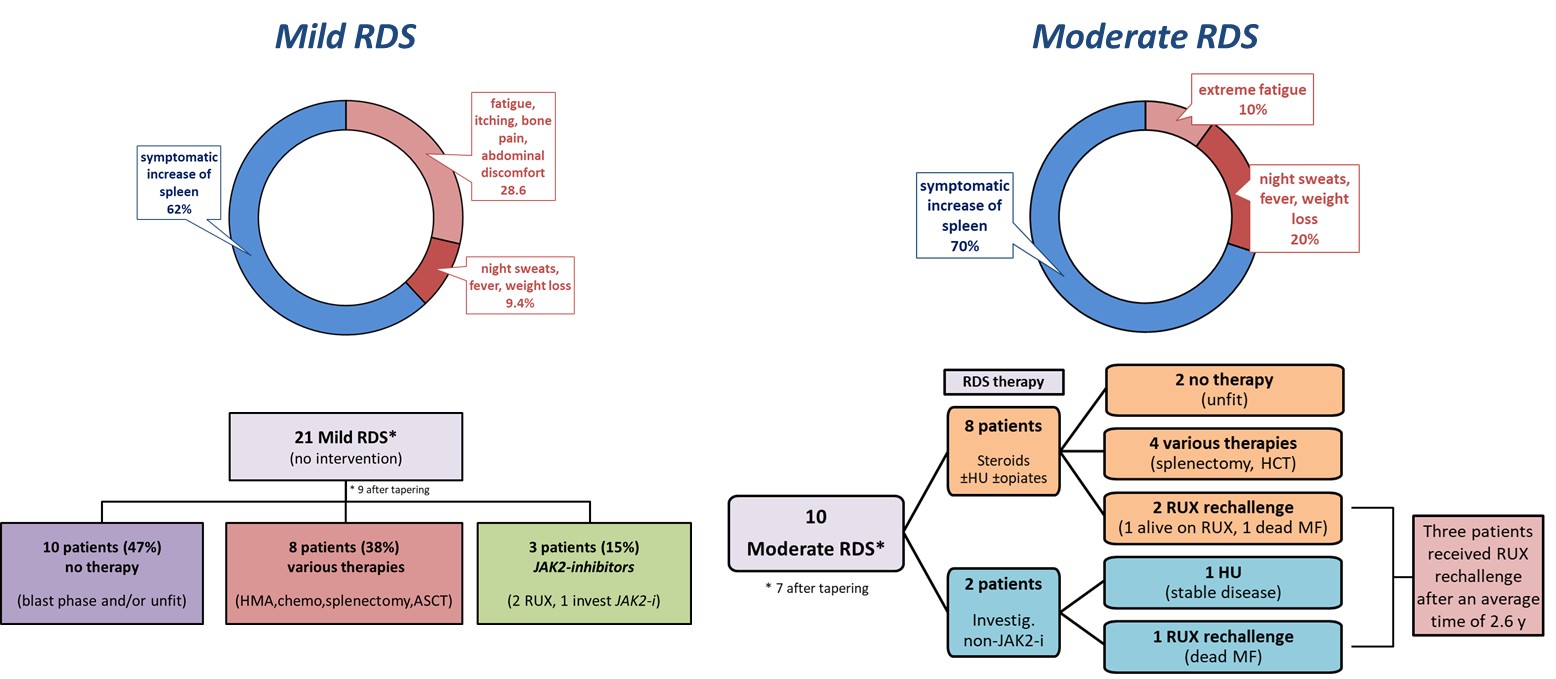
Three cases of RDS were severe, but no RDS was fatal.
We also found that thrombocytopenia and large splenomegaly at RUX stop predicted a higher RDS risk. Therefore, RDS may occur also in patients deemed to be refractory to the drug.
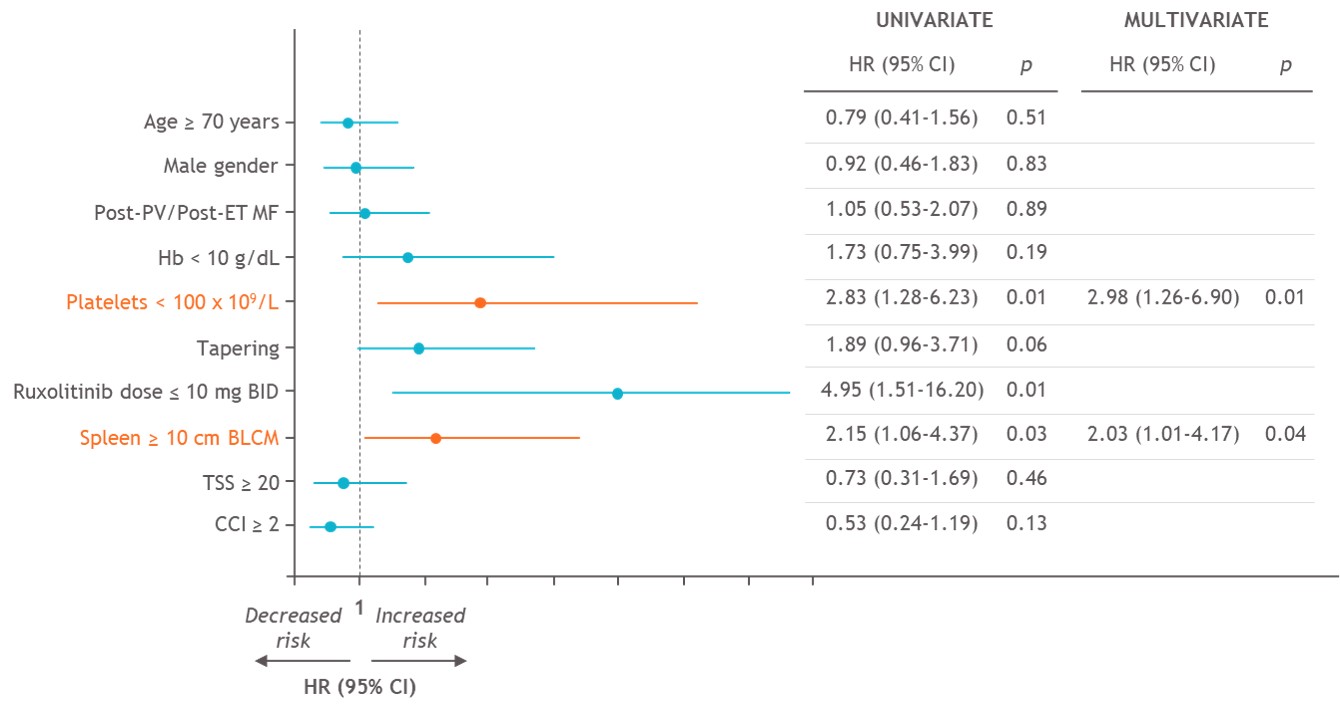
Our results confirm the need for a careful surveillance of MF patients at the time of RUX discontinuation. A quick switch to alternative treatments, if indicated, should be planned especially for patients with large splenomegaly. In the absence of available alternatives, the occurrence of RDS may indicate residual disease control activity and identify a population that may still benefit from JAK2i.
Follow the Topic
-
Blood Cancer Journal

This journal seeks to publish articles of the highest quality related to hematologic malignancies and related disorders.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in